Class 4 Exam > Class 4 Notes > Mathematics for Class 4: NCERT > Learning Poster: Guess the Time
Class 4 Maths Learning Poster Chapter 12 Clock
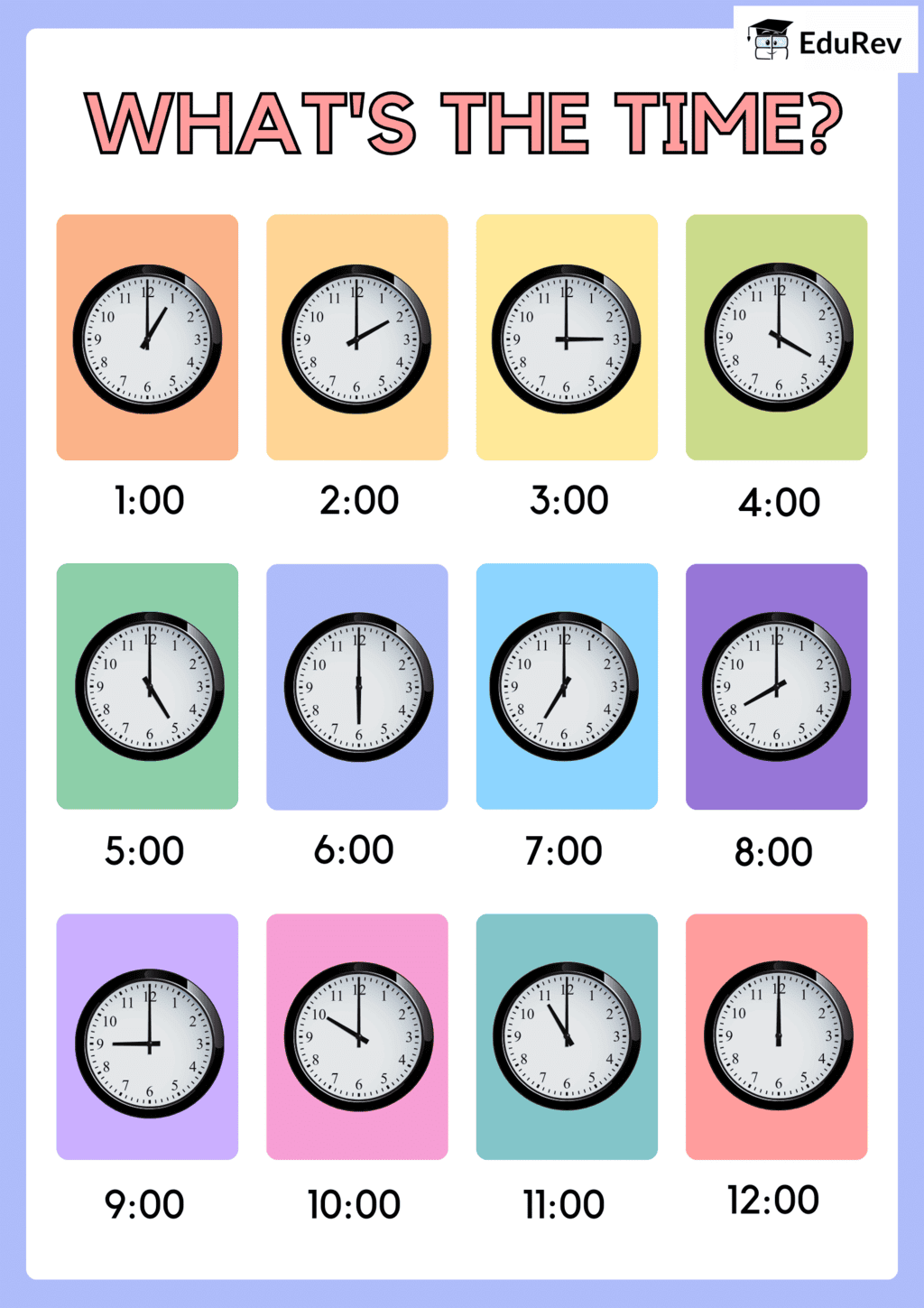
The document Class 4 Maths Learning Poster Chapter 12 Clock is a part of the Class 4 Course Mathematics for Class 4: NCERT.
All you need of Class 4 at this link: Class 4
|
26 videos|142 docs|34 tests
|
FAQs on Class 4 Maths Learning Poster Chapter 12 Clock
| 1. What are the different types of clocks and how do they work? |  |
Ans. There are several types of clocks, including analog clocks, digital clocks, and atomic clocks. Analog clocks use a mechanical movement driven by gears and a pendulum or quartz crystal to keep time, displaying hours and minutes with hands on a dial. Digital clocks display the time using numerical digits and often use electronic circuits, which can be more accurate than analog clocks. Atomic clocks rely on the vibrations of atoms to measure time and are the most precise type of clock available.
| 2. How do you read an analog clock? |  |
Ans. To read an analog clock, observe the position of the hour and minute hands. The shorter hand indicates the hour, while the longer hand shows the minutes. The clock face is divided into 12 hours, and each hour is further divided into 5-minute increments. To determine the time, note the hour indicated by the hour hand and count the minutes based on the position of the minute hand.
| 3. What is the significance of daylight saving time in relation to clocks? |  |
Ans. Daylight Saving Time (DST) involves setting clocks forward by one hour during warmer months to extend evening daylight. This practice helps to make better use of daylight, reduce energy consumption, and promote outdoor activities in the evenings. Clocks are typically set forward in spring and set back in fall, which can cause confusion regarding timekeeping during transitions.
| 4. Why do some clocks lose or gain time, and how can this be fixed? |  |
Ans. Clocks may lose or gain time due to factors like mechanical wear, temperature changes, or power supply issues in digital clocks. To fix this, ensure that the clock is properly maintained, batteries are replaced regularly, and for mechanical clocks, periodic servicing is recommended. Additionally, adjusting the time manually when discrepancies are noticed can help keep the clock accurate.
| 5. What are the key components of a clock mechanism? |  |
Ans. A typical clock mechanism consists of several key components, including a power source (like a battery or mainspring), gears that transfer energy and regulate movement, an escapement that controls the release of energy at a consistent rate, and hands that display the time. In digital clocks, an electronic circuit replaces many mechanical parts to keep time accurately.
Related Searches




















