Key Concepts - Natural Vegetation and Wildlife | Geography for Grade 9 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Natural Vegetation? |

|
| Types of Vegetation |

|
| Wildlife |

|
| Government Initiatives to Protect Flora and Fauna |

|
India, with approximately 47,000 plant species and 90,000 animal species, is recognized as one of the 12 mega biodiversity countries worldwide. It holds the tenth position globally and ranks fourth in Asia for its remarkable plant diversity, comprising 15,000 flowering plants, alongside an assortment of non-flowering plants and a diverse range of fish.

Let's explore the key concepts presented in the chapter titled "Natural Vegetation and Wildlife" within this document.
What is Natural Vegetation?
Natural vegetation refers to plant communities that grow naturally without human intervention and have been undisturbed for a long time. Also termed as virgin vegetation. Thus, cultivated crops, fruits and orchards are a part of vegetation but not natural vegetation.
 Natural Vegetation
Natural Vegetation
Flora: The term flora is used to denote plants of a particular region or period.
Fauna: The species of animals are referred to as fauna.
Types of Vegetation
In India, the following major types of vegetation are found:
- Tropical Evergreen Forests
- Tropical Deciduous Forests
- Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs
- Montane Forests
- Mangrove Forests
Tropical Evergreen Forests
Tropica Evergreen Forests are located in Western Ghats, Lakshadweep, Andaman and Nicobar islands, upper Assam, and Tamil Nadu coast. These forests possess the following characteristics:
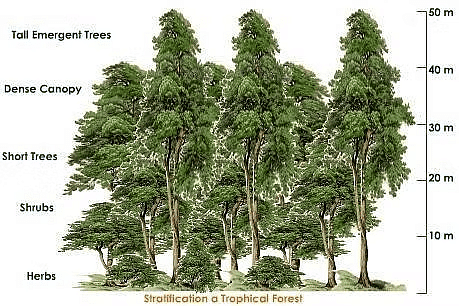 Tropical Evergreen Forest
Tropical Evergreen Forest
- Requires rainfall over 200 cm and a brief dry season for optimal growth.
- Trees can reach heights of 60 meters or more.
- Multilayered structure with trees, shrubs, and creepers.
- Evergreen appearance throughout the year.
- Notable tree species include ebony, mahogany, rosewood, rubber, and cinchona.
- Typical animal inhabitants are elephants, monkeys, lemurs, and deer.
Tropical Deciduous Forests
Tropical deciduous forests, also known as monsoon forests, are found in regions with rainfall ranging from 70 cm to 200 cm.
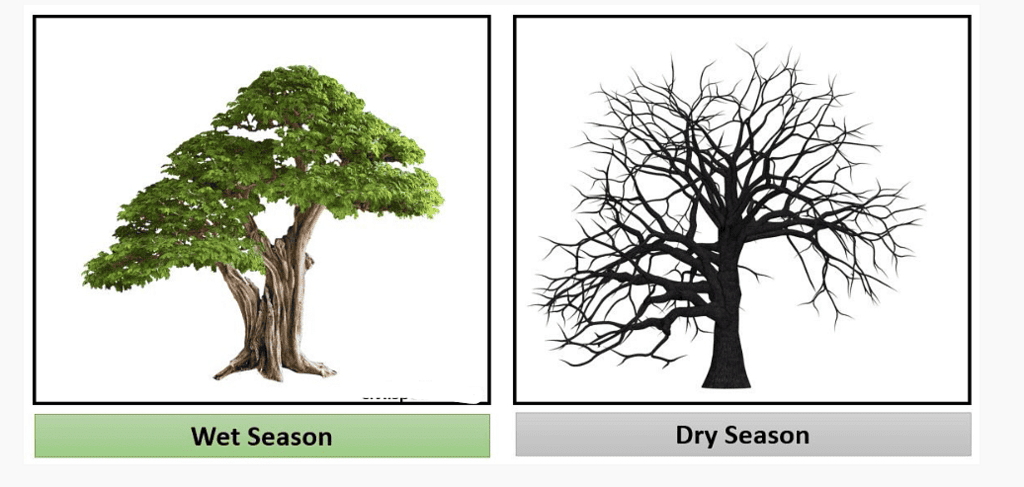 Tropical Deciduous Forests
Tropical Deciduous Forests
They are characterized by trees shedding their leaves for 6 to 8 weeks during the dry summer season. These forests are home to various animals such as lions, tigers, pigs, deer, and elephants.
Deciduous forests can be further classified into two categories:
1. Moist deciduous forests: These forests thrive in areas with a rainfall of 100 cm to 200 cm. Teak is the predominant species found in these forests, along with other economically valuable species like bamboo, sal, shisham, sandalwood, Khair, Kusum, Arjun, and mulberry.
