Class 5 Exam > Class 5 Notes > Science Class 5 > Learn at a Glance: States of Change of Matter
Learn at a Glance: States of Change of Matter | Science Class 5 PDF Download
The document Learn at a Glance: States of Change of Matter | Science Class 5 is a part of the Class 5 Course Science Class 5.
All you need of Class 5 at this link: Class 5
|
42 videos|230 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Learn at a Glance: States of Change of Matter - Science Class 5
| 1. What are the main states of matter? |  |
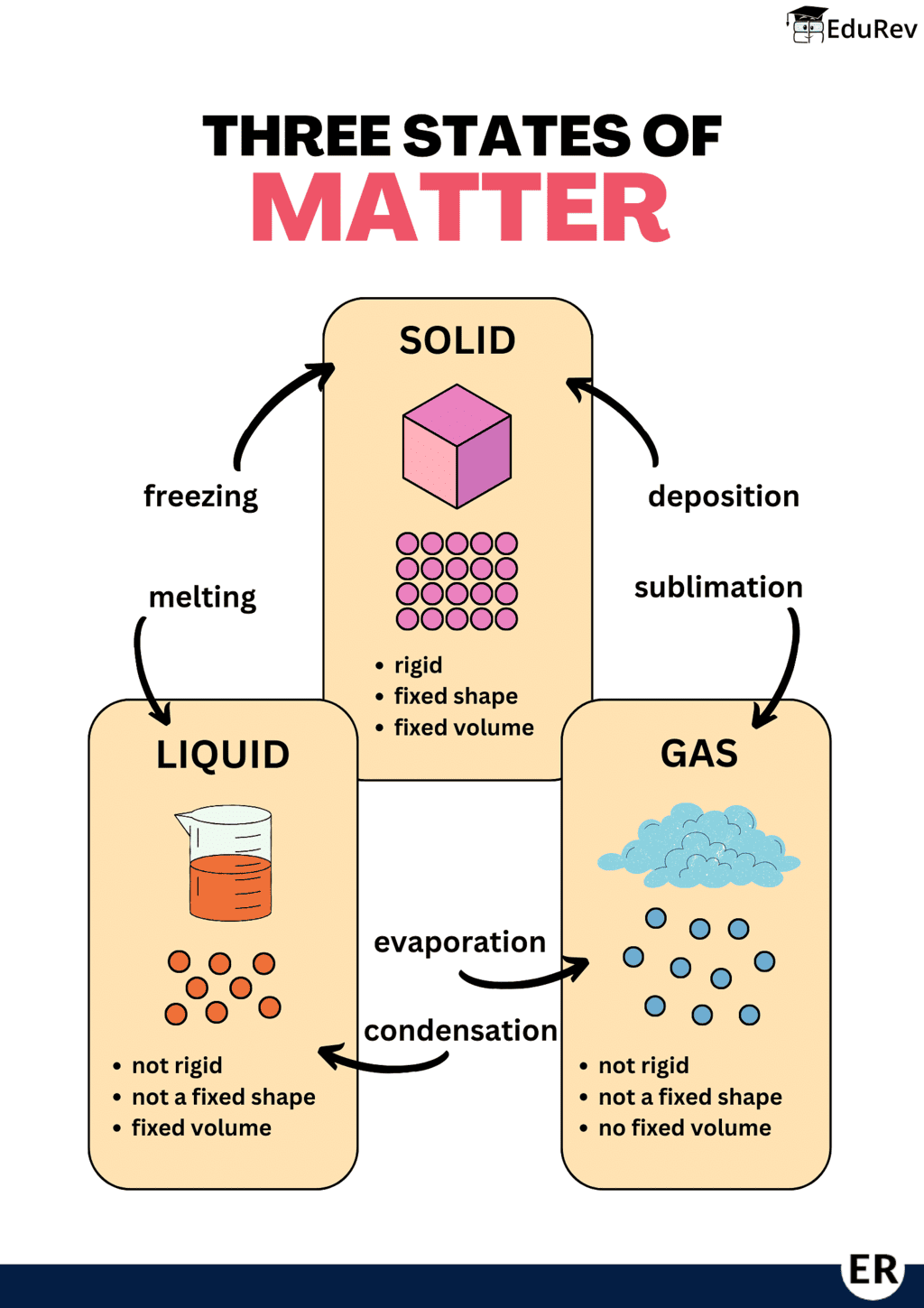
Ans. The main states of matter are solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Each state has distinct properties. Solids have a fixed shape and volume, liquids have a fixed volume but take the shape of their container, gases have neither fixed shape nor volume, and plasma is a high-energy state where atoms lose electrons.
