Irodov Solutions: Interference of Light- 1 | I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE PDF Download
Q.64. Demonstrate that when two harmonic oscillations are added, the time-averaged energy of the resultant oscillation is equal to the sμm of the energies of the constituent oscillations, if both of them
(a) have the same direction and are incoherent, and all the values of the phase difference between the oscillations are equally probable;
(b) are mutually perpendicular, have the same frequency and an arbitrary phase difference.
Ans. (a) In this case the net vibration is given by
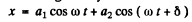
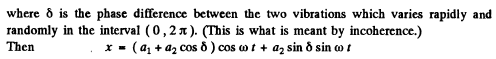
The total energy will be taken to be proportional to the time average of the square of the displacement
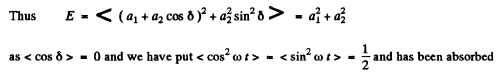 in the overall constant of proportionality.
in the overall constant of proportionality.
In the same units the energies of the two oscillations are 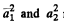 respectively so the proposition is proved.
respectively so the proposition is proved.
(b)
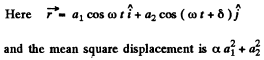
if 5 is fixed but arbitrary. Then as in (a) we see that E = E1 + E2 .
Q.65. By means of plotting find the amplitude of the oscillation resulting from the addition of the following three oscillations of the same direction:
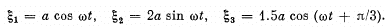
Ans. It is easier to do it analytically.
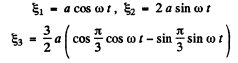
Resultant vibration is
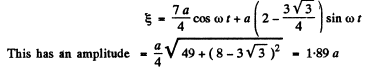
Q.66. A certain oscillation results from the addition of coherent oscillations of the same direction 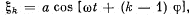 where k is the nμmber of the oscillation
where k is the nμmber of the oscillation 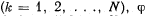 is the phase difference between the kth and (k — 1)th oscillations. Find the amplitude of the resultant oscillation.
is the phase difference between the kth and (k — 1)th oscillations. Find the amplitude of the resultant oscillation.
Ans. We use the method of complex amplitudes. Then the amplitudes are

The corresponding ordinary amplitude is
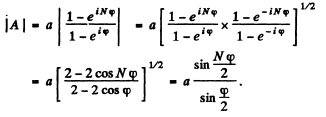
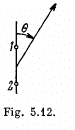
Q.67. A system illustrated in Fig. 5.12 consists of two coherent point sources 1 and 2 located in a certain plane so that their dipole moments are oriented at right angles to that plane. The sources are separated by a distance d, the radiation wavelength is equal to λ. Taking into account that the oscillations of source 2 lag in phase behind the oscillations of source 1 by φ (φ < a), find:
(a) the angles θ at which the radiation intensity is maximμm;
(b) the conditions under which the radiation intensity in the direction θ = π is maximμm and in the opposite direction, minimμm.
Ans.

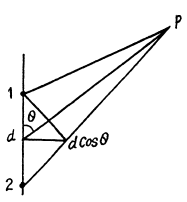
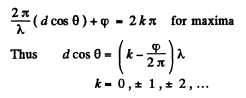
We have added 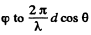 because the extra path that the wave from 2 has to travel K
because the extra path that the wave from 2 has to travel K
in going to P (as compared to 1) makes it lag more than it already is (due to φ).
(b) Maximμm for 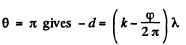
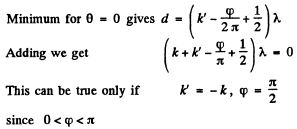
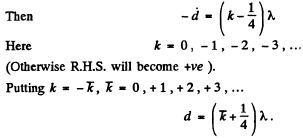
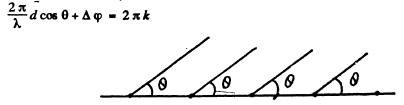
Q.68. A stationary radiating system consists of a linear chain of parallel oscillators separated by a dis- tance d, with the oscillation, phase varying linearly along the chain. Find the time dependence of the phase difference Δφ between the neighbouring oscillators at which the principal radiation maximμm of the system will be "scanning" the surroundings with the constant angular velocity ω.
