Light Shadow and Reflections Class 6 Worksheet Science
Q1: Fill in the blanks
i. The sun is a source of light.
Ans: natural
ii. Light is a form of .
Ans: energy
iii. A shadow is in color.
Ans: black

iv. Candles, oil lamps and earthen lamps are sources of light.
Ans: man-made
v. An image has the of the object.
Ans: color
vi. A highly polished furniture acts like a .
Ans: mirror
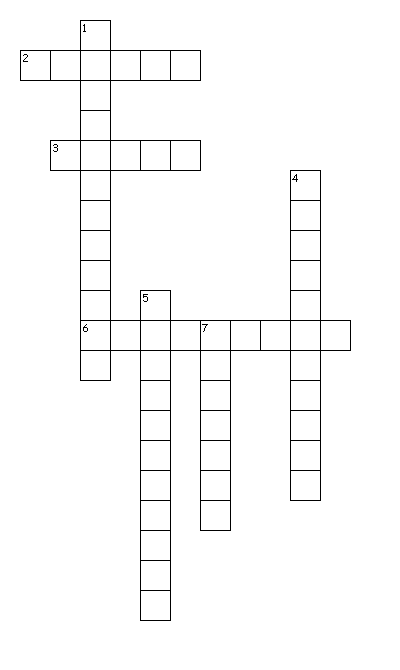
Q2: Crossword
Across
2. These objects does not allow light to pass through them
3. it travels in straight line
6. it is a device to see hidden corners
Down
1. This device uses reflection to create beautiful picture
4. These objects allows light to pass fully
5. These objects allow the light to pass partially
7. It is formed when opaque objects come in the path of light
Ans:
1. Kaleidoscope
2. opaque
3. Light
4. Transparent
5. translucent
6. periscope
7. Shadows
Q3: True or False
i. Any non-luminous body can be made luminous by heating it.
Ans: True
Yes, you can make a non-luminous object luminous by heating it to a high enough temperature.
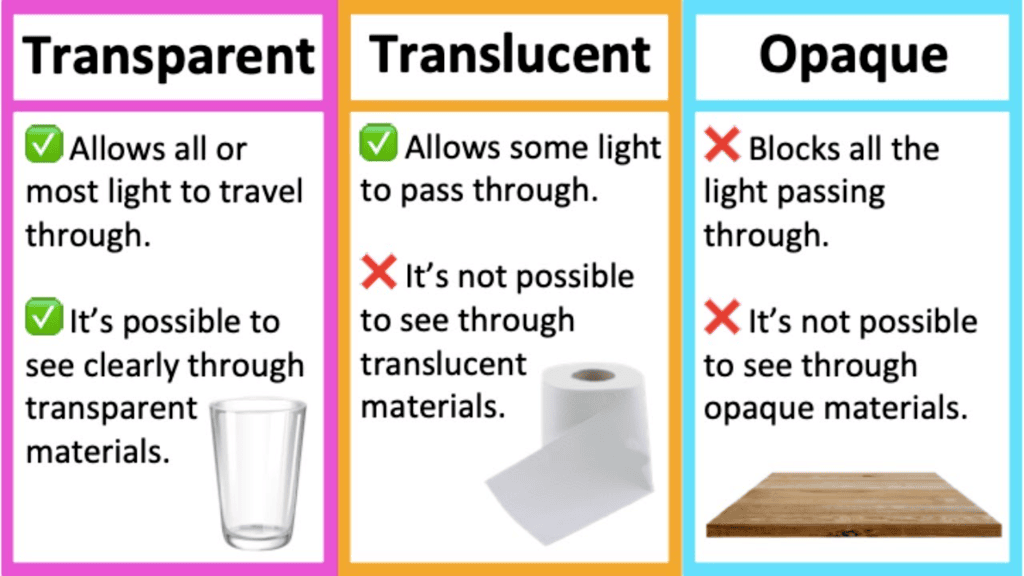
ii. Any material through which light energy pass partially or wholly is called an opaque object.
Ans: False
Materials that allow light to pass partially or wholly are called translucent or transparent, not opaque.
iii. A cardboard is an example of an opaque object.
