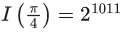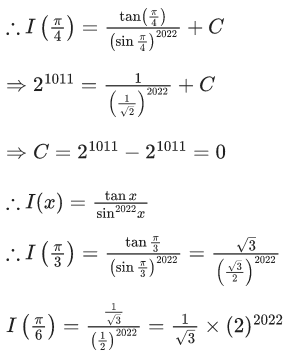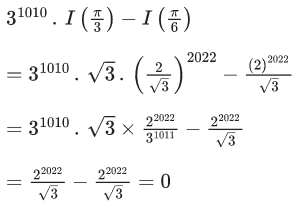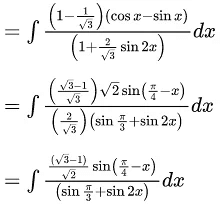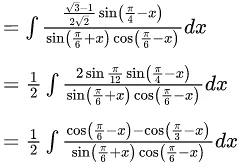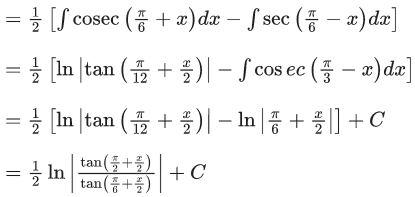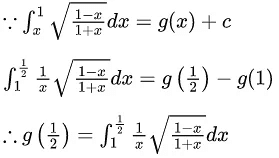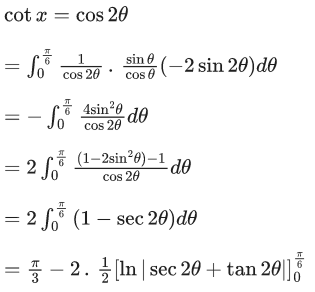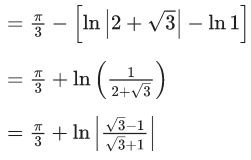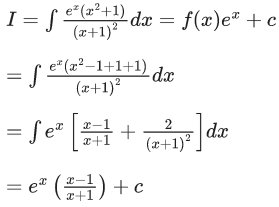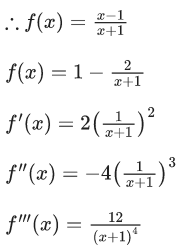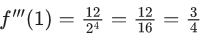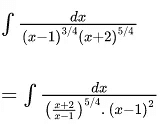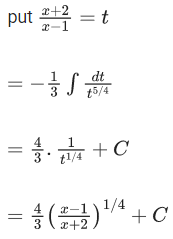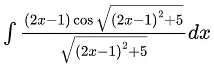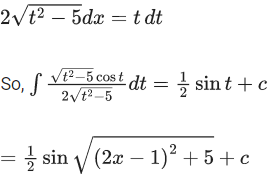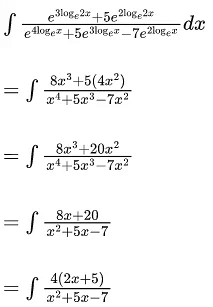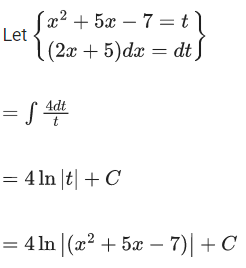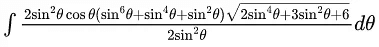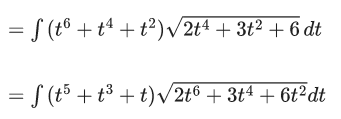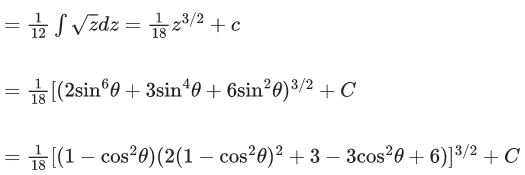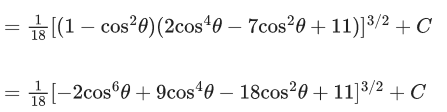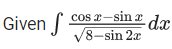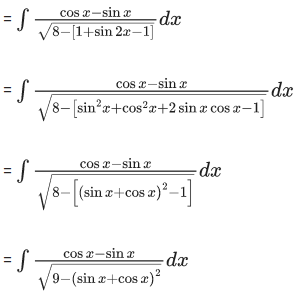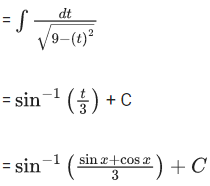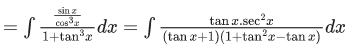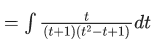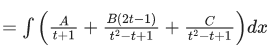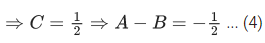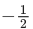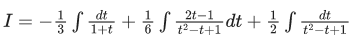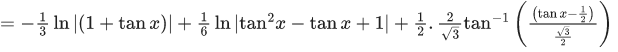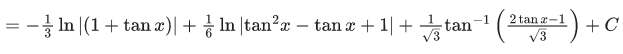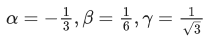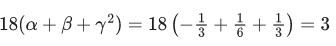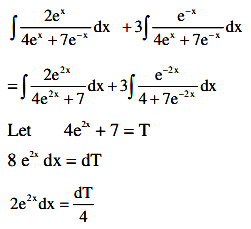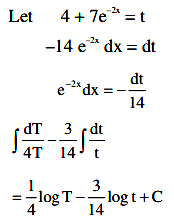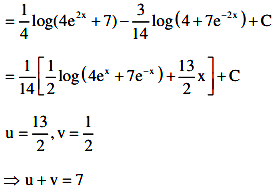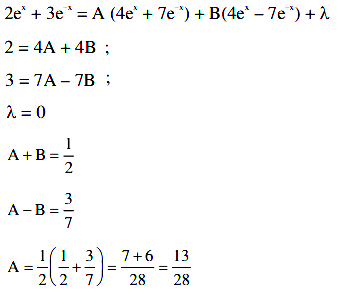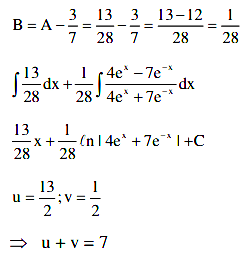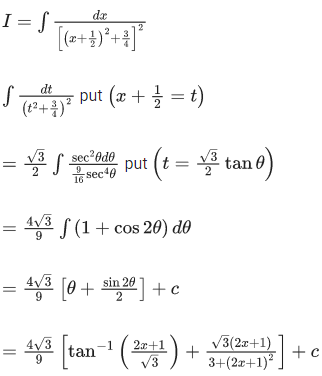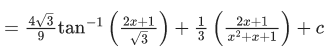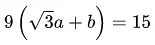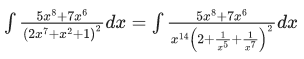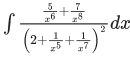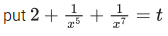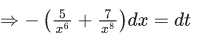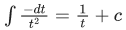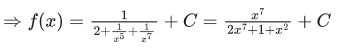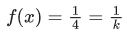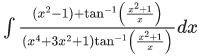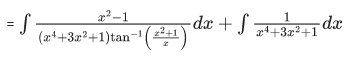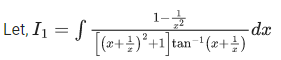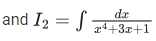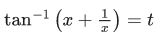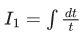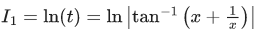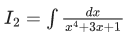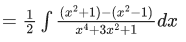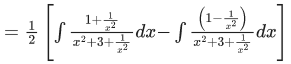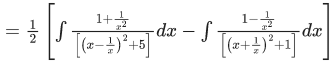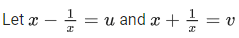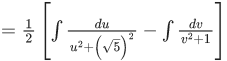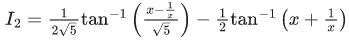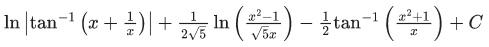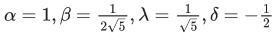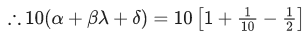JEE Main Previous year questions (2021-2025): Indefinite Integrals | 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE PDF Download
