Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur: Some Natural Phenomena- 2 | Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur Solutions: Class 8 Science PDF Download
Short Answer Type Questions
Short Answer Type Questions
Q.26. Why does a plastic comb rubbed with dry hair attract tiny pieces of paper?
The electric charges generated by rubbing are static electric charges. These electric charges remain bound on the surface of the charged object. When a plastic comb is dry hair, it becomes negatively charged. The negatively charged comb induces a positive charge on the pieces of paper which are neutral in nature. As we know that the unlike charges attract each other, plastic comb attracts tiny pieces of paper.
Q.27. How will you charge a glass rod by the method of friction?
The electric charges generated by rubbing are static electric charges. These electric charges remain bound on the surface of the charged object. A glass rod can be charged by rubbing it with silk cloth. When a glass rod is rubbed with silk, some of the electrons from the glass atoms are transferred to silk. Due to the deficiency of electrons in the glass atoms, it becomes positively charged. Whereas the silk has acquired electrons, it becomes negatively charged.
Q.28. How will you charge an inflated rubber balloon by the method of friction?
An inflated balloon can be charged by rubbing it against the woolen cloth.
Explanation: Upon rubbing, the wool loses electrons and it causes the electrons to move from the wool to the balloon’s surface. The rubbed part of the balloon now has a negative charge.
Q.29. How will you charge a plastic comb (plastic scale or plastic pen) by the method of friction?
The electric charges generated by rubbing are static electric charges. These electric charges remain bound on the surface of the charged object. A plastic comb can be charged by rubbing. The plastic comb will carry a negative charge.
Q.30. How will you charge a ballpoint pen refill by the method of friction?
A ballpoint pen refill can be charged by rubbing it against the wool cloth. It becomes negatively charged. When we bring it close to bits of paper, the paper gets attracted to it. Paper is electrically neutral. The negative charge on the pen induces a positive charge on the paper bits which are close to it that causes the paper to fly and stick to the pen.
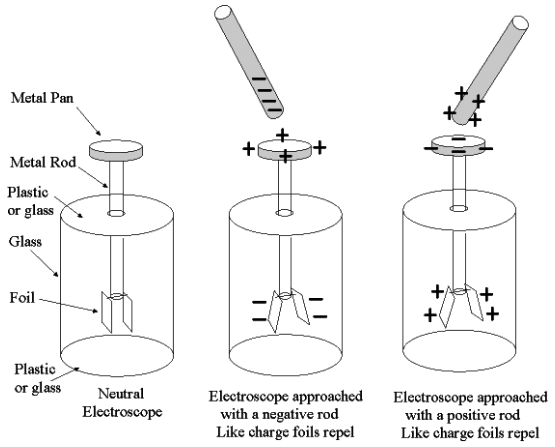
Q.31. What will you observe when the metal top of an electroscope is touched with a glass rod which has been rubbed with silk cloth? Give reason for your answer.
When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk cloth, it acquires positive charge. When it is touched with the metal top of an electroscope, both the metal top and leaves acquires a positive charge due to conduction. As a result of the positive charge on both the leaves, the divergence of leaves takes place.
Q.32. What will you observe when the metal top of an electroscope is touched with a plastic comb rubbed in dry hair? Give reason for your answer.
After rubbing the plastic comb, it acquires a negative charge. When it is touched with the metal cap of an electroscope, both the metal cap and the leaves acquire negative charge due to conduction. As a result of negative charge on both the leaves, divergence of leaves takes place.
Q.33. What happens when we touch the metal top of a charged electroscope with our finger? What is this process known as?
The leaves of an electroscope will collapse when we touch the metal cap with our hand. This is because the leaves of the charged electroscope lose charge to the earth or gets discharged through our body. This process is called Earthing. The process of transfer of charge from a charged body to the earth is called Earthing.
Q.34. Explain why, a charged body loses its charge when we touch it with our hand.
A charged body loses its charge or gets discharged when we touch it with our hand. This process is called Earthing. The process of transfer of charge from a charged body to the earth is called Earthing.
Q.35. What happens when the two plates of earth’s crust moving in opposite directions slide past one another?
The outermost layer of the earth is fragmented. Each fragment is called a plate. These plates are in continual motion. When they brush past one another, or a plate goes under another due to collision they cause disturbance. This disturbance in the earth’s crust shows up as an earthquake on the surface of the earth.
Q.36. What happens when two moving plates of earth’s crust collide head on with each other?
The outermost layer of the earth is fragmented. Each fragment is called a plate. These plates are in continual motion. When two plates collide head on, they push each other up and form mountains. The Himalayas and other great mountain ranges were created by this process.
Q.37. How will you find out whether an object is charged or not?
In order to find out if an object is charged or not, we can test it by using an electroscope.
When the object is touched with the metal cap of an electroscope, both the metal cap and the leaves acquire the charge due to conduction. As a result of
As a result of both, the leaves of the electroscope will have the same charge. It will cause the leaves to diverge showing that the object was charged, as shown in the pic:
Q.38. Explain why, it might be dangerous to raise an umbrella over our head in a thunderstorm.