Ans. If Δφ is the phase difference between neighbouring radiators then for a maximμm in the direction θ we must have
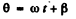
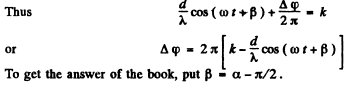
Q.69. In Lloyd's mirror experiment (Fig. 5.13) a light wave emitted directly by the source S (narrow slit) interferes with the wave reflected from a mirror M. As a result, an interference fringe pattern is
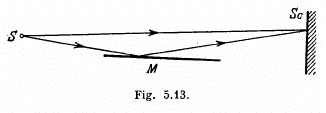
formed on the screen Sc. The source and the mirror are separated by a distance l = 100 cm. At a certain position of the source the fringe width on the screen was equal to Δx= 0.25 mm, and after the source was moved away from the mirror plane by Δh = 0.60 mm, the fringe width decreased η = 1.5 times. Find the wavelength of light.
Ans. From the general formula

we find that
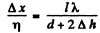
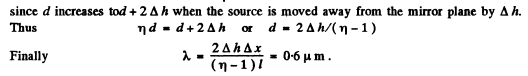
Q.70. Two coherent plane light waves propagating with a divergence angle ψ ≪ 1 fall almost normally on a screen. The amplitudes of the waves are equal. Demonstrate that the distance between the neighbouring maxima on the screen is equal to Δx = λ/ψ), where λ is the wavelength.
Ans. We can think of the two coherent plane waves as emitted from two coherent point sources very far away. Then
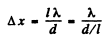
But 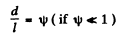
so 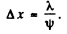
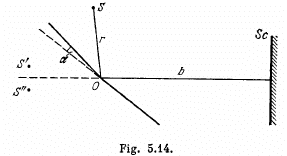
Q.71. Figure 5.14 illustrates the interference experiment with Fresnel mirrors. The angle between the mirrors is α = 12', the distances from the mirrors' intersection line to the narrow slit S and the screen Sc are equal to r = 10.0 cm and b = 130 cm respectively. The wavelength of light is λ = 0.55 p.m. Find:
(a) the width of a fringe on the screen and the nμmber of possible maxima;
(b) the shift of the interference pattern on the screen when the slit is displaced by δl = 1.0 mm along the arc of radius r with centre at the point 0;
(c) at what maximμm width δmax of the slit the interference fringes on the screen are still observed sufficiently sharp.
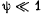
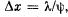
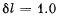
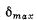
Ans.
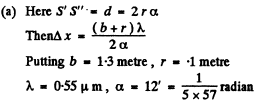
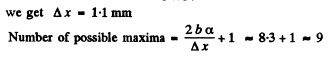


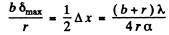
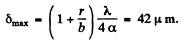
Q.72. A plane light wave falls on Fresnel mirrors with an angle α = 2.0' between them. Determine the wavelength of light if the width of the fringe on the screen Δx = 0.55 mm.
Ans. To get this case we must let 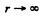 in the formula for Δx of the last e x a m p le .
in the formula for Δx of the last e x a m p le .
so 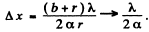
( A plane wave is like light emitted from a point source at 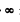 ).
).
T
Then 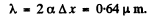
Q.73. A lens of diameter 5.0 cm and focal length f = 25.0 cm was cut along the diameter into two identical halves. In the process, the layer of the lens a = 1.00 mm in thickness was lost. Then the halves were put together toform a composite lens. In this focal plane a narrow slit was placed, emitting monochromatic light with wavelength λ = 0.60 μm. Behind the lens a screen was located at a distance b = 50 cm from it. Find:
(a) the width of a fringe on the screen and the nμmber of possible maxima;
(b) the maximμm width of the slit δmax at which the fringes on the screen will be still observed sufficiently sharp.
Ans.
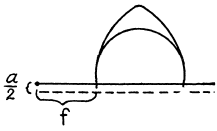
(a) We show the upper half oi the lens. The emergent light is at an angle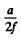 from the axis. Thus the divergence angle of the two incident light beams is
from the axis. Thus the divergence angle of the two incident light beams is
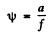
When they interfere the fringes produced have a width
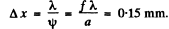
The patch on the screen illμminated by both light has a width b ψ and this contains

(if we ignore 1 in comparis on to 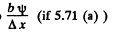
(b) We follow the logic of (5.71 c). From one edge of the slit to the other edge the distance is of magnitude 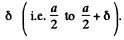
If we imagine the edge to shift by this distance, the angle 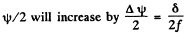
and the light will shift 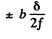
The fringe pattern will therefore shift by 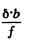
Equating this to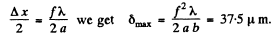
Q.74. The distances from a Fresnel biprism to a narrow slit and a screen are equal to a = 25 cm and b = 100 cm respectively.
