Irodov Solutions: Diffraction of Light- 3 | I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE PDF Download
Q.138. Using a diffraction grating as an example, demonstrate that the frequency difference of two maxima resolved according to Rayleigh's criterion is equal to the reciprocal of the difference of propagation times of the extreme interfering oscillations, i.e. δv = = 1/δt.
Ans. For the just resolved waves the frequency difference
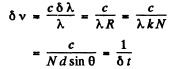
since N d sinθ is the path difference between waves emitted by the extremities o f the grating.
Q.139. Light composed of two spectral lines with wavelengths 600.000 and 600.050 nm falls normally on a diffraction grating 10.0 mm wide. At a certain diffraction angle θ these lines are close to being resolved (according to Rayleigh's criterion). Find θ.
Ans.
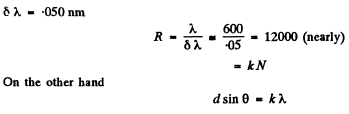
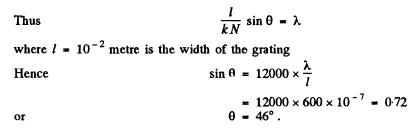
Q.140. Light falls normally on a transparent diffraction grating of width l = 6.5 cm with 200 lines per millimetre. The spectrum under investigation includes a spectral line with λ = 670.8 nm consisting of two components differing by δλ = 0.015 nm. Find: (a) in what order of the spectrum these components will be resolved; (b) the least difference of wavelengths that can be resolved by this grating in a wavelength region λ ≈ 670 nm.
Ans. We see that
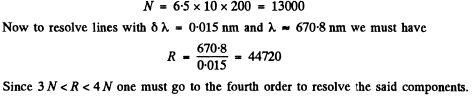
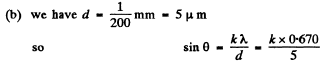
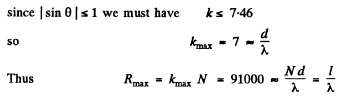
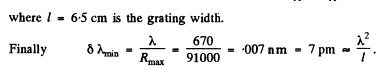
Q.141. With light falling normally on a transparent diffraction grating 10 mm wide, it was found that the components of the yellow line of sodium (589.0 and 589.6 nm) are resolved beginning with the fifth order of the spectrum. Evaluate:
(a) the period of this grating;
(b) what must be the width of the grating with the same period for a doublet λ = 460.0 nm whose components differ by 0.13 nm to be resolved in the third order of the spectrum.
Ans. Here
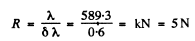
so
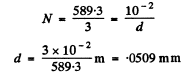
(b) To resolve a doublet with 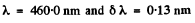 in the third order we must have
in the third order we must have
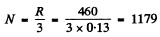
This means that the grating is
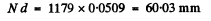
wide = 6cm wide.
Q.142. A transparent diffraction grating of a quartz spectrograph is 25 mm wide and has 250 lines per millimetre. The focal length of an objective in whose focal plane a photographic plate is located is equal to 80 cm. Light falls on the grating at right angles. The spectrum under investigation includes a doublet with components of wavelengths 310.154 and 310.184 nm. Determine:
(a) the distances on the photographic plate between the components of this doublet in the spectra of the first and the second order;
(b) whether these components will be resolved in these orders of the spectrum.
Ans.
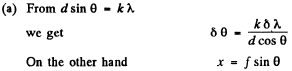
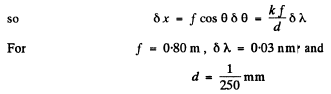
we get 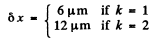
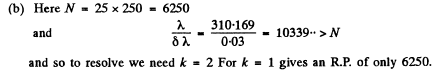
Q.143. The ultimate resolving power λδλ of the spectrograph's trihedral prism is determined by diffraction of light at the prism edges (as in the case of a slit). When the prism is oriented to the least deviation angle in accordance with Rayleigh's criterion,
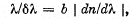
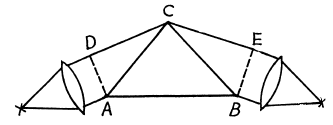
where b is the width of the prism's base (Fig. 5.28), and dnIdk is the dispersion of its material. Derive this formula.