It is not safe to carry an umbrella during thunderstorm. Umbrellas are made up of metals. Thunderstorms are accompanied with lightening. The electric discharge from the clouds can travel through the metal rod of the umbrella. It can result into the electric discharge to the person carrying it. Hence, it might be dangerous to carry an umbrella during thunderstorm.
Q.39. A person is in open space during a thunderstorm with no shelter (not even a tree) available nearby. Describe the safe position which he should take to protect himself from lightning. Why is this position considered safe?
If there is no shelter available, we must stay away from all trees, poles or other metal objects. We must not lie on the ground but we should squat low on the ground. Hands must be placed on the knees and the head should be between the hands. This position will make us the smallest target to be struck.
Q.40. Suggest three measures to protect ourselves from lightning.
We must protect ourselves from lightening in the following ways:
- We must find a safe place to stay. A house or building are safe to stay in. If we are in a car or a bus, we must keep the windows and doors of the vehicle shut.
- If there is no shelter available, we must remain in the squat position.
- We must avoid the use of telephone cords, electrical wires and metal pipes.
- Bathing should be avoided during thunderstorms to avoid contact with running water.
- Electrical appliances like computers, TVs, etc., should be unplugged.
Q.41. Explain why, sometimes when we take off the woollen sweater or a polyester shirt in a dark room, we can see tiny sparks of light and hear a crackling sound.
We can see tiny sparks of light and hear a crackling sound when we take off the woolen sweater or a polyester shirt. It happens because the sweater or a polyester shirt gets charged due to friction between the sweater and the body.
Q.42. (a) Name the material of which a lightning conductor is made.
(b) What is the shape of the top end of a lightning conductor?
(c) Where is the upper end of the lightning conductor fixed in a building?
(d) Where is the lower end of the lightning conductor fixed and how?
(a) Lightening conductor is a device which is used to protect a tall building from lightening. Lightening conductor is made up of metal which is a good conductor of electricity.
(b) The lightening conductor is made of metal rod with a sharp pointed edge on the top. They are made of conductive material such as copper and aluminium. Copper and its alloys are the most common materials used in lightening conductors.
(c) A metallic rod which is taller than the building is installed in the walls of the building during its construction. One end of the rod is kept out in the air and the other end is buried deep in the ground. The rod provides easy route for the transfer of electric charge to the ground.
(d) A metallic rod, taller than the building, is installed in the walls of the building during its construction. The lower end of the rod is buried deep in the ground and the upper end is kept out in the air. The metallic rod transfers the electric charge to the ground.
Q.43. What precautions would you take to protect yourself during an earthquake if you are inside the house?
In order to protect ourselves during an earthquake we must protect ourselves in the following ways:
- We must take shelter under the table and should stay until the shaking stops.
- We must stay away from the heavy objects to avoid them to fall on us.
- If we are in bed we must stay in it and should protect our head with a pillow.
Q.44. What precautions would you take to protect yourself during an earthquake if you are outdoors?
We must take the following precautions for protection during an earthquake if we are outdoors:
- We must find a clear spot, away from the buildings, trees and overhead power lines. We must drop to the ground.
- While driving, we must remain inside the car or a bus. We must drive slowly to a clear spot. We must not come out of the car or a bus till the tremors stop.
Q.45. State any two precautions which should be observed by people living in seismic zones for protection against earthquakes.
People living in seismic zones should take the following measures for protection against earthquakes:
- The buildings in these zones should be designed so that they can withstand tremors. Modern building technology can make it possible.
- Mud and timber should be used as a construction material instead of heavy construction material. The roofs should be kept as light as possible.
- The cupboards and shelves should be fixed to the walls so that they should not fall easily.
- Clocks, photo frames and water heaters etc. should be hanged carefully at proper places to avoid damage by them.
- Sometimes the buildings may catch fire during earthquakes. All the buildings, especially the tall buildings should have the firefighting equipment in working order.
Long Answer Type Questions
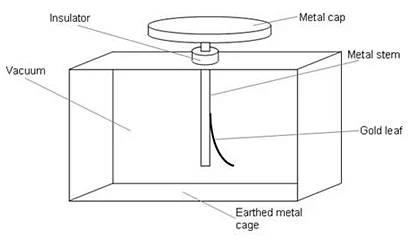
Q.46. What is an electroscope? Draw a labelled diagram of an electroscope and explain its working.
Electroscope is the device which is used to detect charge on a body. It is used for detecting, measuring and finding the nature of a charge. An electroscope consists of a large jar. A metal rod is fitted into the mouth of the jar with the help of the cork. At the lower end of the metal rod a pair of thin leaves of gold or aluminium is suspended. If the leaves of the electroscope diverge or open up when an object is touched, the body is charged. The extent of divergence or opening up of the leaves is a measure of the charge on the body. A body with higher charge will cause greater opening up of the leaves.
Q.47. (a) What is lightning? How is lightning produced between clouds in the sky?
(b) Why does lightning usually strike tall buildings?
(c) What damage can be done when lightning strikes on the earth?
