Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 8 > Key Concepts: Universal Franchise and India’s Electoral System
Key Concepts: Universal Franchise and India’s Electoral System | Social Studies (SST) Class 8 PDF Download
Universal Adult Franchise
- Every adult citizen (18+) in India has one vote of equal value, regardless of caste, religion, gender, education, or income.
- The foundation of Indian democracy is enshrined in Article 326 of the Constitution.
- Voting age was lowered from 21 to 18 in 1988 to increase participation.
- Voting is an individual right; proxy voting is not allowed.

Bridging Barriers, Enabling Participation: Ensuring Universal Franchise
- India’s vast geography and diverse population pose challenges to election accessibility.
- Election Commission of India (ECI) ensures elections reach remote and inaccessible areas using technology and logistics support.
- Special provisions like home voting for the elderly and disabled, braille voter cards, wheelchair availability, and postal voting enhance inclusivity.
- Despite efforts, voter turnout issues remain, especially in urban areas.
 ECI Logo
ECI Logo
Question for Key Concepts: Universal Franchise and India’s Electoral SystemTry yourself: What special measure did India implement for voting in 2024?View Solution
The Role of the Election Commission of India (ECI)
Election Commission of India — A Brief Introduction
- An independent constitutional body established in 1950.
- Headed by the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC).
Conducts elections for:
1. Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha
2. State Assemblies
3. President and Vice President
Managing the Electoral Process
- Conducts large-scale elections involving millions of voters, thousands of constituencies, and polling stations.
- Uses Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) and Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT) for transparency.
- Polling officers verify voters, ink fingers, provide ballots, and ensure the secrecy of votes.
- The "None of the Above" (NOTA) option enables voters to reject all candidates.
Model Code of Conduct (MCC)
- Rulebook ensuring free and fair elections by regulating campaign behaviour and government conduct.
- Prohibits misuse of official resources, hate speech, gift distribution for votes, and excessive campaign spending.
- Enforced since 1991, with reforms initiated by Chief Election Commissioner T.N. Seshan.

Understanding Elections in India — A Very Brief Overview
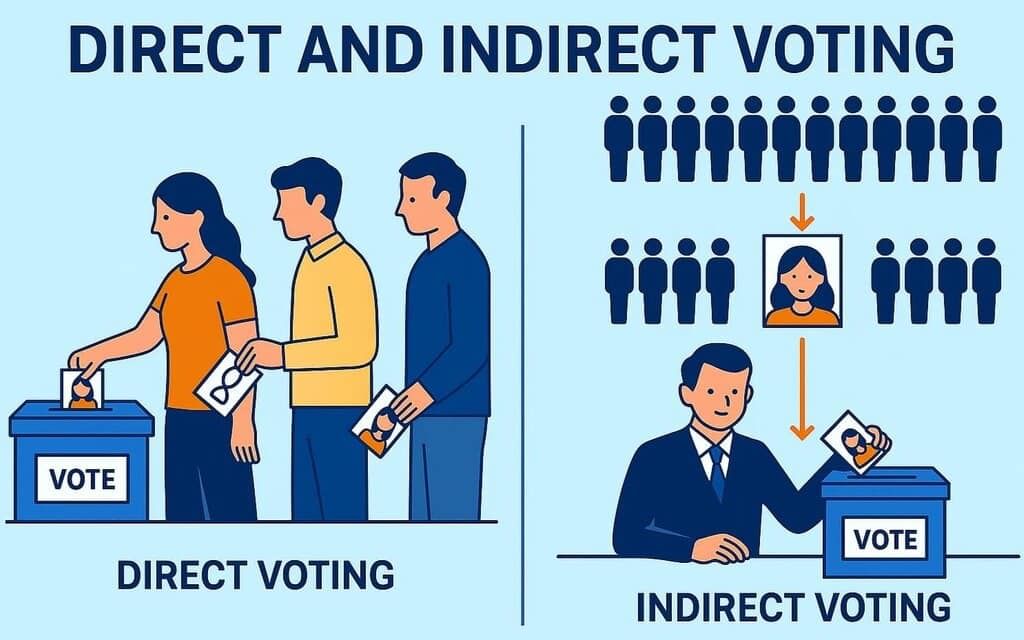
Election to the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies
- Lok Sabha MPs and State MLAs are directly elected by citizens using the First-Past-the-Post system.
- The party or coalition with majority seats forms the government, with the Prime Minister (national) or Chief Minister (state) as leader.
- Seats are reserved for the Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes to ensure representation.
Election to the Rajya Sabha
- Indirect election by MLAs of state legislative assemblies using the Single Transferable Vote.
- Rajya Sabha is a permanent body with staggered retirement of one-third members every two years.
- The President nominates 12 members for distinguished service.
Election of the President of India
- The Electoral College includes MPs and MLAs who vote by Single Transferable Vote.
- Weighted voting ensures a balance between the central and state governments.
- Only directly elected representatives vote, excluding nominated members.
 MLAs and MPs Voting for President
MLAs and MPs Voting for President
Election of the Vice President of India
- The Electoral College consists of elected and nominated MPs of both Parliaments.
- Elected via Single Transferable Vote.
- The Vice President chairs the Rajya Sabha and acts as the President when required.
Question for Key Concepts: Universal Franchise and India’s Electoral SystemTry yourself: What does the Lok Sabha represent?View Solution
Challenges and The Road Ahead
- Challenges include the influence of money, candidates with criminal backgrounds, and urban voter apathy.
- The importance of voter awareness, education, and media for informed voting is emphasised.
- Universal adult franchise requires responsible participation for democracy to thrive.
The document Key Concepts: Universal Franchise and India’s Electoral System | Social Studies (SST) Class 8 is a part of the Class 8 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
87 videos|558 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Key Concepts: Universal Franchise and India’s Electoral System - Social Studies (SST) Class 8
| 1. What is Universal Adult Franchise? |  |
Ans. Universal Adult Franchise refers to the right of all adult citizens to vote in elections, regardless of their race, gender, caste, or socio-economic status. In India, this principle was established to promote equality and inclusivity within the electoral process, allowing every eligible individual to participate in shaping the government.
| 2. How does the Election Commission of India (ECI) ensure fair elections? |  |
Ans. The Election Commission of India (ECI) is responsible for conducting free and fair elections in the country. It ensures this by implementing a strict code of conduct for political parties and candidates, overseeing the electoral process, managing voter registration, and addressing complaints regarding electoral malpractices. The ECI also provides information and education to voters about the electoral process.
| 3. What are the main challenges to achieving Universal Adult Franchise in India? |  |
Ans. Several challenges hinder the full realization of Universal Adult Franchise in India, including voter apathy, lack of awareness about voting rights, misinformation, and social inequalities that discourage participation. Additionally, issues such as electoral fraud, violence during elections, and barriers for marginalized groups also pose significant challenges.
| 4. Why is understanding the electoral system important for citizens? |  |
Ans. Understanding the electoral system is crucial for citizens as it empowers them to make informed choices during elections. Knowledge about how the system works, the significance of their vote, and the electoral process helps individuals engage more actively in democracy, hold elected officials accountable, and advocate for their rights.
| 5. What role do elections play in a democratic society? |  |
Ans. Elections are fundamental to a democratic society as they provide a mechanism for citizens to choose their representatives and influence government policies. They ensure accountability, transparency, and responsiveness from elected officials. Additionally, elections help in the peaceful transfer of power and reflect the will of the people, thereby reinforcing the principles of democracy.
Related Searches
















