Key Concepts: Federalism | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Federalism? |

|
| What makes India a Federal Country? |

|
| How is Federalism Practised? |

|
| Decentralisation in India |

|
| Frequently Asked Questions |

|
What is Federalism?
Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country.
A federation has two levels of government. Both these levels of government enjoy their power independent of the other.
- One is the government for the entire country that is usually responsible for a few subjects of common national interest.
- Governments at the level of provinces or states that look after much of the day-to-day administering of their state.
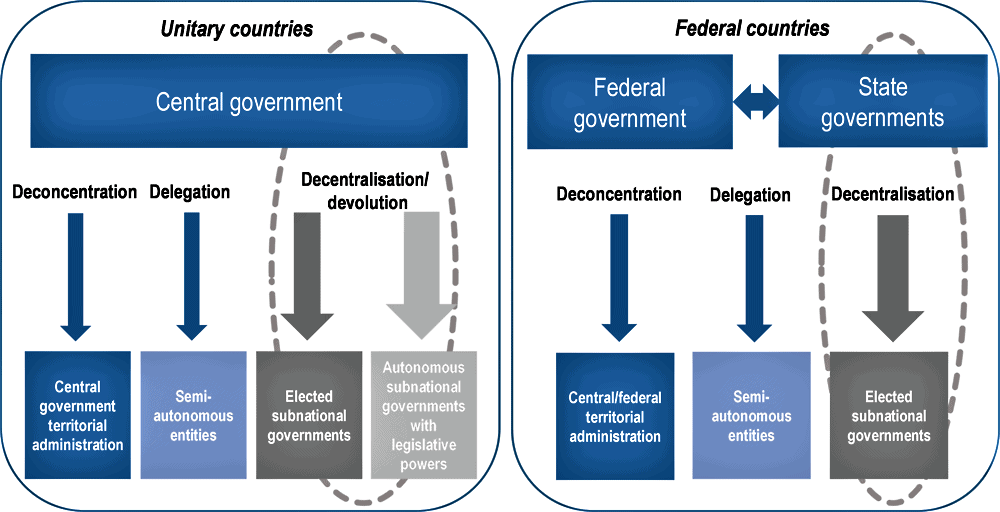
Difference Between Unitary Government & Federal Government
Different Routes Through Which Federations Can be Formed
Note: Only 25 countries of the world’s 192 countries have the federal system. Most of the large countries of the world are federations.
What makes India a Federal Country?
All the features of the federal system apply to the provisions of the Indian Constitution. The Indian Constitution is a three-fold distribution of legislative powers between the Union Government and the State Governments. The 3 lists are mentioned below:
- Union List: It includes subjects of national importance such as the defence of the country, foreign affairs, banking, communications and currency. The Union Government alone can make laws relating to the subjects mentioned in this list.
- State List: It contains subjects of State and local importance such as police, trade, commerce, agriculture and irrigation. The State Governments alone can make laws relating to the subjects mentioned in this list.
- Concurrent List: It includes subjects of common interest to both the Union Government as well as the State Governments. The list includes education, forest, trade unions, marriage, adoption and succession. Both the Union as well as the State Governments can make laws on the subjects mentioned in this list. If their laws conflict with each other, the law made by the Union Government will be considered.
Special Features of the Indian Federation
The centre is more powerful than the states. All states do not have the same powers.- No dual citizenship, like the USA. Every citizen votes as an Indian.
- The Constitution provides special powers to the Centre if there is an emergency in the country.
- Chandigarh, Lakshadweep or the capital city of Delhi are too small in area to become independent states and are called Union Territories. The Union government has the power to run them.
- According to the Constitution, the powers of the states and the Union government is specified, therefore if any change is needed, it has to be passed by both houses of the Parliament with at least 2/3 majority. Then it has to be ratified by the legislatures of at least 1/2 of the total states.
