Key Concepts - Poverty as a Challenge | Social Studies (SST) Class 9 PDF Download
Overview of Poverty
Poverty is a multidimensional issue characterized by hunger, lack of shelter, inadequate access to clean water, sanitation, healthcare, education, and regular employment, leading to a sense of helplessness.
- Significance: Poverty is one of the biggest challenges for independent India. Mahatma Gandhi emphasized that true independence is achieved when the poorest are free from human suffering.
- Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI): NITI Aayog uses the MPI to measure poverty based on health, education, and living standards. The MPI ratio in India fell from 55% (2005-06) to 25% (2015-16) and 15% (2019-21), with an expectation to reach single digits soon.

Two Typical Cases of Poverty
Urban Case (Ram Saran):
- Profile: A 33-year-old daily-wage laborer in a flour mill near Ranchi, Jharkhand, earning ~Rs. 3,500/month when employed.
- Family: Supports a family of six (wife, four children), plus elderly parents and a brother.
- Challenges: Irregular employment, insufficient income, lives in a temporary shack, limited food (dal-rice twice daily), no new clothes, no shoes, and children (except one daughter) cannot attend school.
- Additional Income: Wife earns Rs. 1,500 as a part-time maid; elder son earns Rs. 700 as a tea shop helper.
Rural Case (Lakha Singh):
- Profile: A landless laborer in a village near Meerut, Uttar Pradesh, earning ~Rs. 200/day or in-kind payments (e.g., wheat, dal).
- Family: Supports a family of six; father died of tuberculosis, and mother is ill.
- Challenges: Irregular work, insufficient food, lives in a kuchha hut, no access to soap/oil, new clothes are rare, and health issues due to lack of medical care.
- Education: Children attend school, unlike Lakha, who never did.
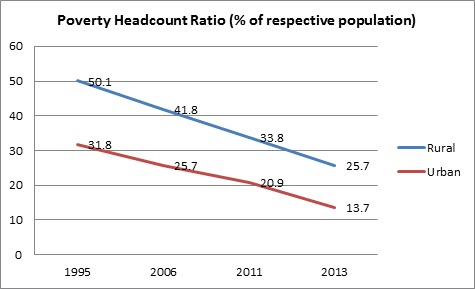 Rural Poverty is higher than Urban
Rural Poverty is higher than Urban
Issues for Discussion:
- Landlessness: Both families lack land, limiting income stability.
- Unemployment: Irregular work leads to financial insecurity.
- Large Families: Large family sizes strain limited resources.
- Literacy: Low literacy levels, though children are starting to attend school.
- Health/Nutrition: Malnutrition and lack of healthcare access.
- Helplessness: Social exclusion and lack of opportunities create a sense of despair.
Poverty as seen by social scientists
- Social scientists look at poverty through a variety of indicators. Usually, the indicators are used to relate to the levels of income and consumption.
- But now poverty is looked at through other social Indicators like illiteracy level, lack of general resistance due to malnutrition, lack to access to healthcare etc.
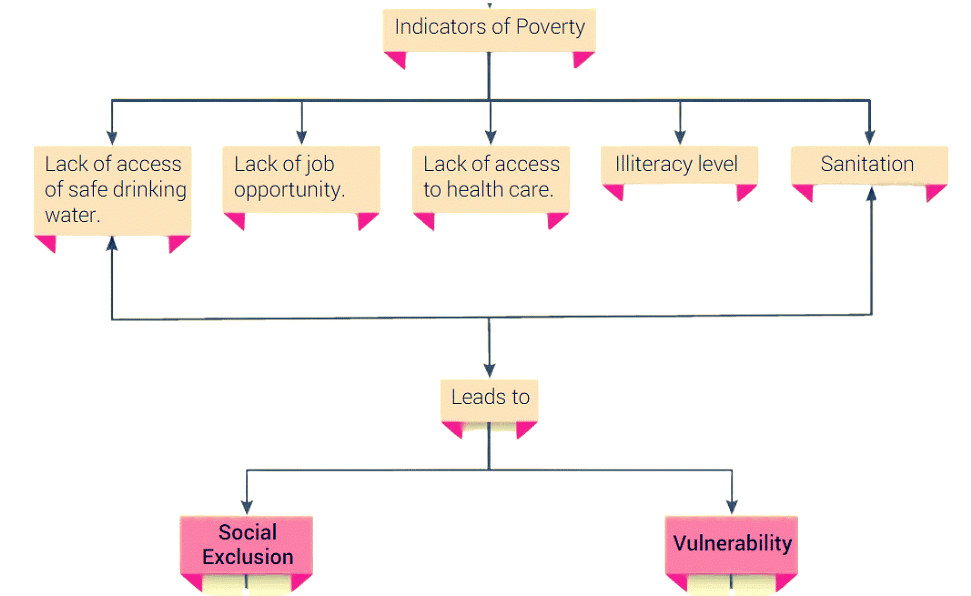
Social exclusion
- For the analysis of poverty, social exclusion is very useful.
