JEE Advanced (True/False): The d & f-Block Elements & Coordination Compounds | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. Copper metal reduces Fe2+ in an acid medium. (1982 - 1 Mark)
Ans. F
Solution. False : Copper metal does not reduces Fe2+ in an acidic medium
Q.2. Silver fluoride is fairly soluble in water. (1982 - 1 Mark)
Ans. T
Solution. True : Hydration energy of AgF is appreciably higher than its lattice energy because of smaller F– ion and thus AgF is soluble in water. In rest of the halides, lattice energy is more than hydration energy to make them insoluble.
Q.3. Silver chloride is more soluble in very concentrated sodium chloride solution than in pure water. (1984 - 1 Mark)
Ans. T
Solution. True : Insolubility of AgCl in H2O is due to its high lattice energy on account of strong van der Waals attraction between silver and chloride ions in addition to electrostatic attraction between them. Further AgCl forms a complex with conc. NaCl solution and is therefore soluble.
Q.4. Dipositive zinc exhibits paramagnetism due to loss of two electrons from 3d-orbital of neutral atom. (1987 - 1 Mark)
Ans. F
Solution. False : Dipositive zinc exhibits diamagnetism (and not paramagnetism) because it has no unpaired electron.
Q.5. Both potassium ferrocyanide and potassium ferricyanide are diamagnetic. (1989 - 1 Mark)
Ans. F
Solution. False : Octahedral complexes of Fe(III) like [Fe(CN)6]3– are low spin (d2sp3 hybridization) with one unpaired electron and have magnetic moment of about 1.9 BM. On the other hand, complexes of Fe(II) like [Fe(CN)6]2– are low spin complex (d2sp3) has no unpaired electron and thus diamagnetic.
Q.6. Cu+ disproportionates to Cu2+ and elemental copper in solution. (1991 - 1 Mark)
Ans. T
Solution. True : Cu+ is the intermediate oxidation state between Cu++ and Cu. If the reduction potential from the intermediate oxidation state to the lower one is more positive than from the higher to the intermediate, then the intermediate state will undergo disproportional.
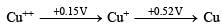
|
481 docs|964 tests
|
