Ans: True
Cardboard does not allow light to pass through it, so it is opaque.
iv. Glass is a transparent object.
Ans: True
Glass allows light to pass through completely, so it is transparent.
Answer the following
Q4: What is a luminous object?
Ans: A luminous object is something that produces its own light, such as the Sun, a lamp, or a torch. These objects emit light that helps us see them and other objects around them.
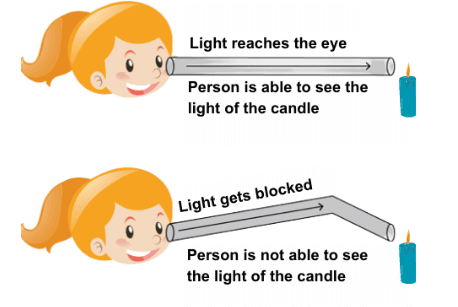
Q5: What happens to light when it hits an opaque object?
Ans: When light hits an opaque object, it cannot pass through the object. Instead, the light is blocked, and a shadow is formed on the other side of the object where the light is prevented from reaching.
Q6: Can you see objects in total darkness?
Ans: No, in complete darkness, you cannot see objects because there is no light to reflect off them and reach your eyes. Light is necessary for visibility.
Q7: What kind of object allows all light to pass through it?
Ans: A transparent object allows all light to pass through it completely, making it possible to see clearly through the object, like clear glass or water.
Q8: How do shadows change with the position of the light source?
Ans: Shadows change in size and shape depending on the angle and distance of the light source. For example, a shadow might be long and narrow when the light source is low and close but short and wide when the light source is high and far away.
Q9: What is an example of a translucent object?
Ans: An example of a translucent object is frosted glass. It allows some light to pass through, but the light is scattered, so objects on the other side are not clearly visible.
Q10: Why do we see reflections in a mirror?
Ans: We see reflections in a mirror because mirrors have a smooth surface that reflects light back to us. This reflection allows us to see a clear image of whatever is in front of the mirror.
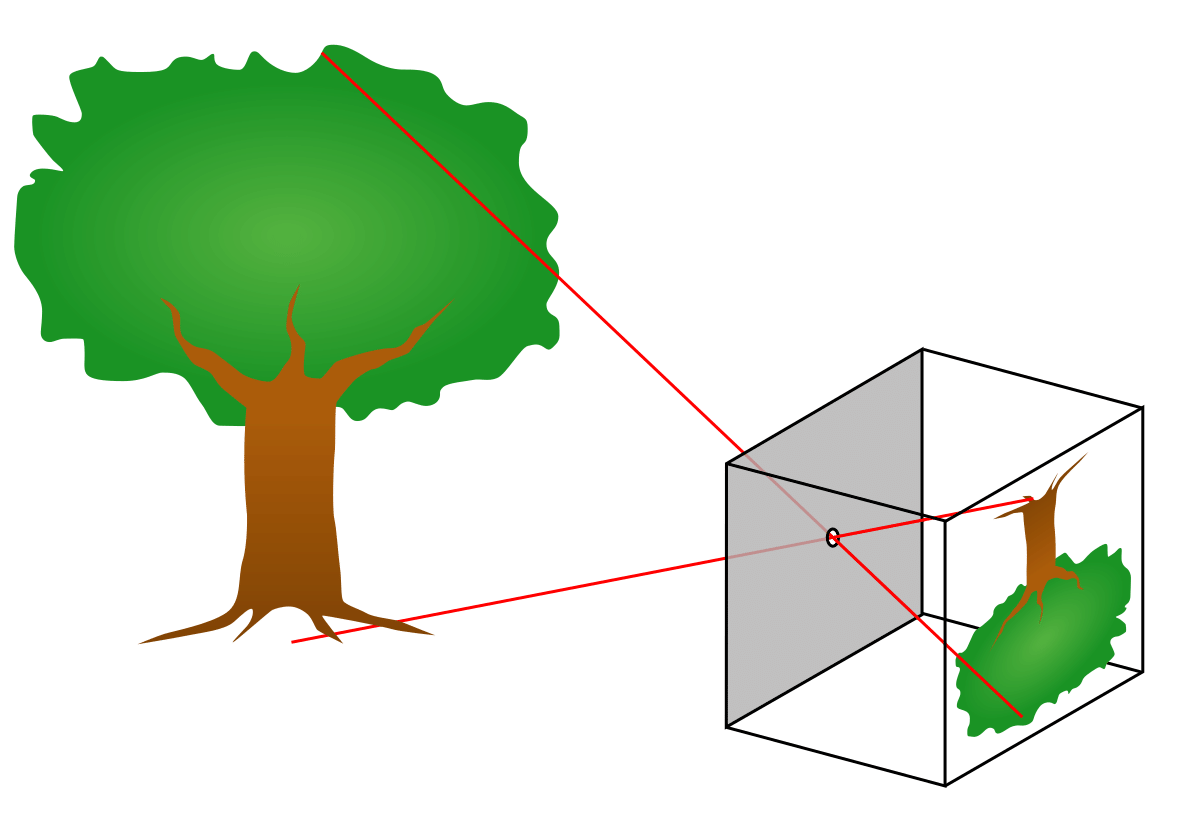
Q11: What is a pinhole camera used for?
