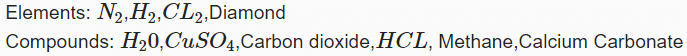Is Matter Around Us Pure Class 9 Worksheet Science

Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. Kerosene and Petrol are miscible liquids. The difference between their boiling points is more than 25°C. The two liquids can be separated from each other by _____.
(a) Simple distillation
(b) Steam distillation
(c) Fractional distillation
(d) Any of these
Correct Answer is Option (a)
By simple distillation. Vapours of the liquid which has low boiling point will be formed first and collected. The liquid having higher boiling point will remain in the vessel.
Q.2. How can a saturated solution be made unsaturated?
(a) By heating the solution
(b) By cooling the solution
(c) By increasing the amount of solute
(d) By centrifugation of the solution
Correct Answer is Option (a)
A saturated solution can be made unsaturated by increasing the temperature of solution by heating it or by increasing the amount of solvent in the solution i.e. diluting it.
Q.3. The cause of Brownian movement is:
(a) Heat changes in liquid state
(b) Convection currents
(c) Impact of molecules of dispersion medium on on dispersed phase
(d) Attractive forces between the particles of dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Zig-zag path of colloidal particles is called Brownian Movement. Zig-zag path of particles is due to collision of particles of dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
Q.4. In which of the following, dispersed phase is a liquid and dispersion medium is a gas?
(a) Cloud
(b) Smoke
(c) Gel
(d) Soap bubble
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- In a cloud, tiny water droplets are suspended in air.
- This makes it an example of a liquid dispersed phase in a gas dispersion medium.
Q.5. At room temperature, a non-metal which is a liquid is:
(a) Sulphur
(a) Bromine
(a) Chlorine
(a) Nitrogen
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Bromine is the only non-metal that exists in liquid form at room temperature. Here are some key points:
- It is a reddish-brown liquid.
- Bromine has a strong, unpleasant odour.
- It is used in various applications, including flame retardants and pesticides.
Fill in the Blanks
1. Common salt is _________.
Ans: Compound
Common salt, chemically known as sodium chloride (NaCl), is a compound formed from the chemical combination of sodium and chlorine.
2. A mixture contains more than ______ substance mixed in ______ proportion.
Ans: One, any
A mixture is defined as a combination of two or more substances that can be present in any proportion.
3. Properties of a __________ are different from its constituent elements, whereas a _______
shows the properties of its constituting elements.
Ans: Compound, mixture
A compound has distinct properties that differ from those of its individual elements, while a mixture retains the properties of its components.
4. A solution is defined as a mixture that is_________
Ans: Homogeneous
A homogeneous mixture has a uniform composition throughout, meaning the components are evenly distributed.
5. We can remove salts from a solution by using the process of _________
Ans: Evaporation
Evaporation is a method used to separate a solute from a solvent by heating the solution until the solvent turns into vapor.
6. A pure substance has a fixed__________ or ______ at constant temperature.
Ans: Melting Point, Boiling Point
A pure substance has specific melting and boiling points that do not change under constant temperature conditions.
7. An element is made up of only one kind of _________.
Ans: Atoms
Elements consist of only one type of atom, which defines their unique properties.
8. Miscible liquids are separated by ________ .
Ans: Fractional distillation
Fractional distillation is a technique used to separate miscible liquids based on their different boiling points.
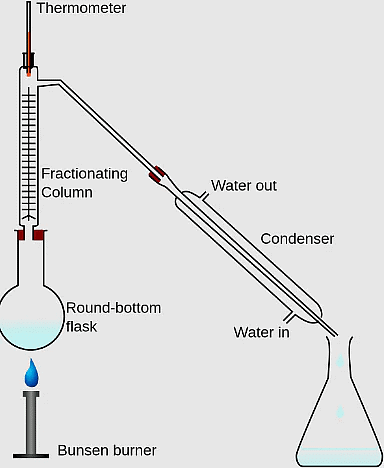
9. Immiscible liquids are separated by using a _______.
Ans: Separating funnel
A separating funnel is used to separate immiscible liquids based on their different densities.
10. Filtered tea is a _________ mixture.
Ans: Homogeneous
Filtered tea is homogeneous because it has a uniform composition throughout after the solid tea leaves are removed.
11. Alloy is a _______.
Ans: Solid solution
An alloy is a solid solution of two or more metals, which results in improved properties compared to the individual metals.
12. Sublimation of camphor is a _________ change.
Ans: Physical
Sublimation is a physical change where a substance transitions directly from solid to gas without passing through the liquid state.