- As per this concept, poverty must be seen in terms of the poor living only in a poor surrounding with other poor people.
Vulnerability
- Vulnerability describes the greater probability of being more adversely affected than other people, which is done due to an earthquake or simply a fall in the availability of jobs.
- Measurement of vulnerability to poverty describes the greater probability of certain communities i.e., members of a backward caste or individuals i.e. a widow or a physically handicapped person.
Poverty Line
A threshold to identify the poor based on income or consumption levels needed to meet basic needs (food, clothing, shelter, education, health).
Methodology in India:
- Based on calorie requirements: 2,400 calories/day (rural), 2,100 calories/day (urban).
- Includes minimum needs like food, clothing, footwear, fuel, electricity, education, and medical care, converted to monetary terms.
- Adjusted periodically for price changes.
Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI): Complements income-based measures by assessing deprivations in 12 indicators (see below).
Variations: Poverty lines differ by country and time due to varying development levels and social norms (e.g., owning a car is a necessity in the USA but a luxury in India).
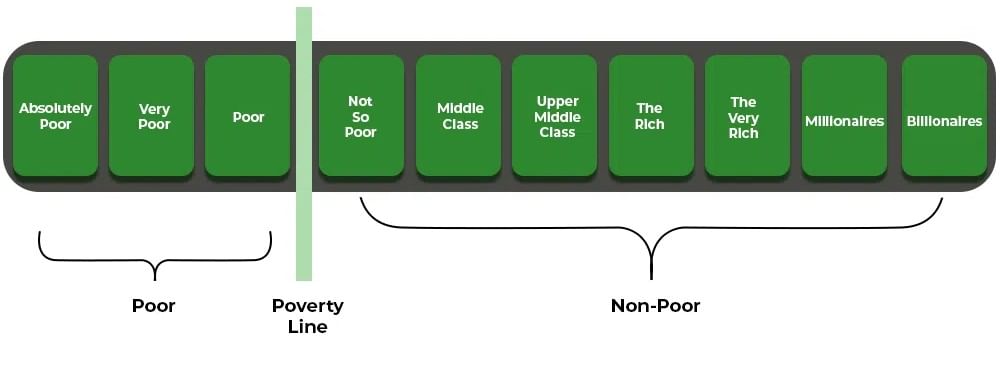 Poverty line Explanation
Poverty line Explanation
Poverty Estimates
Consumption-Based:
- 1993-94: 45% (404 million poor).
- 2004-05: 37% (407 million poor; number stable due to population growth).
- 2009-10: 30% (355 million).
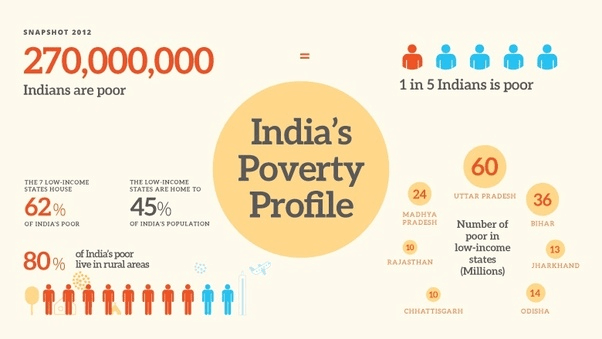
- 2011-12: 22% (270 million).
Multidimensional (MPI):
- 2015-16: 25% (rural: 32.6%, urban: 8.7%).
- 2019-21: 15% (rural: 19.3%, urban: 5.3%; 13.5 crore escaped poverty).
Key Observation: Rural poverty decline is sharper than urban due to targeted interventions.
Inter-State Disparities
Variations:
- Low Poverty (<10% in 2019-21): Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Delhi, Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Maharashtra.
- High Poverty: Bihar (highest), Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan (but showing improvement).
- Lowest: Jammu & Kashmir (~3.5%).
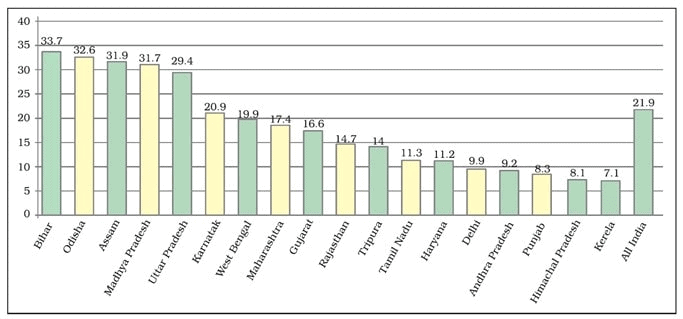 Poverty ratios vary across states
Poverty ratios vary across states
State Strategies:
- Kerala: Human resource development (education, health).
- West Bengal: Land reforms.
- Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu: Public distribution of food grains.