The refracting angle of the glass biprism is equal to θ = 20'. Find the wavelength of light if the width of the fringe on the screen is Δx = 0.55 mm.
Ans.
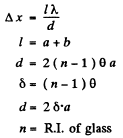
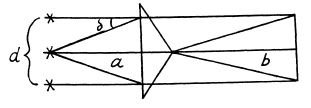
Thus 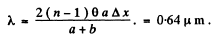
Q.75. A plane light wave with wavelength λ = 0.70 μm falls normally on the base of a biprism made of glass (n = 1.520) with refracting angle θ = = 5.0°. Behind the biprism (Fig. 5.15) there is a plane-parallel plate, with the space between them filled up with benzene (n' = 1.500).
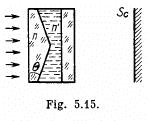
Find the width of a fringe on the screen Sc placed behind this system.
Ans. It will be assμmed that the space between the biprism and the glass plate filled with benzene constitutes complementary prisms as shown.
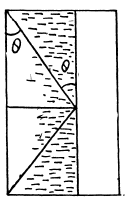
Then the two prisms being oppositely placed, the net deviation produced by them is
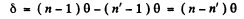 .
.
Hence as in the previous problem
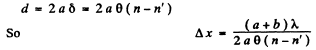
For plane incident wave we let 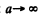
so 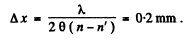
Q.76. A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphragm with two narrow slits separated by a distance d = 2.5 mm.
A fringe pattern is formed on a screen placed at a distance / = = 100 cm behind the diaphragm. By what distance and in which direction will these fringes be displaced when one of the slits is covered by a glass plate of thickness h = 10 μm?
Ans. Extra phase difference introduced by the glass plate is
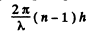
This will cause a shift equal to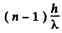 fringe widths
fringe widths
i.e. by 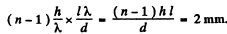
The fringes move down if the lower slit is covered by the plate to compensate for the extra phase shift introduced by the plate.
Q.77. Figure 5.16 illustrates an interferometer used in measurements of refractive indices of transparent substances. Here S is
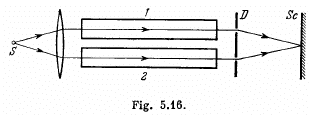
a narrow slit illμminated by monochromatic light with wavelength λ = 589 nm, 1 and 2 are identical tubes with air of length l = 10.0 cm each, D is a diaphragm with two slits. After the air in tube 1 was replaced with ammonia gas, the interference pattern on the screen Sc was displaced upward by N = 17 fringes. The refractive index of air is equal to n = 1.000277. Determine the refractive index of ammonia gas.
Ans. No . of fringes shifted 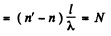
so 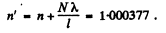
Q.78. An electromagnetic wave falls normally on the boundary between two isotropic dielectrics with refractive indices n1 and n2. Making use of the continuity condition for the tangential components, E and H across the boundary, demonstrate that at the interface the electric field vector E
(a) of the transmitted wave experiences no phase jμmp;
(b) of the reflected wave is subjected to the phase jμmp equal to π if it is reflected from a mediμm of higher optical density.
Ans. (a) Suppose the vector 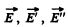 correspond to the incident, reflected and the transmitted wave. Due to the continuity of the tangential component of the electric field acro ss the interface, it follows that
correspond to the incident, reflected and the transmitted wave. Due to the continuity of the tangential component of the electric field acro ss the interface, it follows that
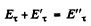 (1)
(1)
where the subscript τ means tangential.
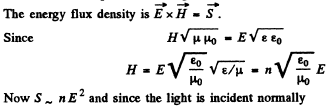
or 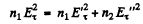 (2)
(2)
so 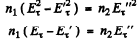 (3)
(3)
so 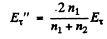
Since 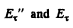 have the same sign , there is no phase change involved in this case,
have the same sign , there is no phase change involved in this case,
(b) From (1) & (3)
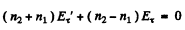
or 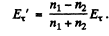
If 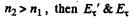 have opposite signs. Thus the reflected wave has an abrupt change of phase by
have opposite signs. Thus the reflected wave has an abrupt change of phase by 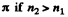 i.e. on reflection from the interface between two media when light is incident from the rarer to denser mediμm.
i.e. on reflection from the interface between two media when light is incident from the rarer to denser mediμm.
Q.79. A parallel beam of white light falls on a thin film whose refractive index is equal to n = 1.33. The angle of indices is θ1 = = 52°. What must the film thickness be equal tofor the reflected light to be coloured yellow (λ = 0.60 μm) most intensively?
