-Class-9
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Democracy? Key Concepts of Democracy |

|
| Defining Democracy |

|
| Features of Democracy |

|
| Why Democracy? |

|
| Broader Meaning of Democracy |

|
| Role of Citizens |

|
| Conclusion |

|
| Key Terms |

|
What is Democracy? Key Concepts of Democracy
Democracy originates from the Greek words "Demos" (people) and "Kratia" (rule), meaning "rule by the people." It is a form of government where the people elect rulers through popular elections.
Simple Definition: Democracy is a form of government in which the people elect the rulers.
Note: This definition alone is insufficient, as it may misclassify governments with elections but lacking democratic principles. A deeper understanding requires examining its features.
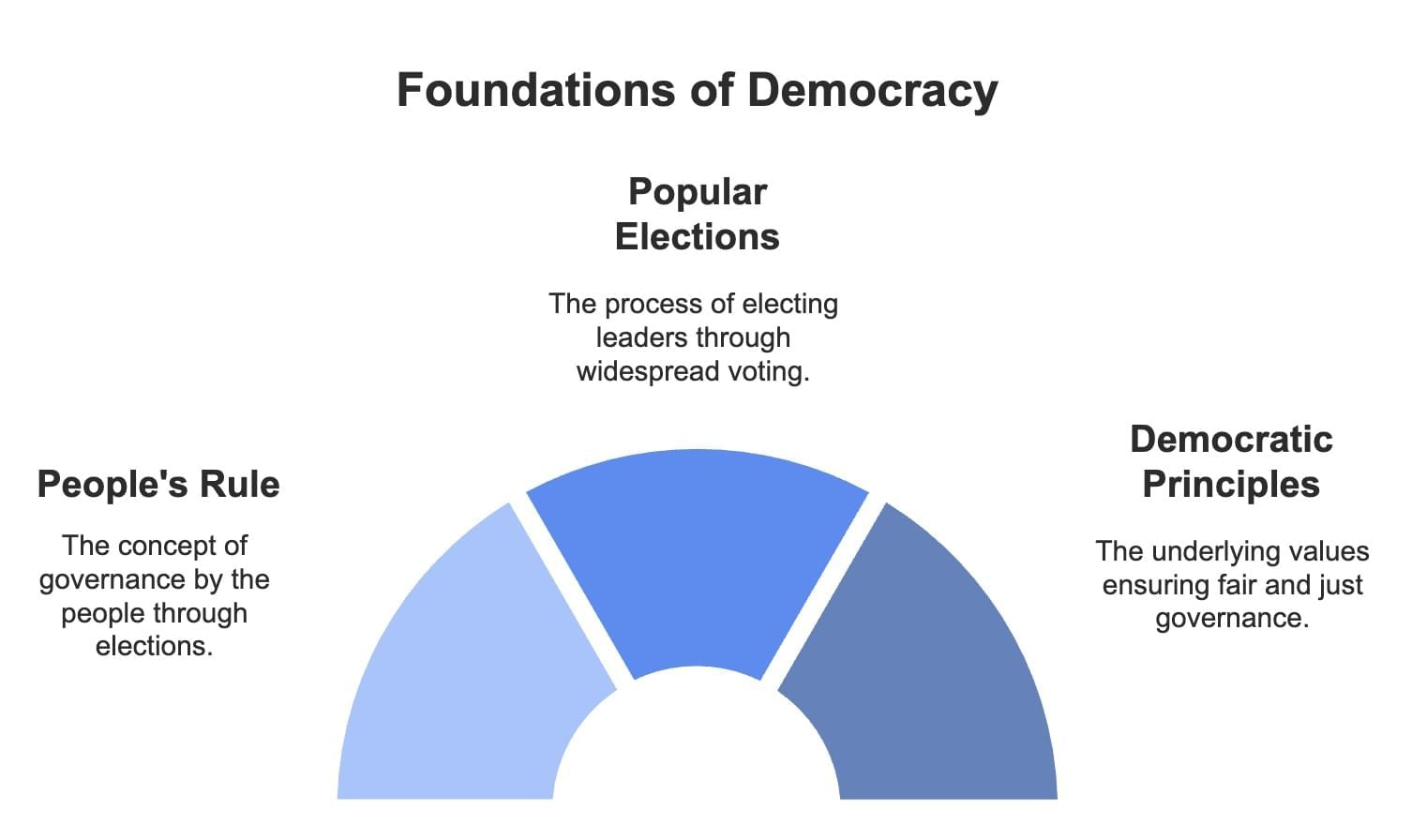
Defining Democracy
Defining democracy helps distinguish it from non-democratic systems, clarifying how governments operate. Below is a comparison:
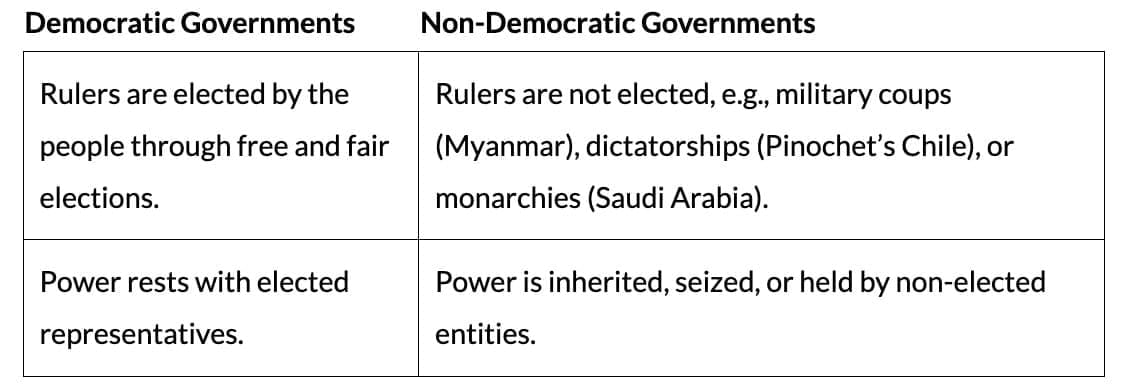
Features of Democracy
1. Major Decisions by Elected Leaders
- In a democracy, final decision-making power rests with those elected by the people.
- Case Study: Pakistan
Under General Pervez Musharraf (1999), elected representatives existed, but real power was held by non-elected military leaders, undermining democracy.
2. Free and Fair Electoral Competition
- Elections must be free, fair, and provide a genuine chance for those in power to lose.
- Case Study: China
Elections occur every five years, but candidates require Communist Party approval, ensuring single-party rule. - Case Study: Mexico
Until 2000, the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI) dominated elections through manipulation, such as government pressure and polling booth issues, limiting democratic fairness.
3. One Person, One Vote, One Value
