Irodov Solutions: Radioactivity- 2 | I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE PDF Download
Q.231. A radionuclide A1 goes through the transformation chain A1 → A2 → A3 (stable) with respective decay constants λ1 and λ2. Assuming that at the initial moment the preparation contained only the radionuclide A1 equal in quantity to N10 nuclei, find the equation describing accumulation of the stable isotope A3.
Ans. Here we have the equations
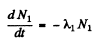
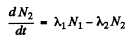
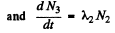
From problem 229
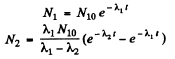
Then 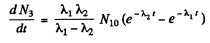
or 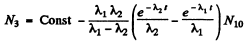
since N3 = 0 initially
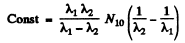
So 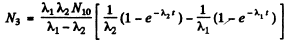
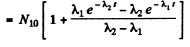
Q.232. A Bi21° radionuclide decays via the chain
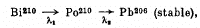
where the decay constants are 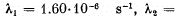 5.80.10-8 s-1. Calculate alpha- and beta-activities of the Bi210 preparation of mass 1.00 mg a month after its manufacture.
5.80.10-8 s-1. Calculate alpha- and beta-activities of the Bi210 preparation of mass 1.00 mg a month after its manufacture.
Ans We have the chain
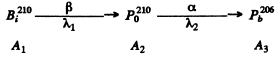
of the previous problem initially
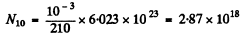
A month after preparation
N1 = 4.54 x 1016
N2 = 2.52 x 1018
using the results of the previous problem.
Then
Aβ = λ1N1 = 0.725 x 1011 dis/sec
Aα = λ2N2 = 1.46 x 1011 dis/sec
Q.233. (a) What isotope is produced from the alpha-radioactive Ra228 as a result of five alpha-disintegrations and four β-disintegrations?
(b) How many alpha- and β-decays does U 238 experience before turning finally into the stable Pb206 isotope?
Ans. (a) Ra has Z - 88, A - 226 After 3 a emission and 4 p (electron) emission
A - 206
Z - 88 + 4-5x2 - 82
The product is 82pb206
(b) We require
- ΔZ = 10 = 2 n - m
- ΔA = 32 = ft x 4
Here n = no. of α emissions
m = no. of β emissions
Thus n = 8, m = 6
Q.234. A stationary Pb200 nucleus emits an alpha-particle with kinetic energy Tα = 5.77 MeV. Find the recoil velocity of a daughter nucleus. What fraction of the total energy liberated in this decay is accounted for by the recoil energy of the daughter nucleus?
Ans. The momentum of the α-particle is
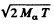 This is also the recoil m om entum o f the daughter nuclear in opposite direction. The recoil velocity of the daughter ntideus is
This is also the recoil m om entum o f the daughter nuclear in opposite direction. The recoil velocity of the daughter ntideus is
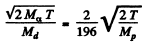 = 3.39x105 m/S
= 3.39x105 m/S
The eneigy of the daughter nucleus is 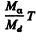 and this represents a fraction
and this represents a fraction
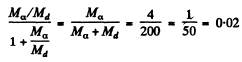
of total eneigy. Here Md is the mass of the daughter nudeus.
Q.235. Find the amount of heat generated by 1.00 mg of a Po210 preparation during the mean lifetime period of these nuclei if the emitted alpha-particles are known to possess the kinetic energy 5.3 MeV and practically all daughter nuclei are formed directly in the ground state.
Ans. The number of nuclei initially present is
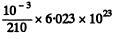
In the mean life time of these nuclei the number decaying is the fraction 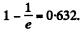 Thus the eneigy released is 2.87 x 1018 x 0.632 x 5.3 x 1.602 x 10-13 J = 1.54MJ
Thus the eneigy released is 2.87 x 1018 x 0.632 x 5.3 x 1.602 x 10-13 J = 1.54MJ
Q.236. The alpha-decay of Po210 nuclei (in the ground state) is accompanied by emission of two groups of alpha-particles with kinetic energies 5.30 and 4.50 MeV. Following the emission of these particles the daughter nuclei are found in the ground and excited states. Find the energy of gamma-quanta emitted by the excited nuclei.
