Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur: Conservation of Plants And Animals- 2 | Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur Solutions: Class 8 Science PDF Download
Q.31. What is meant by the ‘flora’ and ‘fauna’ and which belong to ‘flora of the Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve ?
Sal, Arjun, Cheetal, Teak, Leopard, Fern, Blue bull, Barking deer, Mango, Wolf.
- Sal flora
- Arjun flora
- Teak flora
- Fern flora
- Mango flora
- Leopard Fauna
- Blue bull Fauna
- Deer Fauna
- Wolf Fauna
Q.32. What is the difference between ‘flora’ and ‘fauna’?
- Flora refers to plants
- Fauna refers to animals.
Q.33. What is meant by ‘Species’ ? Give any five examples of species.
A group of living organisms comprising similar individuals capable of exchanging genes or interbreeding.
- Alpaca: Vicugna pacos.
- Anole lizard: Anolis carolinensis.
- Armadillo: Dasypus novemcinctus.
- Bushbaby: Otolemur garnettii.
- Cat: Felis catus.
- Chicken: Gallus gallus.
Q.34. What’s do you understand by ‘endemic species’ ? Name two plant species and two animal species endemic to Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve area.
Species having relatively small ranges are called endemic species. On remote oceanic islands, almost all the native species are endemic.
- The endemic ‘fauna’ animal species are chinkara and nilgai.
- The endemic ‘flora’ plant species are Acacia nilotica and Anogeissus latifolia.
Q.35. Name two man-made causes of deforestation and two natural causes of deforestation.
- The two man made causes of deforestation are land required for agriculture and urbanisation.
- The two natural cause of deforestation are flood and wildfire.
Q.36. What is a Wildlife Sanctuary? Name any two Wildlife sanctuaries in India. Where are these Sanctuaries located?
A wildlife refuge, also called a wildlife sanctuary, is a naturally occurring sanctuary, such as an island, that protects species from hunting, predation or competition; it is a protected area, a geographic territory within which wildlife is protected.
The two wild life sanctuary are:
- Gulmarg in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Gandhi Sagar Sanctuary in Madhyapradesh.
Q.37. Name any two Bird Sanctuaries in India. Where are these located?
The two bird sanctuaries are Atapaka Bird sanctuary and Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary in Andhra Pradesh.
Q.38. What are the difference between a Biosphere Reserve & a Wildlife Sanctuary?
The difference between Wildlife Sanctuaries and Biosphere:
- Wildlife sanctuaries: limited number of activities are permitted inside it
- Biosphere reserves: limited economic activity (sand mining and stone mining) is permitted.
Q.39. State the difference between Wildlife Sanctuary and Zoo.
Wildlife sanctuary is a selected spot of living for animals and birds. Also, birds and animals are not bred and taken care of in a sanctuary. Instead they take care of themselves and they look after their own living.
A zoo is a created and an artificial habitat for animals and birds. In a zoo, the animals and birds are held in captive. It is a place that is created by man with an intention to keep the birds and animals to be watched by visitors and people as part of the tourism of a country.
Q.40. What is a National Park? Name any two National Parks of India. Where are these National Park located?
A national park is a park in use for conservation. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or wns
- Gir Forest national park Gujarat.
- Jim corbett National Park Uttrakhand.
Q.41. What are the differences between a Wildlife Sanctuary and a National Park?
Differences between Wildlife Sanctuary and National Park are:
- A National Park is an area of great scenic beauty while Wildlife Sanctuary may or may not be an area of great Scenic beauty.
- A National Park protects and Preserves wild animals and their environment as well as scenic beauty, historical objects and habitats of scientific interest in the area, while A wildlife sanctuary protects ans preserves only the wild animals in their natural environment.
- In a National Park, wild animals are kept for recreation, enjoyment. However, National Park protects the wild animals as well. A Wildlife Sanctuary is not meant for enjoyment of the public. A Wildlife Sanctuary is dedicated to the protection of wild animals only.
Q.42. What do the rock painting found in rock shelters of Satpura National Park depict?
The rock painting found in rock shelters of Satpura National Park depict about the Bhimbetka caves one of the oldest known human habitations, dating back to some 10,000 years ago. These caves have paintings dating back from various periods during which they would have been inhabited. So they depict the historical importance of old era.
Q.43. What is ‘Project Tiger’? What was the aim of these projects?
Project Tiger is a tiger conservation programme launched in 1973 by the Government of India. The project aims at ensuring a viable population of Bengal tigers in their natural habitats and also to protect them from extinction and preserving areas of biological importance as a natural heritage forever represented as close as possible the diversity of ecosystems across the tiger’s distribution in the country.
To factors that leads to reduction of tiger habitats and to mitigate them by suitable management. The damages done to the habitat were to be rectified to facilitate the recovery of the ecosystem to the maximum possible extent.
To ensure a viable population of tigers for economic, scientific, cultural, aesthetic and ecological values.
Q.44. Why even protected forests are not safe for wild animals?
The protected forests are not safe for wild animals because the people from adjacent areas use natural forests resource to fulfill their needs. The smugglers kill animals for money and also set forest on fire to eliminate technology to safeguard animals.
Q.45. What is meant by extinct species? Name any two extinct animals?
An “extinct species” is a species of organism that can no longer be found in the wild or in captivity.
The example of extinct species are Dinosaur and Dodo.
Q.46. What is meant by endangered species? Name any two endangered animals?
The plant or animal species existing in such small numbers it is in danger of becoming extinct, especially such a species placed in jeopardy because of human activity. One of the principal factors in the endangerment or extinction of a species is the destruction or pollution of its habitat.