- Democracy grants a universal adult franchise, ensuring all adults can vote without discrimination, and each vote has equal value.
- Examples of Violations:
- Saudi Arabia: Women cannot vote.
- Estonia: Russian minorities face voting restrictions.
- Fiji: Indigenous Fijian votes have more value than Indian Fijian votes.
4. Rule of Law and Respect for Rights
- A democratic government respects constitutional law, citizens’ rights, and an independent judiciary.
- Case Study: Zimbabwe
Under Robert Mugabe, Zanu-PF won elections using unfair practices, ignored court judgments, and suppressed opposition, violating democratic principles.
Summary: Definition of Democracy
Democracy is a form of government where:- Rulers elected by the people make major decisions.
- Elections offer a fair opportunity to change rulers.
- All citizens have equal voting rights.
- The government operates within constitutional limits and respects citizens’ rights.
Why Democracy?
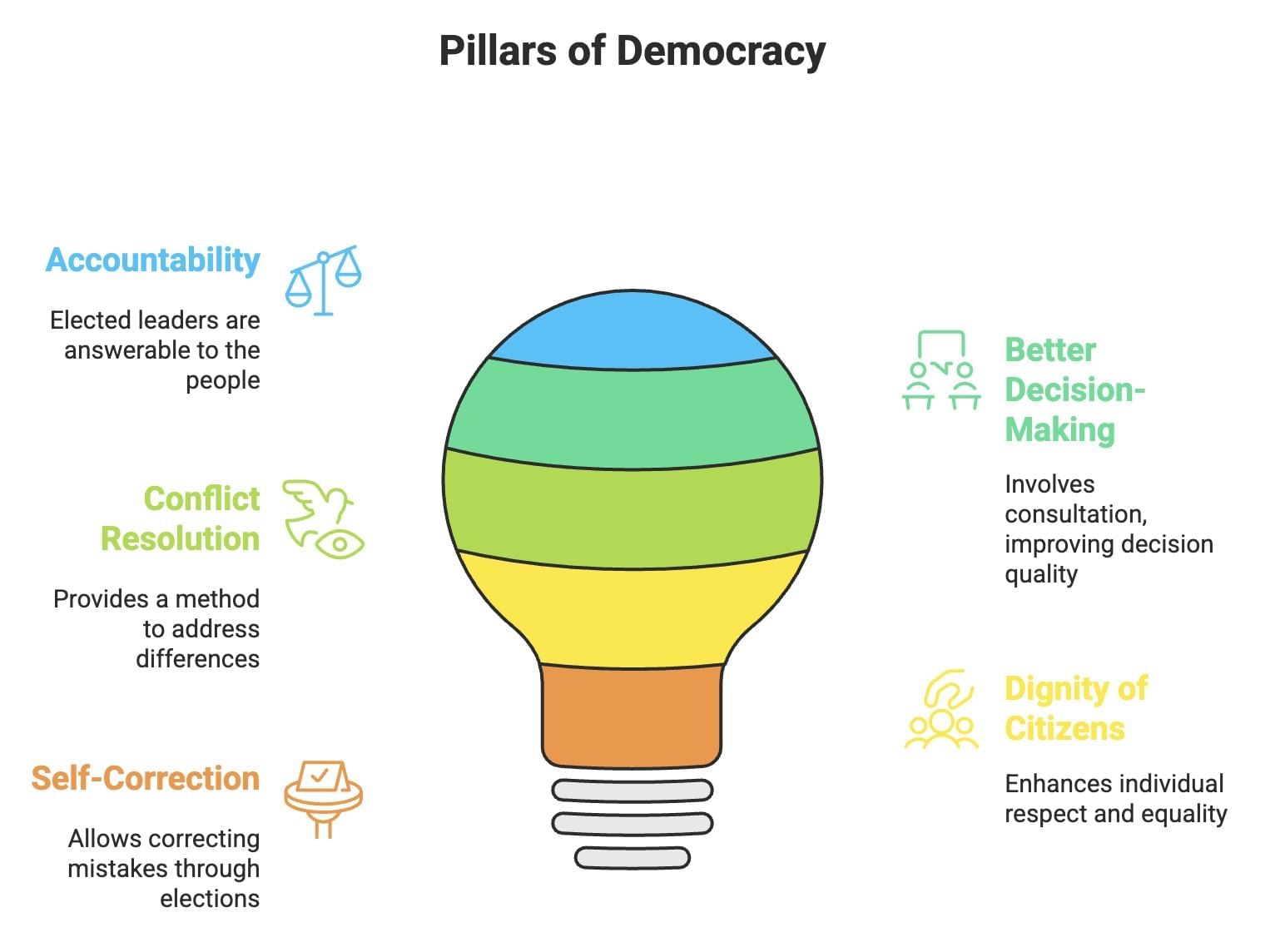
Democracy is considered the best form of government for the following reasons:
- Accountability: Elected leaders are answerable to the people.
- Better Decision-Making: Involves consultation, improving decision quality.
- Conflict Resolution: Provides a method to address differences.
- Dignity of Citizens: Enhances individual respect and equality.
- Self-Correction: Allows correcting mistakes through elections.
Arguments Against Democracy:
- Instability due to changing leaders.
- Delays from consultations.
- Potential for corruption or uninformed decisions.
Broader Meaning of Democracy
Representative Democracy: Citizens elect representatives to form the government and make decisions. It is necessary due to large populations and practical constraints.
Nominal vs. Ideal Democracy:
- Nominal Democracy: Elections occur, but essential democratic features may be absent.