13. Most common chemical change we observe in our routine life is rusting of______.
Ans: Iron
Rusting is a chemical reaction that occurs when iron reacts with oxygen and moisture, forming iron oxide.
Very Short Answer Question
Q.1. Classify the substances given in below figure into elements and compounds
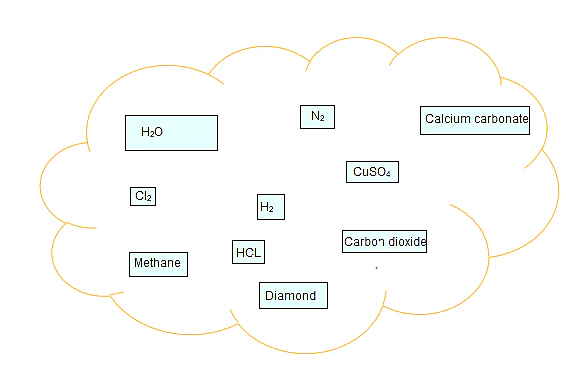
Ans:
Q.2. Give one example each of homogeneous and heterogeneous mixture.
Ans: Homogeneous mixture: An example is brass, which is a uniform mixture of metals. Heterogeneous mixture: An example is sand and water, where the components remain distinct and easily separable.
Q.3. Name the apparatus by which mixture of oil and water can be separated.
Ans: Separating funnel is the apparatus used to separate a mixture of oil and water.
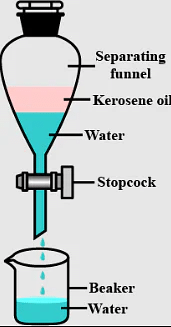 Q.4. Is brass a mixture or a compound?
Q.4. Is brass a mixture or a compound?
Ans: Brass is classified as a mixture rather than a compound. This is due to the following reasons:
- Brass is made up of approximately 30% zinc and 70% copper.
- In a mixture, the individual components retain their own properties.
- Brass can vary in composition, which is characteristic of mixtures.
- It cannot be separated into its components through physical methods.
Q.5. What type of solution is an alloy? Liquid solution or solid solution
Ans: Alloy is a type of solid solution. Key points:
- An alloy consists of two or more metals or a metal and a non-metal.
- It cannot be separated into its components by physical methods.
- Alloys exhibit the properties of their constituent materials.
- For example, brass is made of approximately 30% zinc and 70% copper.
Q.6. A mixture consisting of two miscible liquids 'A' and 'B' whose boiling points differ by 50 C can be separated by which process?
Ans: Fractional distillation is the process used to separate a mixture of two miscible liquids, 'A' and 'B', when their boiling points differ by 50°C.
Q.7. Give one example of solid- liquid homogeneous mixture.
Ans: Salt in water solution
Q.8. What is a Aqua regia?
Ans: Aqua regia is a highly-corrosive mixture of - nitric acid and hydrochloric acid. The mixture is formed by freshly mixing concentrated nitric acid and hydrochloric acid, usually in a volume ratio of 1:3
Q.9. Which method is used to separate two immiscible liquids?
Ans: Separating two immiscible liquids can be effectively achieved using a separating funnel.
- The separating funnel allows the two liquids to separate based on their density.
- Each liquid forms a distinct layer, making it easy to pour out one layer while leaving the other behind.
- This method is commonly used in laboratories for liquid-liquid extractions.
Q.10. Name two elements which are in liquid state at room temperature?
Ans: The only liquid elements at standard temperature and pressure arebromine (Br) and mercury (Hg). Although, elements caesium (Cs),rubidium (Rb), Francium (Fr) and Gallium (Ga) become liquid at or just above room temperature.
Short Answer Types Questions
Q.1. Try segregating the things around you as pure substances or mixtures.
You can separate materials around you into pure substances or mixtures by performing simple experiments. Here’s how:
- Mix chalk powder with water.
- Observe that the chalk powder does not dissolve.
- Let the mixture settle; the chalk will form a layer at the bottom.
- Carefully pour off the water to separate the chalk.
This method demonstrates how mixtures can be separated into their individual components.
Q.2. What is meant by a substance?
A substance is a type of matter that consists of particles that cannot be separated by any physical process. Key characteristics include:
- All particles have similar chemical properties.
- Substances can be classified as either elements or compounds.
- Elements cannot be broken down into simpler substances.
- Compounds consist of two or more different elements chemically combined.
In summary, a substance is a pure form of matter with consistent properties throughout.
Q.3. What type of mixtures are separated by the technique of crystallisation?