The two endangered species in India are Great Indian Bustard and snow leopard.
Q.47. Different between ‘endangered species’ and extinct species.
An “extinct species” is a species of organism that can no longer be found in the wild or in captivity. It is already dead and can no longer be found in any part of the world.
The plant or animal species existing in such small numbers it is in danger of becoming extinct, especially such a species placed in jeopardy because of human activity. The specie is on the verge of extinction and have few numbers. If proper measures are not taken then it can also become extinct if proper care and measures are taken then their population can be increased.
Q.48. By taking the example of snakes, explain how by killing small animals, we are actually harming ourselves.
The killing of small animals disturb the life cycle and food chain. For example if we kill snakes, rodents that are eaten by snakes will increase in number and destroy the crop at mass level. In another case if we kill frogs then the number of insects that destroy our crops and are eaten by frogs will damage the crop. In nutshell killing of any animal leads to our own harm.
Q.49. What is Red Data Book?
The Red Data Book is the state document established for documenting rare and endangered species of animals, plants and fungi and some local subspecies that exist within the territory of the state or country. This book provides authentic central information for studies and monitoring programmes on rare and endangered species and their habits. Red list has 132 species of plants and animals from India.
Q.50. State one advantage of maintaining Red Data Book.
The one advantage of maintaining Red Data Book is that as it contains the information about the species that are endangered and threatened so it helps the government agencies to take the measures to protect them and also increase their number through different modes of rearing and preservation.
Q.51. What do you understand by the term migration?
Migration refers to the movement of a group of animals from one region to another, usually seasonally.
It is found in all major animal groups, including birds, mammals, fish, reptiles, amphibians, insects, and crustaceans. It is done by the species itself to find better and favorable habitat or by human authorities to locate animals or birds to better and safe habitat for breeding.
Q.52. What is meant by the migration of birds? why do birds migrate?
Bird migration is the regular seasonal movement, often north and south along a flyway, between breeding and wintering grounds. Many species of bird migrate. Migration carries high costs in predation and mortality, including from hunting by humans, and is driven primarily by availability of food. BIrds also migrate for favourable weather for their survival and breeding.
Q.53. What are migratory birds? Name one migratory bird which comes to warmer regions of India every year.
Migratory birds are those birds that fly hundreds and thousands of kilometres to find the best ecological conditions and habitats for feeding, breeding and raising their young. When conditions at breeding sites become unfavourable, it is time to fly to regions where conditions are better.
The migratory bird which comes to warmer regions of India every year is Pelican.
Q.54. Why does Siberian crane come from Siberia to places like Bharatpur in In India every year.
Siberian cranes comes to India during winter because in Siberia, it is cold, daylight is of shorter duration, food is scarce. So they look for better living conditions else where to rear their young ones and to come to India as it has favourable conditions for their survival.
Q.55. What can be done to retain our ‘green wealth’ for the future generations?
- We can retain our Green Wealth for the future generations by taking the following steps
- We can focus on afforestation and sustainable development without harming the flora and Fauna of our country and world at large.
- We can levy and follow rules and regulations for the conservation, management and increase of green wealth.
- We can focus on recycling and reuse of resources.
Q.57. What is meant by ‘reforestation’? What are the advantages of reforestation?
Reforestation: Reforestation is the reestablishment of destroyed forests by planting trees.
The advantages of reforestation are reforestation helps protect important species of plants and provides natural habitat to animals and birds.
It leads to maintaining and improving the social and biological levels of an entire ecosystem.
Q.57. What are the aims of the ‘Forest Conservation Act, in India ?
THE FOREST (CONSERVATION) ACT, 1980 ACT NO. 69 OF 1980 is an act to provide for the conservation of forests and for matters connected therewith or ancillary or incidental thereto. It says any forest land or any portion thereof may be assigned by way of lease or otherwise to any private person or to any authority, corporation, agency or any other organisation not owned, managed or controlled by Government and any forest land or any portion thereof may be cleared of trees which have grown naturally in that land or portion, to use it for reafforestation. The cultivation of tea, coffee, spices, rubber, palms, oil-bearing plants, horticultural crops or medicinal plants; (b) any purpose other than afforestation, but includes none work relating or ancillary to conservation, development and management of forests and wildlife the establishment of check-posts, fire lines, wireless communications and construction of fencing, bridges and culverts, dams, waterholes, trench marks, boundary marks, pipeline or other like purposes.
Q.58. Why should we save, reuse and recycle paper?
Reducing, reusing and recycling are important because they decrease the amount of waste on the planet and preserve natural resources by maintaining space and cutting down on landfills. Reducing, reusing and recycling reduce consumption of new materials and save energy.
Q.59.Explain how, recycling of paper helps it n the conservation of forests.
Reducing, reusing and recycling are important because they decrease the amount of waste on the planet and preserve natural resources by maintaining space and cutting down on landfills. Reducing, reusing and recycling reduce consumption of new materials and save energy.
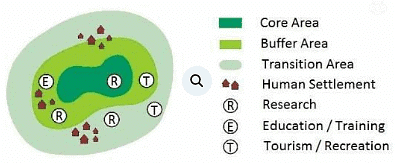
Q.60. With the help of a labeled diagram, describe the basic design of a Biosphere Reserve.
The biosphere reserves are traditionally organized into three interrelated zones, known as the core area, the buffer zone, and a transition zone or ‘area of cooperation.’
Core area: includes protected areas, as they act as reference points on the natural state of the ecosystems represented by the biosphere reserves. Information from these core areas may assess the sustainability of activities, or the maintenance of environmental quality, in surrounding areas.