Vulnerable Groups
- Social Groups: Scheduled Castes (29% poor), Scheduled Tribes (43% poor).
- Economic Groups: Rural agricultural laborers (34% poor), urban casual laborers (34% poor).
- Intra-Family Inequality: Women, the elderly, and female infants often face greater deprivation.
- Trend: Except for Scheduled Tribes, poverty in other vulnerable groups declined in the 1990s.
Global Poverty Scenario
World Bank Standard: Poverty is defined as living on less than $2.15/day (2017 PPP).
Trends:
- Global: Declined from 16.27% (2010) to 9.05% (2019).
- China: Dropped to 0.1% (2020) due to economic growth and human resource investment.
- South Asia: Declined from 13% (2017) to 11% (2021); number of poor reduced from 233 million to 207 million.
- Sub-Saharan Africa: Slight decline from 36.6% (2017) to 35% (2019); the highest concentration of poor (9 in 10 extreme poor by 2030).
- Latin America: Increased from 4.4% (2017) to 4.6% (2021).
- Former Socialist Countries: Poverty resurfaced (e.g., Russia at 3% in 2000).
Causes of Poverty
- The rapid growth of the population, particularly among the poor, is considered a major cause of Indian poverty.
- Our agricultural sector has failed to generate many employment opportunities for farm labourers. Similarly, our industries could not provide many jobs for job seekers.
- One of the major causes of poverty is the unequal distribution of land and other resources. Various land reform measures introduced after Independence could not improve the lives of millions of rural poor because of their poor implementation.
- Social factors: People in India, including the very poor, spend a lot of money on social occasions like marriages, festivals, etc. Poor people hardly have any savings; they are thus forced to borrow. Unable to pay because of poverty, they became victims of indebtedness.
- The joint family system has prevented people from doing hard work.
Anti Poverty Measures
Two-Pronged Strategy:
1. Economic Growth: Higher growth rates (3.5% in the 1970s to 6% in the 1980s-1990s) reduce poverty by creating opportunities and resources for human development.
2. Targeted Programs:
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), 2005: Provides 100 days of wage employment per rural household, with one-third reserved for women; addresses drought, deforestation, and soil erosion.
- Pradhan Mantri Poshan Shakti Abhiyan (PM Poshan): Improves nutrition and school enrollment for children in Classes I-VIII.
- Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan (2016): Ensures quality antenatal care to reduce maternal and infant mortality.
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY), 2016: Provides free LPG connections to BPL households, promoting women’s health and environmental sustainability.
- Other Programs:
- Prime Minister Rojgar Yojana (PMRY, 1993): Self-employment for educated unemployed youth.
- Rural Employment Generation Programme (REGP, 1995): Self-employment in rural areas.
- Swarna Jayanti Gram Swarojgar Yojana (SGSY, 1999): Assists poor families to rise above the poverty line.
- Pradhan Mantri Gramodaya Yojana (PMGY, 2000): Rural development.
- Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY): Food security for the poorest.
- National Food for Work Programme (NFWP, 2004): Employment and food security.
The Challenges Ahead
- Persistent Issues: Wide rural-urban and inter-state disparities; vulnerable groups remain at risk.
- Human Poverty: Beyond income, poverty includes lack of education, healthcare, job security, and freedom from discrimination.
- Future Goals: Achieve universal education, gender equality, and job security; align with UN SDGs to end all forms of poverty by 2030.
Human Poverty
- Definition: A broader concept encompassing lack of education, healthcare, shelter, job security, self-confidence, and freedom from caste/gender discrimination, beyond mere subsistence.
- Significance: Development changes the definition of poverty; a “reasonable” level of living is needed, not just a “minimum” subsistence level.
Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) Indicators
- Nutrition: Undernourishment in children (0-59 months), women (15-49 years), or men (15-54 years).
- Child-Adolescent Mortality: Death of a child/adolescent under 18 in the past 5 years.
- Maternal Health: Lack of skilled medical assistance during childbirth.
- Years of Schooling: No household member (10+ years) has completed 6 years of schooling.
- School Attendance: School-aged child not attending school up to Class 8.
- Cooking Fuel: Use of dung, wood, charcoal, or coal.
- Sanitation: Unimproved or shared sanitation facilities.
- Drinking Water: No access to improved water or water source is a 30-minute walk (round trip).
- Housing: Inadequate housing (natural floor, rudimentary roof/walls).
- Electricity: No electricity access.
- Assets: Lack of ownership of multiple assets (radio, TV, phone, etc.) and no car/truck.
- Bank Account: No household member has a bank/post office account
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Key Concepts - Poverty as a Challenge - Social Studies (SST) Class 9
| 1. What is the poverty line and how is it determined? |  |
| 2. What are the main causes of poverty? |  |
| 3. How do inter-state and global poverty disparities manifest? |  |
| 4. What are some effective anti-poverty measures? |  |
| 5. What challenges do we face in combating poverty? |  |

