(a) The process of electric discharge between clouds and the earth or between different clouds causes lightning. During the development of a thunderstorm, the water droplets move downwards while the air currents move upward. Due to these strong movements, the separation of charges takes place. The positive charges collect near the upper edges of the clouds and the negative charges collect near the lower edges. There is accumulation of positive charges near the ground as well. When the magnitude of the accumulated charges becomes very large, the air which is normally a poor conductor of electricity, is no longer able to resist their flow. Negative and positive charges meet, producing streaks of bright light and sound. We are able to see these streaks as lightening. The process is called an electric discharge.
(b) Lightning strike could destroy life and property. Lightning conductors can protect buildings from the effects of lightning. Lightning strikes the tall buildings and can result in fire.
(c) Lightening can result in electric shocks, damage to the buildings and fire. The electric discharge from the clouds can travel through the metal objects and can result into the electric discharge to the person carrying it.
Q.48. (a) How does a lightning conductor protect a tall building? Name the scientist who invented the lightning conductor.
(b) Why are lightning strikes more frequent in hilly areas?
(a) Lightening conductor is a device which is used to protect a tall building from lightening. Lightening conductor is made up of metal which is a good conductor of electricity. The lightening conductor is made of metal rod with a sharp pointed edge on the top. They are made of conductive material such as copper and aluminium. A metallic rod which is taller than the building is installed in the walls of the building during its construction. One end of the rod is kept out in the air and the other end is buried deep in the ground. The rod provides easy route for the transfer of electric charge to the ground. Lightening conductor was discovered by Benjamin Franklin.
(b) Hills are above the sea levels and are nearer to the sky. The clouds are closer to the hills as compared to the grounds. As a result, the lightening can strike much easily and frequently in hilly areas.
Q.49. (a) What is an earthquake? What are the two main situations in which earthquakes occur?
(b) Define (i) focus, and (ii) epicentre, of an earthquake.
(c) What are the various effects of an earthquake?
(a) Earthquake is the phenomenon in which the earth shakes suddenly for a very short time. It is caused by a disturbance deep inside the earth’s crust. It is the destructive natural phenomenon which cannot be predicted in advance. The earthquakes can cause floods, landslides and tsunamis. Most earthquakes are caused by the movement of earth’s plates. The magnitude (or intensity) of an earthquake is expressed in terms of Richter scale. The destructive earthquakes have magnitudes higher than 7 on the Richter scale. The outermost layer of the earth is fragmented. Each fragment is called a plate. These plates are in continual motion. When they brush past one another, or a plate goes under another due to collision they cause disturbance in the earth’s crust that shows up as an earthquake on the surface of the earth. The tremors on the earth can be caused when a volcano erupts or when a meteor hits the earth. It can also be caused by an underground nuclear explosion.
(b) Focus of an earthquake is located deep under the ground. Focus is the point inside the crust where the pressure is released. The point on the earth’s surface above the focus is called the epicenter.
(c) The various effects of earthquakes are following:
- Earthquakes can cause immense damage to buildings, bridges, dams and people.
- There can be a great loss to life and property.
- The earthquakes can cause floods, landslides and tsunamis.
Q.50. (a) Name the three layers of earth. Draw a labelled diagram to show the structure of earth.
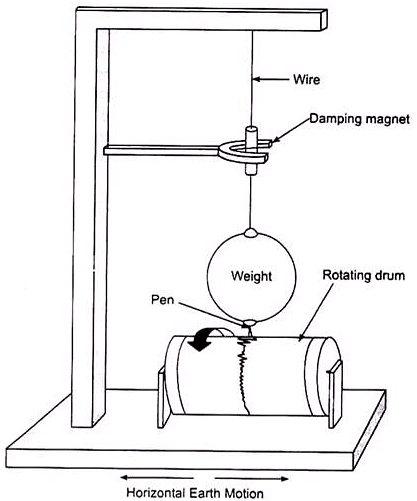
(b) What is a seismograph? Draw a labelled diagram of a seismograph.
(a) The Earth consists of four concentric layers: The inner core, outer core, mantle and the crust. The crust is made up of tectonic plates which are in constant motion. Earthquakes and volcanoes are most likely to occur at plate boundaries.
The Earth is made up of following distinct layers:
- The inner core: It is in the center of the Earth. It is the hottest part of the Earth. It is solid and is made up of iron and nickel. It has a temperature of up to 5,500°C.
- The outer core: It is the layer surrounding the inner core. It is a liquid layer. It is also made up of iron and nickel. It is still extremely hot, with temperatures similar to the inner core.
- The mantle: It is the widest section of the Earth. It has a thickness of approximately 2,900 km. The mantle is made up of semi-molten rock called magma.
- The crust: It is the outer layer of the earth. It is a thin layer between 0-60 km thick. The crust is the solid rock layer upon which we live.
There are two different types of crust: continental crust, which carries land, and oceanic crust, which carries water.
(b) Seismograph is the instrument which is used to measure and record an earthquake. The tremors produce waves on the surface of the earth. These are called seismic waves. These waves are recorded by the seismograph. Following is the well labelled diagram of a seismograph.