- The judiciary has the power to oversee the implementation of the Constitution.
Note: The Citizenship Amendment Act, 2003, has a new scheme called the Overseas Indian Citizenship (OIC) scheme which allows overseas Indians (of specified countries) to hold dual citizenship.
The specified countries are:
- Australia
- Canada
- Finland
- France
- Greece
- Ireland
- Israel
- Italy
- Netherlands
- New Zealand
- Portugal
- Republic of Cyprus
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom
- United States of America.
How is Federalism Practised?
- New states have been created. Areas, boundaries and names of the states have been changed.
- The creation of new states was done on two bases:
(i) Culture, ethnicity or geography, e.g., Nagaland, Uttarakhand and Jharkhand.
(ii) On the basis of language, e.g., Andhra, Maharashtra and many others.
Linguistic States
- The creation of linguistic States was the first and a major test for democratic politics in India.
- From 1947 to 2017, many old States have vanished and many new States have been created. Areas, boundaries and names of the States have been changed.
- Some states have been formed of people who speak the same language. These states are known as the Linguistic States.
Language Policy
- Our Constitution has not made any language the national language of India.
- Hindi is the official language spoken by 40% of the population.
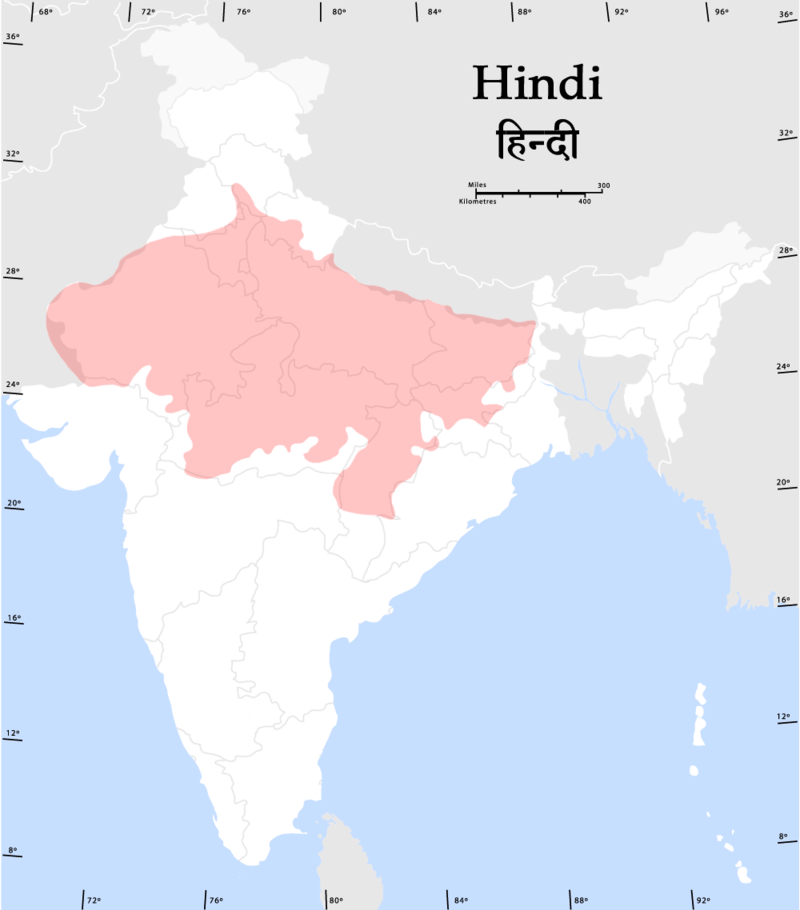 Hindi Belt of India (People Speaking Hindi Language)
Hindi Belt of India (People Speaking Hindi Language)
- Besides Hindi, 21 other languages are recognised by the Constitution.
They are:
1. Assamese
2. Bengali
3. Bodo
4. Dogri
5. Gujarati
6. Kannada
7. Kashmiri
8. Konkani
9. Maithili
10. Malayalam
11. Meitei (Manipuri)
12. Marathi
13. Nepali
14. Odia
15. Punjabi
16. Sanskrit
17. Santhali
18. Sindhi
19. Tamil
20. Telugu
21. Urdu
Some Facts
- Only 0.02 per cent Indians have English as their mother tongue.
- 1% know English as the second or third language. The Census of 1991 recorded 1500 distinct languages claimed by people as their mother tongue.
- After grouping them under some major languages, the census found 114 major languages.
Example: Bhojpuri, Magadhi, Awadhi, Braj, Bundelkhandi, Chhattisgarhi and Rajasthani were grouped under “Hindi”.- Even after grouping, people who knew Hindi as their second and third language, the total number of Hindi-speaking people was less than 50%.
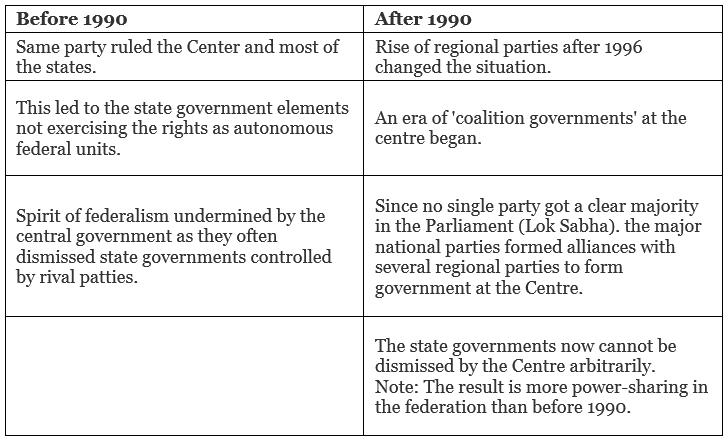
Centre-State Relations
- The way Constitution has made the Centre and the States share powers have also strengthened federalism in India.
Decentralisation in India
- India has a three-tier system of government.
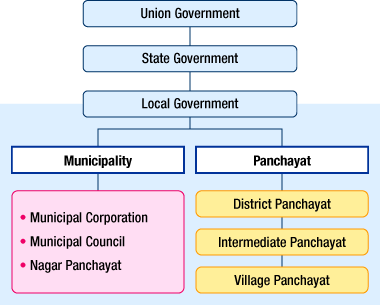