From impure samples of solids, pure solid crystals can be obtained by the method of crystallization for eg to obtain pure sugar from impure sample of the same.
Q.4. What is tyndall effect? Which kinds of solution show it?
The Tyndall effect is the scattering of light by particles in a solution. This effect occurs when light passes through a medium containing small particles, making the path of the light visible. Solutions that exhibit the Tyndall effect include:
- Colloidal solutions: These contain particles that are larger than those in true solutions but smaller than those in suspensions.
- Examples: Milk and fog show the Tyndall effect due to their dispersed particles.
Q.5. What is centrifugation? Where it is used?
Centrifugation is a technique used to separate components of a mixture based on their density. It works by spinning the mixture rapidly, causing denser particles to settle at the bottom while lighter ones rise to the top.
- Commonly used to separate cream from milk.
- Also applied in laboratories for separating blood components.
- Used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals and biotechnology.
Q.6. What is crystallization? Where is it used? Why is this better than simple evaporation technique?
Crystallization is a process that separates a pure solid in the form of crystals from its solution. It is used to purify solids. For e.g. salt from sea water is purified using crystallization.
It is a better technique than simple evaporation because:
(a) Some solid may decompose or get charred on heating to dryness during evaporation.
(b) On evaporation, some of the impurities still remain dissolved in the solution.
Q.7. What is a colloid? What are its various properties?
Colloids are heterogeneous mixtures where the particles are too small to be seen with the naked eye. Their properties include:
- Heterogeneous mixture: Although they are heterogeneous, they often appear homogeneous.
- Particle size: The particles are too small to be individually visible.
- Tyndall effect: They scatter light, making the path of a beam visible.
- Stability: The particles do not settle when left undisturbed.
Q.8. Write a method to separate different gases from air.
Air is a homogeneous mixture of various gases. It can be separated into its components using fractional distillation. The process involves the following steps:
- Compress and cool the air by increasing pressure and decreasing temperature.
- This produces liquid air. Allow the liquid air to warm up slowly in a fractional distillation column.
- The gases will separate according to their boiling points at different heights in the column.
Q.9. Explain the following giving examples.
(a) saturated solution
(b) pure substance
(c) colloid
(d) suspension
(a) saturated solution: It is a solution in which no more solute particles can be dissolved at a particular temperature.
(b) pure substance: Such substance that has a uniform composition i.e. has particles with identical properties is called pure substance eg sugar, salt, water, nitrogen etc.
(c) colloid: It is a kind of heterogeneous mixture/solution in which particle size is between 1nm and 1000nm. Colloids have dispersion medium and dispersed phase.eg smoke, milk, shaving cream, jelly, cheese etc.
(d) suspension: It is a kind of heterogeneous mixture in which insoluble solid particles remain suspended in the medium and dispersion particles are visible to the unaided eyes.eg muddy river water, chalk powder in water, dust storm, sand in water etc.
Q.10. Write the steps you would use for making tea. Use the words solution, solvent, solute, dissolve, soluble, insoluble, filtrate and residue.
To make tea, follow these steps:
- Start by heating a sufficient amount of solvent (water) in a pan.
- Once heated, add a small amount of solute (sugar) to the water. The sugar will dissolve completely, forming a true solution.
- Add tea leaves, which are insoluble, along with a soluble liquid (milk).
- Boil the mixture to enhance flavour.
- After boiling, use a sieve to filter the mixture. The liquid that passes through is the filtrate, which is your tea.
- The leftover tea leaves in the sieve are the residue and should be discarded.
Crossword Puzzle
Across
1. hydrogen ______ is a color gas with a smell of rotten eggs
5. The major components in solution
6. Melting point and boiling point are _______ properties
7. Two elements are liquid at room temperature are mercury and _______
Down
2. In colloids ,The particles are called the ______ phase and the medium in which they are distributed is called the dispersion medium.
3. amount of solute present per unit volume or mass of the solution or solvent
4. denser particles are forced to the bottom and the lighter particles stay at the top when spun rapidly
Ans:
1. sulphide
2. dispersed
3. concentration
4.centrifugation
5. solvent
6. physical
7. bromine
|
85 videos|549 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Is Matter Around Us Pure Class 9 Worksheet Science
| 1. What is the difference between a pure substance and a mixture? |  |
| 2. How can you determine if something is a pure substance or a mixture? |  |
| 3. Give an example of a pure substance and a mixture. |  |
| 4. Can mixtures be classified into different types? |  |
| 5. How can mixtures be separated into their individual components? |  |