| 2. How does matter change from one state to another? |  |
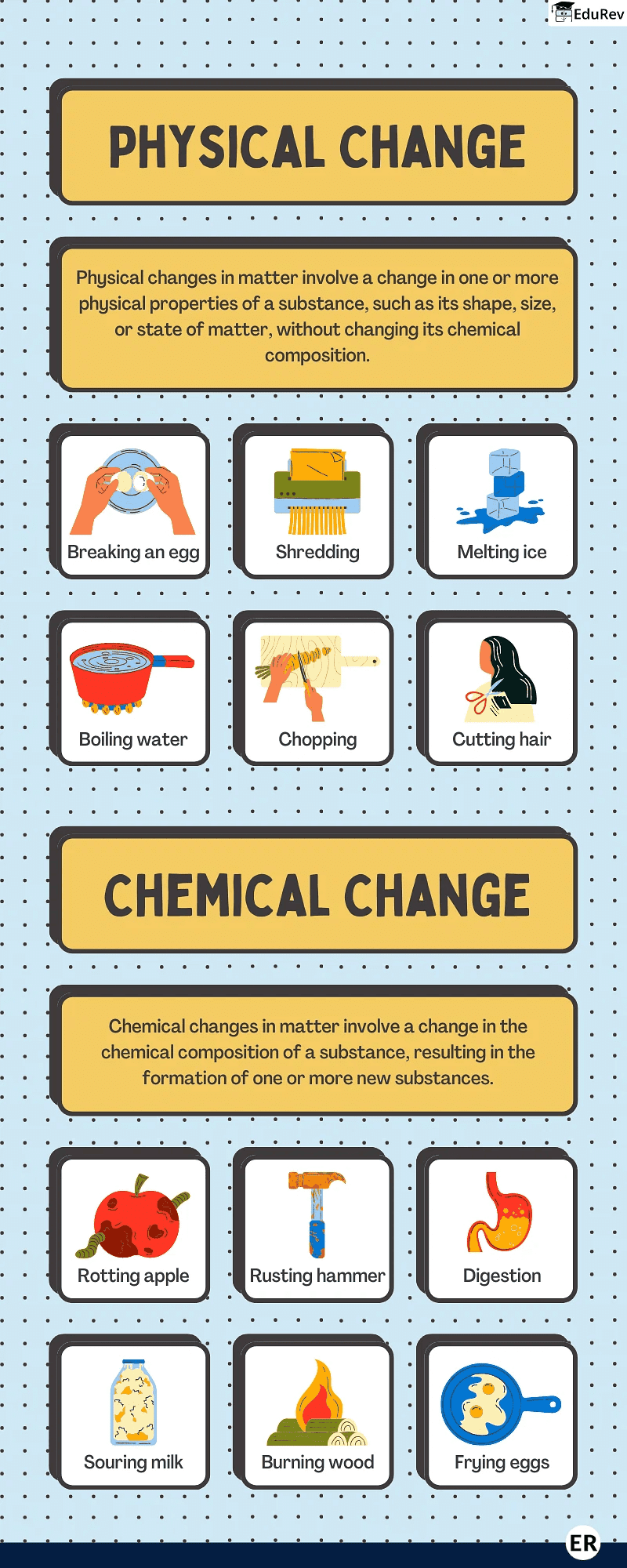
Ans. Matter changes from one state to another through processes such as melting, freezing, condensation, evaporation, sublimation, and deposition. For example, heating a solid can cause it to melt into a liquid, while cooling a liquid can cause it to freeze into a solid.
| 3. What is the process of evaporation? |  |
Ans. Evaporation is the process where liquid water changes into water vapor or gas. This happens when the molecules in the liquid gain enough energy to break free from the surface and enter the air, usually occurring at any temperature.
| 4. What is the difference between boiling and evaporation? |  |
Ans. Boiling is a rapid change from liquid to gas that occurs at a specific temperature called the boiling point, throughout the liquid. In contrast, evaporation is a slower process that can occur at any temperature and only happens at the surface of the liquid.
| 5. Can matter exist in more than one state at the same time? |  |
Ans. Yes, matter can exist in more than one state at the same time. An example is ice water, where solid ice and liquid water coexist. Another example is fog, where tiny water droplets (liquid) are suspended in air (gas).
Related Searches
















