JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): States of Matter- 2 | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.17. An LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) cylinder weighs 14.8 kg when empty. When full, it weighs 29.0 kg and shows a pressure of 2.5 atm. In the course of use at 27º C, the weight of the full cylinder reduces to 23.2 kg. Find out the volume of the gas in cubic meters used up at the normal usage conditions, find the final pressure inside the cylinder.
Assume LPG to be n-butane with normal boiling point of 0ºC. (1994 - 3 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Calculation of volume of gas : Weight of cylinder with gas = 29.0 kg
Weight of empty cylinder = 14.8 kg
∴ Weight of gas in the cylinder = 14.2 kg Pressure in cylinder = 2.5 atm
∴ No. of moles (n) in 14.2 kg (14.2 × 103g) of butane
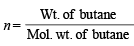
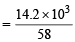 = 244.83 mol
= 244.83 mol
Applying gas equation,
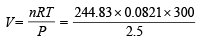 = 2412 litres
= 2412 litres
[27°C = 273 + 27 = 300]
Calculation of pressure in cylinder after use.
Weight of cylinder after use = 23.2 kg
Weight of empty cylinder = 14.8 kg
∴ Wt. of unused gas = 8.4 kg 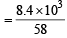 moles of butane
moles of butane
Thus P = 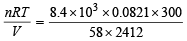 = 1.478 atm [V = 2412 L]
= 1.478 atm [V = 2412 L]
Calculation of volume of used gas at 2.5 atm and 27ºC.
Weight of used gas = 14.2 – 8.4 = 5.8 kg
Pressure under normal usage conditions = 1 atm
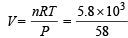
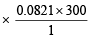
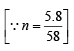
= 2463 litres = 2.463 m3
Q.18. A mixture of ethane (C2H6) and ethene (C2H4) occupies 40 litres at 1.00 atm and at 400 K. The mixture reacts completely with 130 g of O2 to produce CO2 and H2O. Assuming ideal gas behaviour, calculate the mole fractions of C2H4 and C2H6 in the mixture. (1995 - 4 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Let the volume of ethane in mixture = x litre
∴ Volume of ethene = (40 – x) litre
Combustion reactions of ethane and ethene are :
(i) 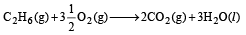
or 2C2 H6 (g) + 7O2 (g) ¾¾→ 4CO2 (g) + 6H2O(l )
(ii) C2H4(g) + 3O2(g) ¾¾→ 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(l )
Volume of O2 required for complete combustion of ethane
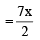 [For x litres]
[For x litres]
Volume of O2 required for complete combustion of ethene = (40–x) × 3 [For (40 – x) L]
∴ Total volume of O2 required
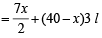
Calculation of number of moles (n)
P = 1 atm, 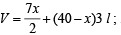 R = 0.082 l atm K–1 mol–1;
R = 0.082 l atm K–1 mol–1;
T = 400 K
Since n = 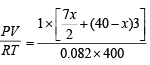
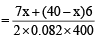
Mass of n moles of O2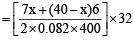 = 130
= 130
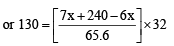
⇒ 8528 = 32 x + 240 × 32 ⇒ 32x = 848 ⇒ or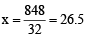
Hence mole fraction (%) of ethane = 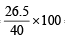 = 66.25%
= 66.25%
Mole fraction (%) of ethene = 33.75%
Q.19. The composition of the equilibrium mixture ( Cl2 2Cl ), which is attained at 1200°C, is determined by measuring the rate of effusion through a pin–hole. It is observed that at 1.80 mmHg pressure, the mixture effuses 1.16 times as fast as krypton effuses under the same conditions. Calculate the fraction of the chlorine molecules dissociated into atoms. (Relative atomic mass of Kr = 84.) (1995 - 4 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Mixture Kr ypton
rmix = 1.16 rKr = 1
Mmix = ? MKr = 84
We know that
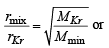
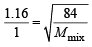
or (1.16)2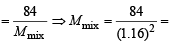 62.426
62.426
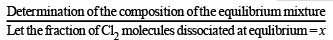
Initially 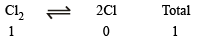
At equilibrium 1 – x 2x 1– x + 2x = 1 + x
∴ Total moles at equilibrium = 1 – x + 2x = 1 + x
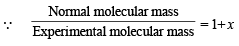
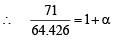
∴ a = 0.137 = 13.7%.
Q. 20. A 20.0 cm3 mixture of CO, CH4 and He gases is exploded by an electric discharge at room temperature with excess of oxygen. The volume contraction is found to be 13.0 cm3. A further contraction of 14.0 cm3 occurs when the residual gas is treated with KOH solution. Find out the composition of the gaseous mixture in terms of volume percentage. (1995 - 4 Marks)
Ans. Sol. TIPS/Formulae :
(i) He does not react with oxygen.
(ii) KOH absorbs only CO2.