Ans. We neglect all recoil effects. Then the following diagram gives the eneigy of the gamma ray
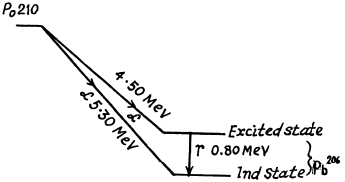
Q.237. The mean path length of alpha-particles in air under standard conditions is defined by the formula R = 0.98.10-27 v3o cm, where v0 (cm/s) is the initial velocity of an alpha-particle. Using this formula, find for an alpha-particle with initial kinetic energy 7.0 MeV:
(a) its mean path length;
(b) the average number of ion pairs formed by the given alphaparticle over the whole path R as well as over its first half, assuming the ion pair formation energy to be equal to 34 eV.
Ans. (a) For an alpha particle with initial K.E. 7.0 MeV, the initial velocity is
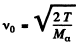
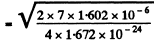
= 1.83 x 109an/sec
Thus R = 6.02an
(b) Over the whole path the number of ion pairs is
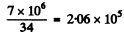
Over the first half of the path We write the formula for the mean path as RαE1/2 where E is the initial energy. Thus if the energy of the a-particle after traversing the first half of the path is E1 then
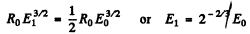
Hence number of ion pairs formed in the first half of the path length is
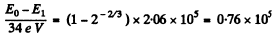
Q.238. Find the energy Q liberated in β-- and β+-decays and in K-capture if the masses of the parent atom MP, the daughter atom Md and an electron m are known.
Ans. In β- decay
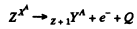
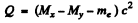
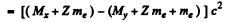
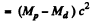
since Mp, Md are the masses of the atoms. The binding energy of the electrons in ignored. In K capture
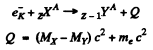
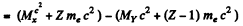
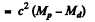
In β+ decay 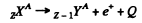
Then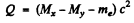
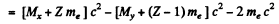
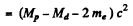
Q.239. Taking the values of atomic masses from the tables, find the maximum kinetic energy of beta-particles emitted by Be10 nuclei and the corresponding kinetic energy of recoiling daughter nuclei formed directly in the ground state.
Ans. The reaction is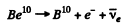
For maximum K.E. of electrons we can put the energy of 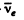 to be zero. The atomic masses are
to be zero. The atomic masses are
Be10 = 10.016711 amu
B10 = 10.016114 amu
So the K.E. of electrons is (see previous problem)
597 x 10-6 amu x c2 = 0.56 MeV
The momentum of electrons with this K.E. is 0.941 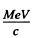
and the recoil energy of the daughter is
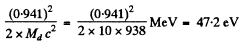
Q.240. Evaluate the amount of heat produced during a day by a β--active Na24 preparation of mass m = 1.0 mg. The beta-particles are assumed to possess an average kinetic energy equal to 1/3 of the highest possible energy of the given decay. The half-life of Na24 is T = 15 hours.
Ans. The masses are
Na24 = 24 - 0.00903 amu and Mg24 = 24 - 0.01496 amu
The reaction is
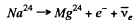
The maximum K.E. of electrons is
0.00593 x 93 MeV = 5.52 MeV
Average K.E. according to the problem is then 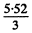 = 1.84 MeV
= 1.84 MeV
The initial number of Na24 is
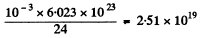
The fraction decaying in a day is
1 - (2) - 24/15 = 0.67
Hence the heat produced in a day is
0.67 x 2.51 x 1019 x 1.84 x 1.602 x 10-13 Joul = 4.95MJ
Q.241. Taking the values of atomic masses from the tables, calculate the kinetic energies of a positron and a neutrino emitted by C11 nucleus for the case when the daughter nucleus does not recoil.
Ans. We assume that the parent nucleus is at rest Then since the daughter nucleus does not recoil, we have
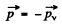
i.e. positron & v mometum are equal and opposite. On the other hand
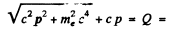 total energy released. (Here we have used the fact that energy
total energy released. (Here we have used the fact that energy
of the neutrino is 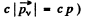
Now 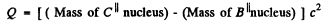
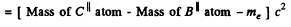
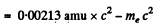
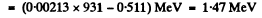
Then 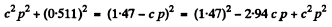
Thus c p = 0.646 M eV = energy of neutrino
Also K.E. of electron = 1.47 - 0.646 - 0.511 = 0.313 MeV
Q.242. Find the kinetic energy of the recoil nucleus in the positronic decay of a Nn nucleus for the case when the energy of positrons is maximum.
Ans. The K.E. of the positron is maximum when the energy of neutrino is zero. Since the recoil energy of the nucleus is quite small, it can be calculated by successive approximation.
