Grade 9 Exam > Grade 9 Notes > Geography for Grade 9 > Key Concepts - Climate
Key Concepts - Climate | Geography for Grade 9 PDF Download
- General weather conditions over a period of thirty years period is said to be the climate of a place.
- Temperature, atmospheric pressure, wind, humidity and precipitation are elements of weather and climate.
- Generalised monthly atmospheric conditions determine the basis on which the year is divided into the seasons — summer, winter or rainy.
- India has a monsoon type of climate.
- Monsoon is basically a seasonal reversal in the wind through the year.
- There is huge difference in temperature from one region to another.
- Form of precipitation, its amount and distribution also differ from one part of India to another.
- Coastal areas observe lesser difference in temperature conditions. It is the interior of India that experiences temperature contrasts.
- Decrease in rainfall is seen from east to west in the Northern Plains. All this influences diversity in professions, food, dress and houses of people.
Climatic Controls
- The interplay of latitude, altitude, distance from the sea, pressure and wind system, ocean currents and relief features determine climatic conditions of a place.
Factors Affecting India’s Climate
- The Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of the country from the Rann of Kuchchh to Mizoram.
- The Himalayas prevent the cold winds from central Asia from entering the subcontinent.
- The climate and associated weather conditions in India are governed by various atmospheric conditions namely pressure and surface winds, upper air circulation, western cyclonic disturbances and tropical cyclones.
- An apparent force caused by the earth’s rotation is the Coriolis Force.
- Jet streams are narrow belts of high-altitude (above 12,000 m) westerly winds in the troposphere.
- The western cyclonic disturbances are weather phenomena of the winter months, brought in by the westerly flow from the Mediterranean region.
Question for Key Concepts - ClimateTry yourself: What is the major factor that prevents cold winds from central Asia from entering India?View Solution
The Indian Monsoon
- The climate of India is strongly influenced by monsoon winds.
- The Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is a broad trough of low pressure in equatorial latitudes where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge.
- Reversal in the pressure conditions and eastern Pacific Ocean having lower pressure than eastern Indian Ocean is a periodic change in pressure condition known as the southern oscillation.
- El Nino is a warm ocean current that flows past the Peruvian coast in place of the cold Peruvian current, every 2 to 5 years.
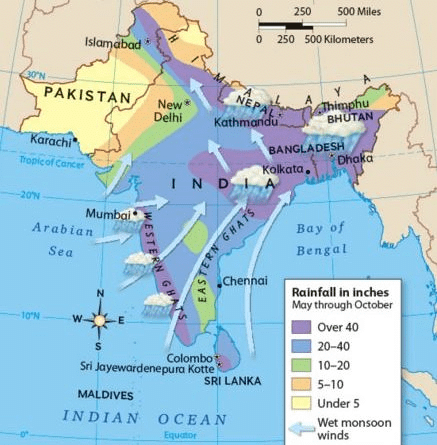
The Onset of the Monsoon and Withdrawal
- The monsoon are pulsating winds affected by different atmospheric conditions encountered by it, on its way over the warm tropical seas.
- Monsoon arrives at the southern tip of the Indian peninsula generally by first week of June.
- The Arbain Sea and the Bay of Bengal branches of the monsoon merge over the north western part of the Ganga plains.
- The withdrawal or the retreat of the monsoon is a more gradual process which begins in the northwestern states of India by early September.
- The retreating monsoon or the transition season sees the change from hot rainy season to dry winter conditions.
- The low pressure conditions over northwestern India get transferred to the Bay of Bengal by early November causing cyclonic depressions originating over the Andaman Sea.
Distribution of Rainfall
- Owing to the nature of monsoons, the annual rainfall is highly variable from year to year.
- Areas of high rainfall are liable to be affected by floods while areas of low rainfall are drought prone.
The Seasons
- Four main seasons can be identified in India — the cold weather season, the hot weather season, the advancing monsoon and the retreating monsoon with some regional variations.
- In the cold weather season the northeast trade winds prevail over India.
- Days are warm and nights are cold.
- Frost is common in the north and the higher slopes of the Himalayas experience snowfall.
- The summer months experience rising temperature and falling air pressure in the northern parts of the country.
- A striking feature of the hot weather season are strong, gusty, hot, dry winds blowing during the day over the north and northwestern India called loo.
- In the advancing monsoon, i.e. the rainy season, the north-western region of the country receives the maximum rainfall.
- Monsoon has ‘breaks’ in rainfall, thus it has wet and dry spells.
- The alternation of dry and wet spells vary in intensity, frequency and duration causing heavy floods in one part and droughts in the others.
Question for Key Concepts - ClimateTry yourself: Which season in India is characterized by strong, gusty, hot, dry winds blowing during the day over the north and northwestern regions?View Solution
Monsoon as a Unifying Bond
- The dependence of farmers on rain, a change in seasonal cycle, variance in temperature, the needs of humans, plants and animals, festival dates etc., all depend on monsoon in India. In this way monsoon is a unifying bond for Indians.
The document Key Concepts - Climate | Geography for Grade 9 is a part of the Grade 9 Course Geography for Grade 9.
All you need of Grade 9 at this link: Grade 9
|
1 videos|178 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Key Concepts - Climate - Geography for Grade 9
| 1. What is climate? |  |
Ans. Climate refers to the long-term patterns of temperature, humidity, wind, and precipitation over a region. It is the average weather conditions of a place over a period of 30 years or more.
| 2. How is climate different from weather? |  |
Ans. Weather refers to the atmospheric conditions of a place at a particular time, whereas climate refers to the long-term patterns of weather over time. Weather is a short-term phenomenon, while climate is a long-term phenomenon.
| 3. What are the factors that affect climate? |  |
Ans. The major factors that affect climate are latitude, altitude, distance from the sea, ocean currents, prevailing winds, topography, and vegetation cover. These factors influence the amount of solar radiation received by a region, the amount of moisture in the air, and the temperature of the region.
| 4. How is climate change affecting the world? |  |
Ans. Climate change is causing an increase in global temperature, rising sea levels, more frequent and severe weather events, and changes in precipitation patterns. This is leading to loss of biodiversity, food and water scarcity, and increased health risks.
| 5. What can we do to mitigate climate change? |  |
Ans. We can mitigate climate change by reducing our carbon footprint through actions such as using public transportation, consuming less meat, using energy-efficient appliances, and planting trees. Governments can also take action by implementing policies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and investing in renewable energy sources.
Related Searches






