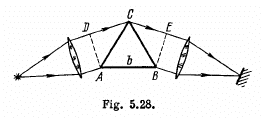
Ans. Suppose the incident light consists of two wavelengths λ and λ + δλ which are just resolved by the prism. Then by Rayleigh’s criterion, the maximum of the line of wavelength λ must coincide with the first minimum of the line of wavelength λ + δλ, Let us write both conditions in terms of the optical path differences for the extreme rays : For the light of wavelength λ
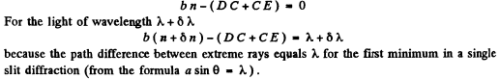
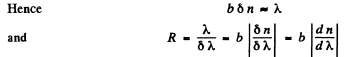
Q.144. A spectrograph's trihedral prism is manufactured from glass whose refractive index varies with wavelength as n = A + B/λ2 where A and B are constants, with B being equal to 0.010 1μm2. Making use of the formula from the foregoing problem, find:
(a) how the resolving power of the prism depends on k; calculate the value of λδλ in the vicinity of λ1 = 434 nm and λ2 = 656 nm if the width of the prism's base is b = 5.0 cm;
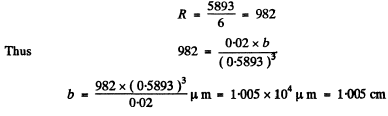
(b) the width of the prism's base capable of resolving the yellow doublet of sodium (589.0 and 589.6 nm).
Ans.
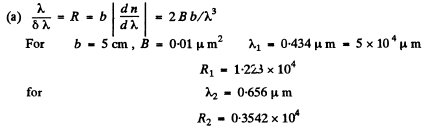
(b) To resolve the D-lines we require
Q.145. How wide is the base of a trihedral prism which has the same resolving power as a diffraction grating with 10 000 lines in the second order of the spectrum if 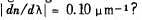
Ans.
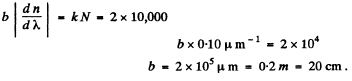
Q.146. There is a telescope whose objective has a diameter D = 5.0 cm. Find the resolving power of the objective and the minimum separation between two points at a distance l = 3.0 km from the telescope, which it can resolve (assume λ = 0.55 μm).
Ans. Resolving power of the objective
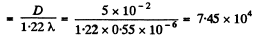
Let 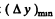 be the minimum distance between two points at a distance of 3.0 km which the telescope can resolve. Then
be the minimum distance between two points at a distance of 3.0 km which the telescope can resolve. Then
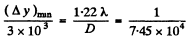
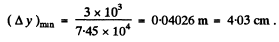
Q.147. Calculate the minimum separation between two points on the Moon which can be resolved by a reflecting telescope with mirror diameter 5 m. The wavelength of light is assumed to be equal to λ = 0.55 μm.
Ans. The limit of resolution of a reflecting telescope is determined by diffraction from the mirror and obeys a formula similar to that from a refracting telescope. The limit of resolution is
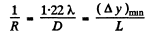

Q.148. Determine the minimum multiplication of a telescope with diameter of objective D = 5.0 cm with which the resolving power of the objective is totally employed if the diameter of the eye's pupil is do = 4.0 mm.
Ans. By definition, the magnification


where d0 = diameter of the pupil
Thus to avail of the resolution offered by the telescope we must have
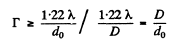
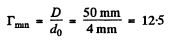
Q.149. There is a microscope whose objective's numerical aperture is sinα = 0.24, where α is the half-angle subtended by the objective's rim. Find the minimum separation resolved by this microscope when an object is illuminated by light with wavelength λ = 0.55 p,m.
Ans.