NOTE : When the mixture of CO, CH4 and He gases (20 ml) are exploded by an electric discharge with excess of O2, He gas remains as such and the other reactions involved are :
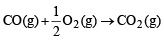 ...(i)
...(i)
CH4 (g ) + 2O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2H 2O(l) ...(ii)
Let the volumes of CO and CH4 to be ‘a’ ml and ‘b’ ml in the mixture then
Volume of He gas = [20 – (a + b)] ml
For the initial contraction of 13 ml,
Volume of left hand side in the above reactions – 13 = Volume of right hand side
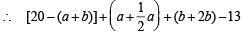
= [20 – (a + 2b)] + a + b [neglect the volume of H2O (l)](Since for gases, volume a no. of moles)
∴ 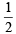 a + 2 b = 13 or a + 4 b = 26 ...(iv)
a + 2 b = 13 or a + 4 b = 26 ...(iv)
NOTE THIS STEP : The CO2 produced above in reactions (ii) & (iii), (a + b) ml, reacts with KOH sol for a further contraction of 14 ml.
CO2(g) + 2KOH(l) → K2 CO3(l) + H2O(l) (a + b) ml
∴ a + b = 14 ...(v)
Solving (iv) & (v) we get, a = 10 ml & b = 4 ml
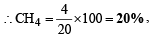
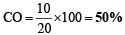
& He = 100 – ( 20 + 50) = 30%
Q. 21. An evacuated glass vessel weighs 50.0 g when empty, 148.0 g when filled with a liquid of density 0.98 g mL–1 and 50.5 g when filled with an ideal gas at 760 mmHg at 300K. Determine the molar mass of the gas. (1998 - 3 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Weight of liquid = 148 – 50 = 98 g
Volume of liquid = 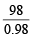 = 100 ml = volume of vessel It means, vessel of 100 ml contains ideal gas at 760 mm Hg at 300 K
= 100 ml = volume of vessel It means, vessel of 100 ml contains ideal gas at 760 mm Hg at 300 K
Weight of gas = 50.5 – 50 = 0.5g
using, 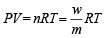
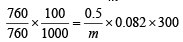
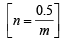
∴ Molecular weight of gas (m) = 123
Q.22. The degree of dissociation is 0.4 at 400 K and 1.0 atm for the gaseous reaction PCl5 PCl3 + Cl2. Assuming ideal behaviour of all gases, calculate the density of equilibrium mixture at 400 K and 1.0 atmosphere. (Relative atomic mass of P = 31.0 and Cl = 35.5) (1998 - 3 Marks)
Ans. Sol. 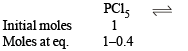
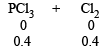
∴ Total moles at equilibrium = 1 – 0.4 + 0.4 + 0.4 = 1.4
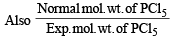 = 1 + a = 1.4
= 1 + a = 1.4
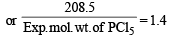
∴ Exp. mol. wt. of PCl5 or m. wt. of mixture =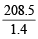
Now using, 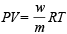 for mixture
for mixture
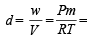
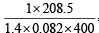 = 4.53 g/litre
= 4.53 g/litre
Q.23. Using van der waal’s equation, calculate the constant, ‘a’ when two moles of a gas confined in a four litre flask exerts a pressure of 11.0 atmospheres at a temperature of 300 K.
The value of ‘b’ is 0.05 L mol–1. (1998 - 4 Marks)
Ans. Sol. van der Waals equation for n moles of gas is
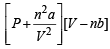 = nRT
= nRT
Given V = 4 litre; P = 11.0 atm, T = 300 K; b = 0.05 litre mole–1, n =2
Thus, 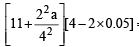 = 2 x 0.082 x 300
= 2 x 0.082 x 300
∴ a = 6.46 atm litre2 mol–2
Q.24. For the reaction, N2O5(g) → 2NO2(g) + 0.5 O2(g), calculate the mole fraction of N2O5(g) decomposed at a constant volume and temperature, if the initial pressure is 600 mm Hg and the pressure at any time is 960 mm Hg. Assume ideal gas behaviour. (1998 - 3 Marks)
Ans. Sol. 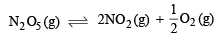
Initial pressure 600 0 0
Final pressure 600-P 2P P/2
P ∝ moles when V and T are constant (where moles equivalent to pressure P are decomposed)
Total pressure = 600 – P + 2 P + P/2 = 960 mm of Hg
∴ P = 240 mm Hg
Thus moles of N2O5 decomposed = 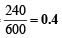
Q.25. One mole of nitrogen gas at 0.8 atm takes 38 s to diffuse through a pinhole, whereas one mole of an unknown compound of xenon with flourine at 1.6 atm takes 57 s to diffuse through the same hole. Calculate the molecular formula of the compound. (1999 - 5 Marks)
Ans. Sol. We know that
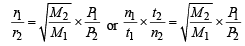
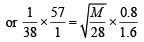 ∴ M = 252
∴ M = 252
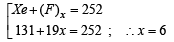
Thus compound of xenon with fluorine is XeF6
Q.26. The pressure exerted by 12 g of an ideal gas at temperature t°C in a vessel of volume V litre is one atm. When the temperature is increased by 10 degrees at the same volume, the pressure increases by 10%. Calculate the temperature t and volume V. (Molecular weight of the gas = 120.) (1999 - 5 Marks)
Ans. Sol. (I) Given P = 1 atm, w = 12 g; T = (t + 273)K; V = V litre
(II) If T = t + 10 + 273 = t + 283 K ; V = V litre,
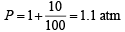
Using gas equation, 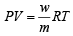
Case I. 1 x V 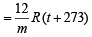 ... (1)
... (1)
Case I. 1.1 x V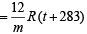 ...(2)
...(2)
From (1) and (2), t = –173ºC or t = 100 K
Also from (1), on substituting t and m (120), V = 0.82 litre
Q.27. Calculate the pressure exerted by one mole of CO2 gas at 273 K if the van der Waal's constant a = 3.592 dm6 atm mol–2. Assume that the volume occupied by CO2 molecules is negligible. (2000 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol.