- Ideal Democracy: Every citizen has equal access to decision-making power, requiring education and resources—rarely achieved but a guiding principle.
Role of Citizens
- Exercise the right to vote to influence government direction.
- Tolerate differing views and practice mutual tolerance.
- Express dissent responsibly through democratic channels.
- Stay informed and participate in shaping public opinion.
Conclusion
Democracy is a government by discussion and persuasion, balancing majority rule with minority rights. It thrives on debate, where policies are discussed thoroughly, and opposition views are considered. Key terms like universal adult franchise, free and fair elections, and rule of law define its principles, making it a cornerstone of accountable governance.
Key Terms
- Universal Adult Franchise: The Right of all adults to vote without discrimination.
- Free and Fair Elections: Impartial elections allow free voting and accurate counting.
- Constitutional Law: Defines government structure and citizens’ rights.
- Rule of Law: Equality and accountability under the law.
- Electoral Competition: A fair contest for political power.
- Multi-party System: Multiple parties compete for power.
- Nominal Democracy: Elections without full democratic features.
- Ideal Democracy: Equal participation by all citizens.
- Representative Democracy: Elected representatives govern on behalf of the people.
- Electoral Manipulation: Actions to unfairly influence election outcomes.
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on -Class-9
| 1. What is the definition of democracy? |  |
| 2. Why is democracy considered important? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of democracy? |  |
| 4. What are some challenges faced by democracies? |  |
| 5. How can citizens promote and protect democracy? |  |
