Ans: A pinhole camera is used to project an image onto a screen using a small hole to let light in. The image appears inverted on the screen. It's a simple way to understand how images are formed.
Q12: Can a shadow be seen without a screen?
Ans: No, a shadow requires a surface or screen to be visible. The shadow itself is the absence of light, so it only becomes visible when it falls on a surface that can catch and display the shadow’s shape.
Q13: What does the color of a shadow depend on?
Ans: The color of a shadow is not affected by the color of the object casting it. Instead, shadows appear as shades of gray or black, depending on the intensity and angle of the light source and the opacity of the object.
Q14: Why does a pinhole camera produces an inverted (upside down) image?
Ans: A pinhole camera produces an inverted image because light travels in straight line.
Q15: What do you understand by rectilinear propagation of light?
Ans: The light travels in straight line. This phenomenon is called the rectilinear propagation of light.
Q16: What is a reflector? Give one example.
Ans: A surface which reflects the light is called reflector. Example: Plane mirror.
Q17: Why do polished surfaces cause glare in our eyes?
Ans: Polished surface produces regular reflections which causes glare in our eyes.
Assertion and Reason Questions
Q22: Assertion (A): When we look into the mirror, we see our own face inside the mirror.
Reason (R): Mirror is made of a transparent substance that allows the light to pass through it.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans: (c)
Assertion (A) is true because we see our own face in the mirror. However, Reason (R) is false because mirrors are not made of transparent substances; they have a reflective coating that bounces light back to us.
Q23: Assertion (A): In cars the windshields made of glass are used.
Reason (R): Those substances through which things can be seen clearly are called transparent substances.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans: (b)
Assertion (A) is true because car windshields are made of glass. Reason (R) is also true because transparent substances allow us to see clearly through them. However, the reason given is not the explanation for why glass is used in windshields; the reason is that glass is durable and provides safety.
Q24: Assertion (A): When the light from a source falls on a mirror it gets reflected.
Reason (R): On being reflected there is no change in the direction of light.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans: (c)
Assertion (A) is true because light does get reflected when it hits a mirror. However, Reason (R) is false because the direction of light does change when it is reflected. It changes direction according to the angle of incidence.
Q25: Assertion (A): Image has the colour of the object.
Reason (R): Image gives only the outline of the object.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans: (c)
Assertion (A) is true because an image reflects the color of the object. Reason (R) is false because an image shows more than just the outline of the object; it shows details, colors, and shapes.
Q26: Assertion (A): Mirror reflection gives clear images.
Reason (R): Images are quite similar to shadows.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans: (c)
Assertion (A) is true because mirrors provide clear images. Reason (R) is false because mirror images are different from shadows; shadows are often blurry and lack detail, whereas mirror images are clear and detailed.
FAQs on Light Shadow and Reflections Class 6 Worksheet Science
| 1. What is a shadow? |  |
| 2. How does light travel? |  |
| 3. What is reflection of light? |  |
| 4. How are shadows formed? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of reflections? |  |