2. Dry deciduous forests: These forests are prevalent in areas with a rainfall between 70 cm and 100 cm. They consist of open stretches where trees such as teak, sal, peepal, and neem can grow.
The Thorn Forests and Scrubs
The natural vegetation in the north-western region of India, including semi-arid areas of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, and Haryana, primarily consists of thorny trees and bushes.
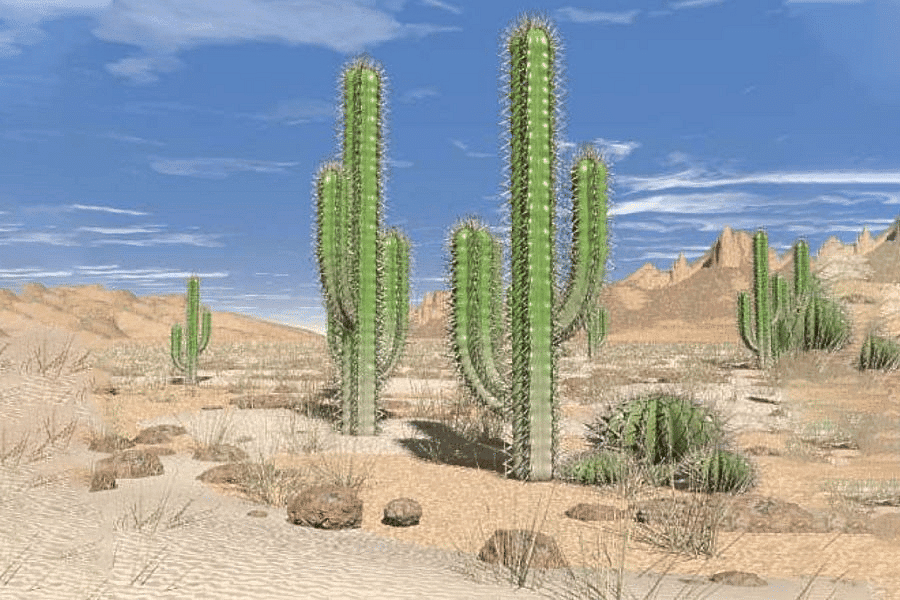 Thorn Forests and Scrubs
Thorn Forests and Scrubs
Some key features of this vegetation type include:
- Scattered trees: The trees are dispersed throughout the landscape to maximize access to resources.
- Deep roots: Trees have long roots that penetrate deep into the soil in order to access moisture.
- Moist stems: The stems of these plants are designed to conserve water, ensuring their survival in arid conditions.
- Thick, small leaves: The leaves of these plants are generally small and thick, which helps to minimize evaporation and conserve water.
- Main plant species: The most common plant species found in these regions are acacias, palms, euphorbias, and cacti.
- Fauna: The animals typically found in these regions include rats, mice, rabbits, foxes, wolves, tigers, lions, wild asses, horses, and camels.
Montane Forests
Montane forests refer to the forests located in mountainous regions.
 Montane Forests
Montane Forests
- Wet temperate forests can be found at elevations between 1000 and 2000 meters above sea level.
- At higher altitudes, typically above 3,600 meters, temperate forests and grasslands transition to Alpine vegetation.
- Alpine grasslands serve as grazing areas for animals.
- In even higher altitudes, tundra vegetation consisting of mosses and lichens can be found.
- A variety of animals inhabit these montane forests, including the Kashmir stag, spotted deer, wild sheep, jackrabbit, Tibetan antelope, yak, snow leopard, squirrels, shaggy horn wild ibex, bear, and the rare red panda, as well as various species of sheep and goats.
Mangrove Forests
Mangroves are trees that live along tropical coastlines, rooted in salty sediments, often underwater.
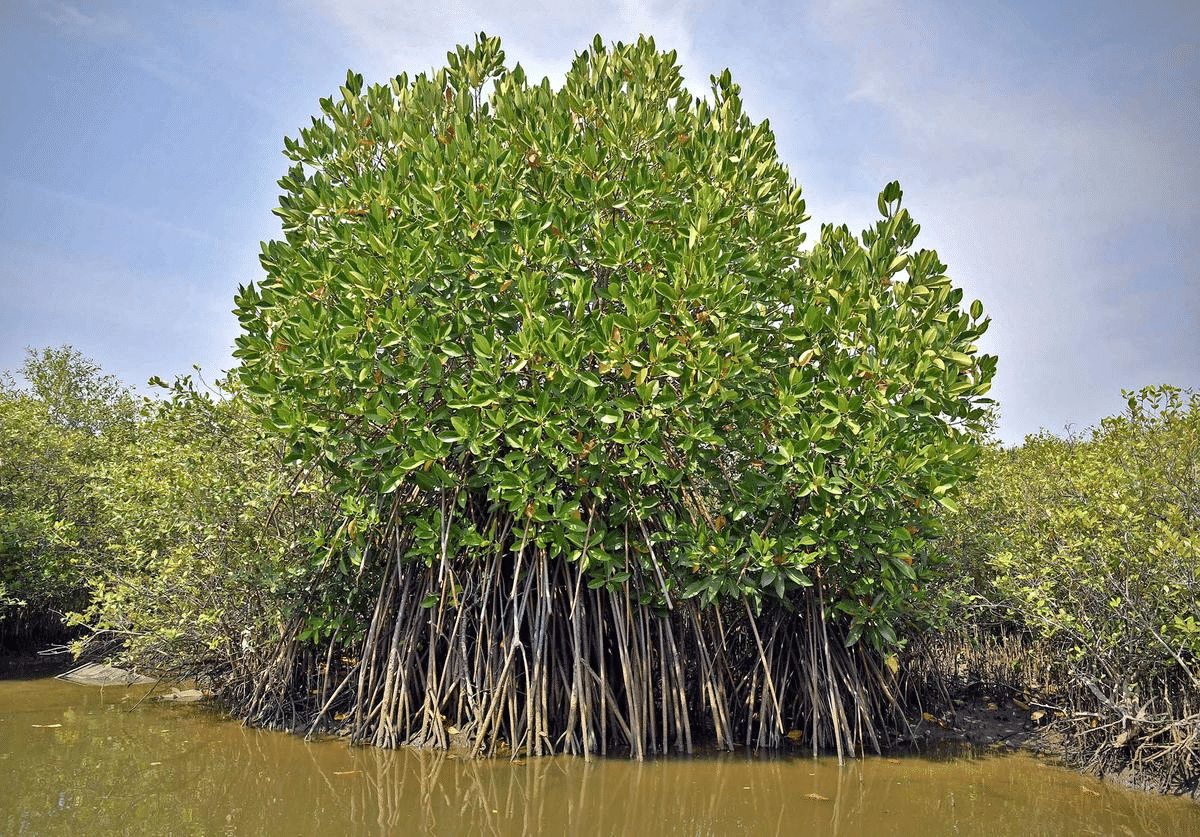 Mangroves
Mangroves
- The mangrove tidal forests are found in the areas of coasts influenced by tides. Mud and silt get accumulated on such coasts.
- Dense mangroves are the common varieties with roots of the plants submerged underwater.
- Sundari trees are found in the Ganga-Brahmaputra delta and provide hard timber.
- Royal Bengal Tiger is a famous animal in these forests.
Wildlife
India boasts a rich biodiversity, with over 1200 bird species, 2500 fish species, and 5-8% of the world's amphibians, reptiles, and mammals. Notably, it is the only country with both tiger and lion populations.