vander Waals’ equation for one mole of a gas is
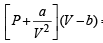 = RT ...(1)
= RT ...(1)
Given that volume occupied by CO2 molecules, ‘b’ = 0
Hence, (1) becomes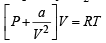
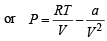
Using R = 0.082, T = 273K, V = 22.4 l for 1 mole of an ideal gas at 1 atm pressure.
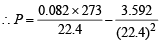 = 0.9922 atm.
= 0.9922 atm.
Q. 28. The compression factor (compressibility factor) for one mole of a van der Waals gas at 0°C and 100 atmospheric pressure is found to be 0.5. Assuming that the volume of a gas molecule is negligible, calculate the van der Waals constant a. (2001 - 5 Marks)
Ans. Sol. We know that, Compressibility factor , 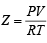
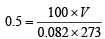 ∴ V = 0.1119L
∴ V = 0.1119L
NOTE : Further when volume of a gas molecule is negligible, van der Waal’s equation becomes
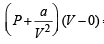 = RT
= RT
or PV = RT - 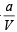 or a = RTV- PV2
or a = RTV- PV2
Substituting the values a = (0.082 × 0.1119 × 273) – (100 × 0.1119 × 0.1119)
= 1.253 atm L2 mol–2
Q.29. The density of the vapour of a substance at 1 atm pressure and 500 K is 0.36 kgm-3. The vapour effuses through a small hole at a rate of 1.33 times faster than oxygen under the same condition. (2002 - 5 Marks)
(a) Determine (i) molecular weight, (ii) molar volume, (iii) compression factor (Z) of the vapour and (iv) which forces among the gas molecules are dominating, the attractive or the repulsive?
(b) If the vapour behaves ideally at 1000 K, determine the average translational kinetic energy of a molecule.
Ans. Sol. (a) d = 0.36 kg m–3 = 0.36 g/L (i)
From Graham’s Law of diffusion
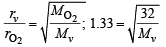
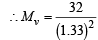 = 18.09;
= 18.09;
where Mv = MW of the vapour
(ii) Thus, 0.36g = 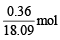
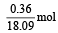 occupies 1 L volume, so 1 mol occupies
occupies 1 L volume, so 1 mol occupies
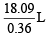 = 50.25L
= 50.25L
Thus, molar volume of vapour = 50.25 L
Assuming ideal behaviour the volume of the vapour can be calculated by
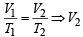
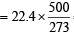 = 41.025L
= 41.025L
(iii) Compressibility factor (Z)
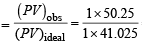 = 1.224
= 1.224
(iv) Z is greater than unit y, hence it is the shor t range repulsive force that would dominate. (∵ actual density is less than given density)
(b)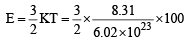
= 2.07 x 10-20 J per molecule
(∵ K, Boltzmann constant = R/N)
Q.30. The average velocity of gas molecules is 400 m/sec. Calculate its rms velocity at the same temperature. (2003 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol. TIPS/Formulae :
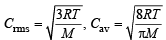
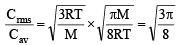 = 1.085
= 1.085
C rms = 1.085 × Cav = 1.085 × 400 = 434 ms–1
Q. 31. A graph is plotted between PVm along Y-axis and P along X-axis, where Vm is the molar volume of a real gas. Find the intercept along Y-axis. (2004 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol. The van der Waal equation (for one mole) of a real gas is
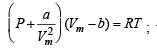
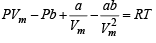
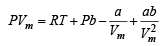 ...(i)
...(i)
NOTE THIS STEP : To calculate the intercept P → 0, hence Vm → ∞ due to which the last two terms on the right side of the equation (i) can be neglected.
∴ PVm = RT + Pb
When P = 0, intercept = RT
|
481 docs|964 tests
|
