Q.1. For 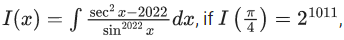 then
then
(a)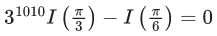
(b)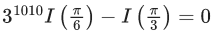
(c)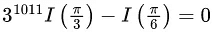
(d)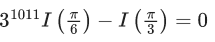
Ans. a
Given,
Given,
From option (A),
Q.2. The integral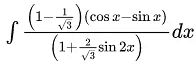 is equal to
is equal to
(a)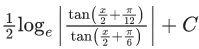
(b)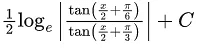
(c)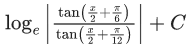
(d)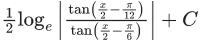
Ans. a
Q.3. If 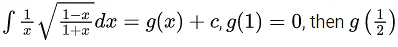 is equal to :
is equal to :
(a)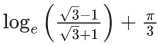
(b)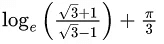
(c)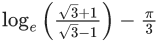
(d)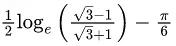
Ans. a
Q.4. If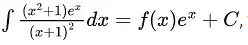 where C is a constant, then
where C is a constant, then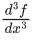 at x = 1 is equal to :
at x = 1 is equal to :
(a)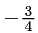
(b) 3/4
(c) 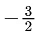
(d) 3/2
Ans. b
for x = 1
Q.5. The integral 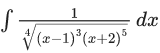 is equal to : (where C is a constant of integration)
is equal to : (where C is a constant of integration)
(a)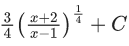
(b)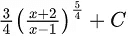
(c)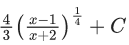
(d)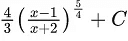
Ans. c
Q.6. The integral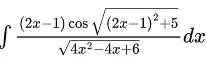 is equal to (where c is a constant of integration)
is equal to (where c is a constant of integration)
(a)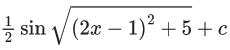
(b)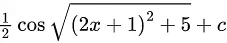
(c)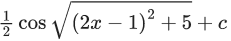
(d)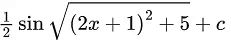
Ans. a
(2x - 1)2 + 5 = t2
(2(2x - 1) 2dx = 2t dt
Q.7. The integral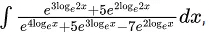 x > 0, is equal to : (where c is a constant of integration)
x > 0, is equal to : (where c is a constant of integration)
(a)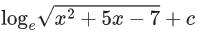
(b)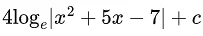
(c)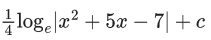
(d)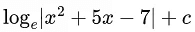
Ans. c
Here c is integral constant.