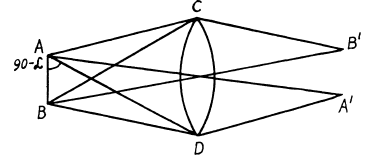
Let A and B be two points in the field of a microscope which is represented by the lens C D. Let A' ,2T be their image points which are at equal distances from the axis of the lens CD. Then all paths from A to A' are equal and the extreme difference of paths from A to B' is equal to
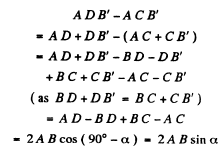
From the theory o f diffraction by circular apertures this distance must be equal to 1.22 λ
when B’ coincides with the minimum o f the diffraction due to A and A' with the minimum o f the diffraction due to B . Thus
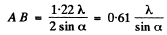
Here 2α is the angle subtended by the objective of the microscope at the object.
Substituting the values
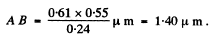
Q.150. Find the minimum magnification of a microscope, whose objective's numerical aperture is sinα = 0.24, at which the resolving power of the objective is totally employed if the diameter of the eye's pupil is do = 4.0 mm.
Ans. Suppose dmn - minimum separation resolved by the microscope ψ = angle subtended at the eye by this object when the object is at the least distance of distinct v ision l0 ( = 2 5 cm ) .
ψ' minimum angular separation resolved by the eye = 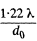

Now
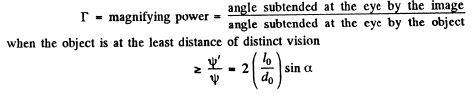
Thus 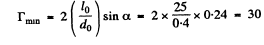
Q.151. A beam of X-rays with wavelength λ falls at a glancing angle 60.0° on a linear chain of scattering centres with period a. Find the angles of incidence corres- ponding to all diffraction maxima if λ = 2a/5.
Ans. Path difference
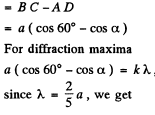
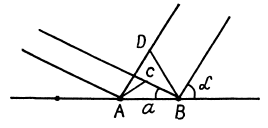
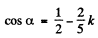
and we get
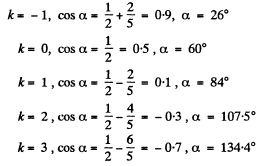
Other values o f k are not allowed as they lead to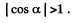
Q.152. A beam of X-rays with wavelength λ = 40 μm falls normally on a plane rectangular array of scattering centres and produces a system of diffraction maxima (Fig. 5.29) on a plane screen re- moved from the array by a distance l = 10 cm. Find the array periods a and b along the x and y axes if the distances between symmetrically located maxima of second order are equal to Δx = 60 mm (along the x axis) and Δy = 40 mm (along the y axis).
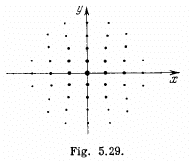
Ans. We give here a simple derivation of the condition for diffraction maxima, known as Laue equations. It is easy to see form the above figure that the path difference between waves scattered by nearby scattering centres P1 and P2 is
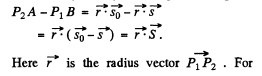
maxima this path difference must be an integer multiple of λ, for any two neighbouring atoms. In the present case of two dimensional lattice with X - rays incident normally Taking successively nearest neighbours in the x - & y - directions
Taking successively nearest neighbours in the x - & y - directions
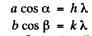
Here cosα and cosβ are the direction cosines o f the ray with respect to the x & y axes o f the two dimensional crystal.
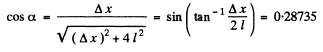
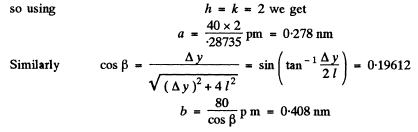
Q.153. A beam of X-rays impinges on a three-dimensional rectangular array whose periods are a, b, and c. The direction of the incident beam coincides with the direction along which the array period is equal to a. Find the directions to the diffraction maxima and the wavelengths at which these maxima will be observed.