The Himalayas provide a diverse habitat for numerous animal species that have adapted to the harsh cold climate. Each of these species plays a crucial role in maintaining the ecosystem, making conservation efforts vital.
Several threats, such as hunting and pollution, endanger the survival of these species.
To safeguard the country's flora and fauna, the government has implemented various measures:
- Establishment of 14 biosphere reserves to protect both flora and fauna.
- Creation of 89 National Parks to conserve natural habitats.
- Setting up of 49 Wildlife Sanctuaries for the preservation of wildlife.
- Designation of Biosphere Reserves to maintain the natural heritage.
Cause of Major Threat to flora and fauna
Every species has an important role in the ecosystem. Hence, the conservation of flora and fauna is essential. About 1,300 plant species are endangered and 20 species are extinct.
The main causes of this major threat to nature are:
- Hunting for commercial purposes
- Pollution due to chemical and industrial waste
- Rapidly cutting of the forests for cultivation and habitation
Government Initiatives to Protect Flora and Fauna
The government has implemented numerous measures to safeguard the country's flora and fauna, including the following:
- Establishment of 18 biosphere reserves in India, with 10 of them being part of the world network of biosphere reserves. This ensures that both plant and animal species are protected and conserved.
- Provision of financial and technical support to botanical gardens since 1992. This aids in preserving diverse plant species and maintaining their natural habitats.
- Launching of various eco-development projects, such as Project Tiger, Project Rhino, and Project Great Indian Bustard, aimed at conserving specific endangered species and their habitats.
- Creation of 106 National Parks, 564 Wildlife Sanctuaries, and Zoological gardens to preserve and maintain the country's natural heritage, as per the National Wildlife Database (December 2021). These protected areas serve as safe havens for various plant and animal species, promoting their well-being and conservation.
|
23 videos|71 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Key Concepts - Natural Vegetation and Wildlife - Geography for Grade 9
| 1. What is natural vegetation and wildlife? |  |
| 2. How does climate affect natural vegetation and wildlife? |  |
| 3. What are some government initiatives to protect flora and fauna? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of wildlife found in natural vegetation? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to protect natural vegetation and wildlife? |  |
