Q.8. The value of the integral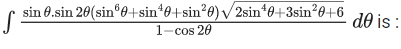
(a)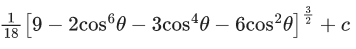
(b)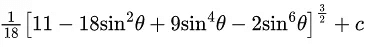
(c)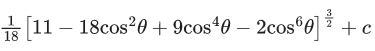
(d)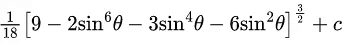
Ans. c
Let sinθ = t, cos θdθ = dt
Let 2t6 + 3t4 + 6t2 = z
12(t5 + t3 + t)dt = dz
Q.9. If 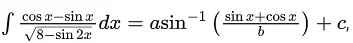 , where c is a constant of integration, then the ordered pair (a, b) is equal to :
, where c is a constant of integration, then the ordered pair (a, b) is equal to :
(a) (-1,3)
(b) (1,3)
(c) (1,-3)
(d) (3, 1)
Ans. b
Write sin2x = 1 + sin2x - 1
put sin x + cos x = t
⇒(cos x – sin x) dx = dt
∴ a = 1 and b = 3
Q.10. If 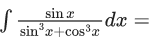
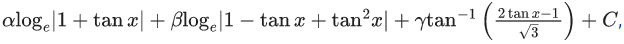
when C is constant of integration, then the value of 18(α + β + y2) is
Ans. 3
Let tan x = t ⇒ sec2x. dx = dt
⇒ A(t2 - t + 1) + B(2t - 1)(t2 - t + 1) + C(t +1)= t
⇒ t2(A + 2B) + t(-A + B + C) + A - B + C = 1
∴ A + 2B = 0.....(1)
- A + B + C = 1 ...(2)
A - B + C = 0 ....(3)
A + 2B = 0
A - B =
Q.11. If 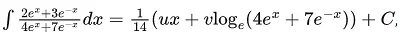 where C is a constant of integration, then u + v is equal to _____________.
where C is a constant of integration, then u + v is equal to _____________.
∫(2ex+3e-x)/(4ex+7e-x)dx = 1/14 ux + v loge(4ex + 7e–x))+ C
Ans. 7
∫(2ex+3e-x)/(4ex+7e-x)dx = 1/14 ux + v loge(4ex + 7e–x))+ CAliter :
Q.12. If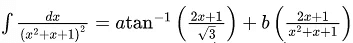 + C, x > 0 where C is the constant of integration, then the value of 9 (√3a + b) is equal to _____________.
+ C, x > 0 where C is the constant of integration, then the value of 9 (√3a + b) is equal to _____________.
Ans. 15
Hence,
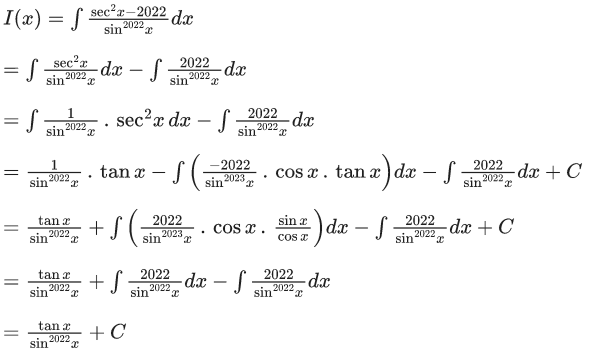
Q.13. If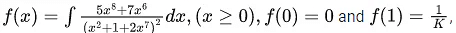 then the value of K is
then the value of K is
Ans. 4
f(0) = 0 ⇒ C = 0⇒ k = 4
Q.14. For real numbers α, β, γ and δ , if
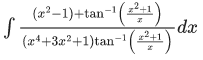
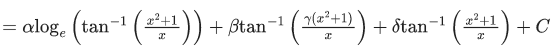
where C is an arbitrary constant, then the value of 10(α, βγ + δ) is equal to _____________
Ans. 6
Now
I = I1 + I2 =
= 1 + 5 = 6
|
347 docs|185 tests
|