Ans. Suppose α, β, and γ are the angles between the direction to the diffraction maximum and the directions of the array along the periods a, b and c respectively ( call them x, y, & z axes). Then the value of these angles can be found from the following familiar conditions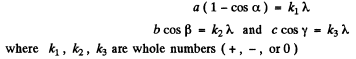
(These formulas are, in effect, Laue equations, see any text book on modem physics). Squaring and adding we g et on using 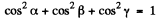
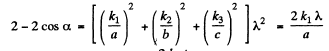
Thus 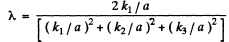
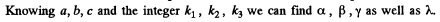
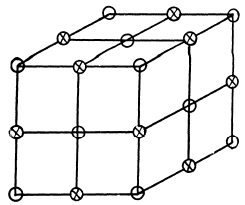
Q.154. A narrow beam of X-rays impinges on the natural facet of a NaCl single crystal, whose density is p = 2.16 g/cm3 at a glancing angle θ = 60.0°. The mirror reflection from this facet produces a maximum of second order. Find the wavelength of radiation.
Ans. The unit cell of NaCl is shown below. In an infinite crystal, there are four 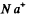 and four Cl- ions per unit cell. (Each ion on the middle of the edge is shared by four unit cells; each ion on the face centre by two unit cells, the ion in the middle of the cell by one cell only and finally each ion on the comer by eight unit cells.) Thus
and four Cl- ions per unit cell. (Each ion on the middle of the edge is shared by four unit cells; each ion on the face centre by two unit cells, the ion in the middle of the cell by one cell only and finally each ion on the comer by eight unit cells.) Thus

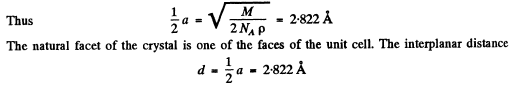
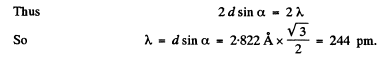
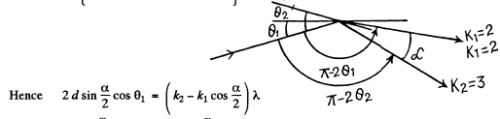
Q.155. A beam of X-rays with wavelength λ = 174 pm falls on the surface of a single crystal rotating about its axis which is parallel to its surface and perpendicular to the direction of the incident beam. In this case the directions to the maxima of second and third order from the system of planes parallel to the surface of the single crystal form an angle θ = 60° between them. Find the corresponding interplanar distance.
Ans. When the crystal is rotated, the incident monochromatic beam is diffracted from a given crystal plane of interplanar spacing d whenever in the coursVof rotation the value of θ satisfies the Bragg equation.
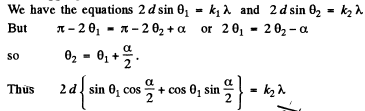
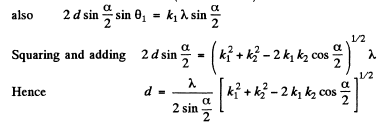
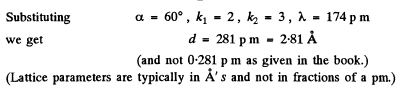
Q.156. On transmitting a beam of X-rays with wavelength λ = 17.8 pm through a polycrystalline specimen a system of diffraction rings is produced on a screen located at a distance l = 15 cm from the specimen. Determine the radius of the bright ring corresponding to second order of reflection from the system of planes with interplanar distance d = 155 pm.
Ans. In a polycrystalline specimen, microcrystals are oriented at various angles with respect to one another. The microcrystals which are oriented at certain special angles with respect to the incident beam produce diffraction maxima that appear as rings.
The radial of these rings are given by
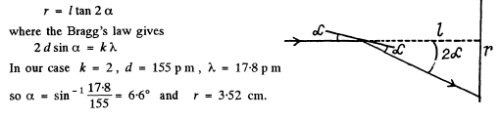

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|

