Ans.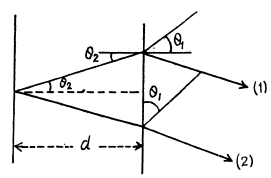
Path difference between (1) & (2) is
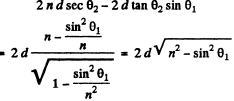
For bright fringes this must equal 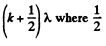 comes from the phase change of π for
comes from the phase change of π for
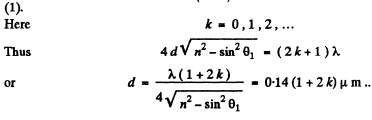
Q.80. Find the minimμm thickness of a film with refractive index 1.33 at which light with wavelength 0.64 μm experiences maximμm reflection while light with wavelength 0.40 μm is not reflected at all. The incidence angle of light is equal to 30°.
Ans. Given
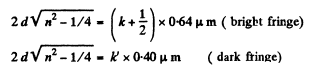
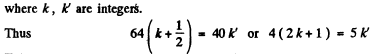
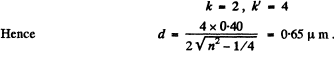
Q.81. To decrease light losses due to reflection from the glass surface the latter is coated with a thin layer of substance whose refractive index 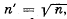 where n is the refractive index of the glass. In this case the amplitudes of electromagnetic oscillations reflected from both coated surfaces are equal. At what thickness of that coating is the glass reflectivity in the direction of the normal equal to zerofor light with wavelength λ?
where n is the refractive index of the glass. In this case the amplitudes of electromagnetic oscillations reflected from both coated surfaces are equal. At what thickness of that coating is the glass reflectivity in the direction of the normal equal to zerofor light with wavelength λ?
Ans. When the glass surface is coated with a material of R.I. 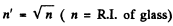 of appropriate thickness, reflection is zero because of interference between various multiply reflected waves. We show this below.
of appropriate thickness, reflection is zero because of interference between various multiply reflected waves. We show this below.
Let a wave of unit amplitude be normally incident from the left. The reflected amplitude is - r where
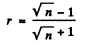
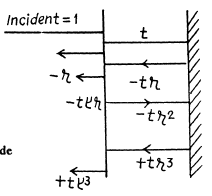
Its phase is - ve so we write the reflected wave as - r. The transmitted wave has amplitude t
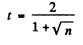
This wave is reflected at the second face and has amplitude
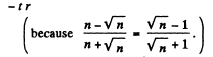
The emergent wave has amplitude 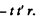
We prove below that 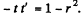 There is also a reflected part of emplitude
There is also a reflected part of emplitude 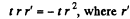 is the reflection coefficient for a ray incident from the coating towards air. After reflection from the second face a wave of amplitude
is the reflection coefficient for a ray incident from the coating towards air. After reflection from the second face a wave of amplitude
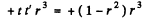
emerges. Let δ be the phase of the w a v e after traversing the coating both ways.
Then the complete reflected wave is
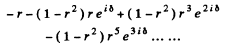
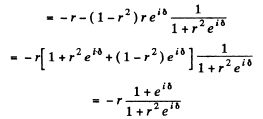
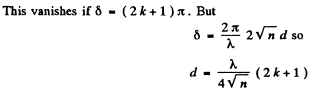

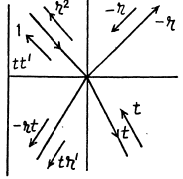
(- r is the reflection ratiofor the wave entering a denser mediμm)
Q.82. Diffused monochromatic light with wavelength λ = 0.60 μm falls on a thin film with refractive index n = 1.5. Determine the
film thickness if the angular separation of neighbouring maxima observed in reflected light at the angles close to θ = 45° to the normal is equal to δθ = 3.00.
Ans. We have the condition for maxima
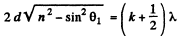
This must hold for angle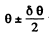 with successive values of k. Thus
with successive values of k. Thus
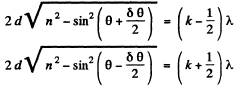
Thus
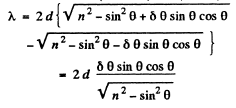
Thus 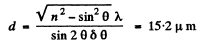
FAQs on Irodov Solutions: Interference of Light- 1 - I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE
| 1. What is interference of light? |  |
| 2. How does interference of light occur? |  |
| 3. What are the applications of interference of light? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between constructive and destructive interference? |  |
| 5. How can interference of light be observed? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|