- The three-tier system was adopted because:
(i) India is a very big country.
(ii) Difficult for the union and state governments to manage big provinces and huge populations. - Decentralisation means that some power is taken away from the central and state governments and given to local governments.
Reasons for Decentralisation
In a big country like India, it is essential to have an elected government at the local level also.
- Local people have better knowledge of local problems.
- Local people have better ideas of where to spend money and which problem to tackle first, of how to manage things more efficiently.
- Common citizens can be involved in decision-making, concerning their needs and how to plan development.
- People can approach a local government for solving their problems easily and quickly. The cost is also reduced to the minimum.
- Local governments provide training in becoming active participants in the working of a democracy. It trains one for leadership.
- Local governments at grass root level ensure stability, strength and health of democracy.
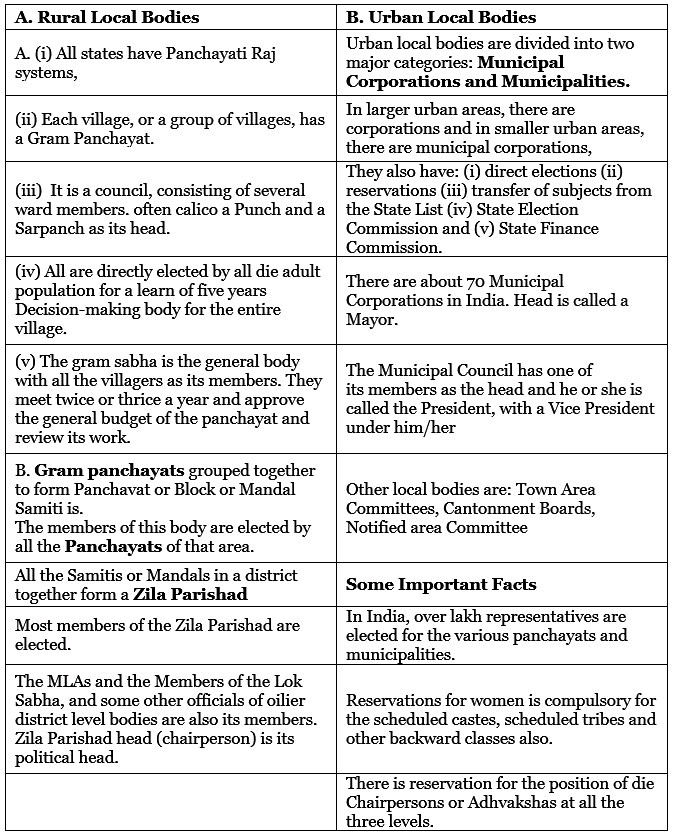
The 73rd Amendment (1992) concerned the rural local bodies (referred to as Panchayati Raj Institutions or PRIs). The 74th Amendment made provisions for urban local governments (Nagar Palika). They came into force in 1993. - 1992: Amendments to the Constitution (the 73rd and 74th amendments) made the three-tier system more powerful and effective.
- Before 1992: The local bodies were directly under the state governments. Regular elections were not held and the local bodies did not have any resources or powers of their own, no real decentralisation.
Rural and Urban Local Bodies
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1: What are the dual objectives of Federalism?
Ans: The dual objectives of Federalism are to safeguard and promote the unity of the country and to accommodate regional diversity.
Q.2: What is the unitary system of government?
Ans: Under the unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub units are subordinate to the central government.
Q.3: What are residuary subjects? Who can make law on these subjects?
Ans: The residuary subjects are those subjects that are not included in any list. The Union Government has the power to legislate on ‘residuary’ subjects.
|
88 videos|630 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Key Concepts: Federalism - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What is the definition of Federalism? |  |
| 2. What are the key features that make India a Federal Country? |  |
| 3. How is Federalism Practiced in India? |  |
| 4. What is Decentralisation, and how does it function in India? |  |
| 5. Why is Federalism important for a diverse country like India? |  |





