The reaction is
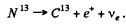
The maximum energy available to the positron (including its rest energy) is
c2 (Mass of N13 nucleus - Mass of C13 nucleus)
= c2 (Mass of N13 atom - Mass of C13 atom - me)
= 0.00239 c2 - mec2
= (0.00239 x 931 - 0.511) MeV
= 1.71 MeV
The momentum corresponding to this energy is 1.636 MeV/c .
The recoil energy of the nucleus is then
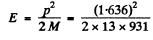 = 111 eV = 0.111 keV
= 111 eV = 0.111 keV
on using Mc2 - 13 x 931 MeV
Q.243. From the tables of atomic masses determine the velocity of a nucleus appearing as a result of K-capture in a Bel atom provided the daughter nucleus turns out to be in the ground state.
Ans. The process is
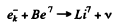
The energy available in the process is
Q = c2 (Mass of Be7 atom - Mass of Li-7 atom)
= 0.00092 x 931 MeV = 0.86 MeV
The momentum of a K electron is negligible. So in the rest frame of the Be7 atom, most of the energy is taken by neutrino whose momentum is very nearly 0.86MeV/c The momentum of the recoiling nucleus is equal and opposite. The velocity of recoil is
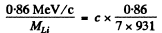 = 3.96 x106 cm/s
= 3.96 x106 cm/s
Q.244. Passing down to the ground state, excited Ag109 in nuclei emit either gamma quanta with energy 87 keV or K conversion electrons whose binding energy is 26 keV. Find the velocity of these electrons.
Ans. In internal conversion, the total energy is used to knock out K electrons. The KE. of these electrons is energy available-B.E. of K electrons
= (87 - 26) = 61 keV
The total energy including rest mass of electrons is 0.511 + 0.061 = 0.572 MeV
The momentum corresponding to this total energy is
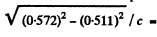 0257 MeV/c.
0257 MeV/c.
The velocity is then =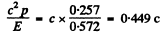
Q.245. A free stationary Ir191 nucleus with excitation energy E = 129 keV passes to the ground state, emitting a gamma quantum. Calculate the fractional change of gamma quanta energy due to recoil of the nucleus.
Ans. With recoil neglected, the y-quantram will have 129 keV eneigy. To a first approximation, its momentrum will be 129 keV/c and the energy of recoil will be
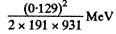 = 4.18 x 10- 8 MeV
= 4.18 x 10- 8 MeV
In the next approximation we therefore write 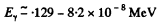
Therefore 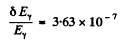
Q.246. What must be the relative velocity of a source and an absorber consisting of free Ir191 nuclei to observe the maximum absorption of gamma quanta with energy ε = 129 keV?
Ans. For maximum (resonant) absorption, the absorbing nucleus must be moving with enough speed to cancel the momentum of the oncoming photon and have just right eneigy (ε = 129 keV) available for transition to the excited state.

Since 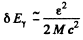 and momentum of the photon is
and momentum of the photon is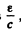 these condition can be satisfied if the velocity of the nucleus is
these condition can be satisfied if the velocity of the nucleus is
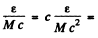 218m/s = 0.218km/s
218m/s = 0.218km/s
Q.247. A source of gamma quanta is placed at a height h = 20m above an absorber. With what velocity should the source be displaced upward to counterbalance completely the gravitational variation of gamma quanta energy due to the Earth's gravity at the point where the absorber is located?
Ans. Because of the gravitational shift the frequency of the gamma ray at the location of the absorber is increased by
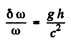
For this to be compensated by the Doppler shift (assuming that resonant absorption is possible in the absence of gravitational field) we must have
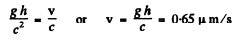
Q.248. What is the minimum height to which a gamma quanta source containing excited Zn67 nuclei has to be raised for the gravitational displacement of the Mossbauer line to exceed the line width itself, when registered on the Earth's surface? The registered gamma quanta are known to have an energy ε = 93 keV and appear on transition of Zn67 nuclei to the ground state, and the mean lifetime of the excited state is ζ = 14μS.
Ans. The natural life time is
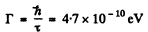
Thus the condition 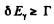 implies
implies 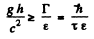
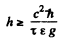 = 4.64 metre
= 4.64 metre
(h here is height of the place, not planck’s constant.)
FAQs on Irodov Solutions: Radioactivity- 2 - I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE
| 1. What is radioactivity and how does it occur? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of radiation emitted during radioactive decay? |  |
| 3. How does radioactivity affect living organisms? |  |
| 4. How is radioactivity measured? |  |
| 5. How is radioactivity used in practical applications? |  |
















