Class 8 Science Question Answers - Stars and the Solar System (Old Syllabus)
Q. 1. Differentiate between stars and planets.
Ans.
Stars | Planets |
(i) Stars twinkle in the sky. (ii) They are fixed at a point. (iii) They have their own light. (iv) They are very big in size. | (i) Planets do not twinkle in the sky. (ii) They revolve around the sun. (iii) They have no light. (iv) Planets are small as compared to star. |
Q. 2. Why can we not hear any sound on the moon?
Ans. Moon is a natural satellite of the earth. It revolves around the earth. But there is no medium on the moon. There is no air on the surface of the moon. Sound travels with the help of any medium. Without the medium it cannot travel from one place to other. So we do not hear any sound on the surface of the moon.
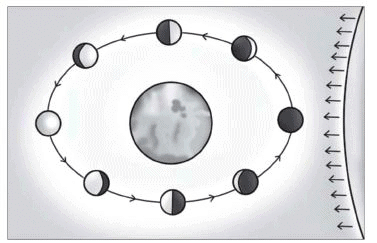
Q. 3. What do you know about the phases of the moon? Why do phases of the moon occur?
Ans. The various shapes of the bright part of the moon as seen during a month are called phases of the moon. The moon does not produce its own light. Whereas the sun and other stars do. We see the moon because the sunlight falling on it is reflected towards us. We therefore see only that part of the moon from which the light of the sun is reflected towards us. The moon revolves around the earth so its position changes every day. The moon appears different at different positions. So the phases of the moon occur.
Q. 4. What is the sun? Name the next nearest star. What is the distance of the sun from the earth? Write the unit of the large distances.
Ans. Sun is the nearest star. It also emits light just like the other stars. The next nearest star is Alpha Centauri. The sun is nearly 150 million km away from the earth. Such large distances are expressed in another unit called light year. The distance travelled by light in one year is called light year. The speed of light is about 300000 km per second. Thus the distance of the sun may be said to be about 8 light minutes.
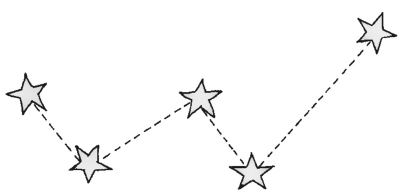
Q. 5. What are constellations? Explain some common constellations.
Ans. The group of stars that has a recognizable shape is called constellation.
Some common constellations are:
(i) Ursa Major: It appears during summer time in the early part of the night. It is also known as Big Dipper or Great Bear or the Saptarshi. There are seven prominent stars in this constellation. It appears like a big ladle or a question mark.
(ii) Orion: This constellation can be seen during winter in the late evenings. It has seven or eight bright stars. Orion is also called the hunter.
(iii) Cassioplia: It is the most common or prominent constellation in the northern sky. It is visible during winter in the early part of the night. It looks like a distorted letter W or M.
Q. 6. What is Pole star? How do you locate the position of Pole star?
Ans. Pole star is the star in the sky which appears stationary and does not move like other stars. It is situated above the north pole of the earth.
Look at the two stars at the end of Ursa Major. Imagine a straight line passing through these stars. Extend this line towards north direction. This line will lead to a star called Pole star.
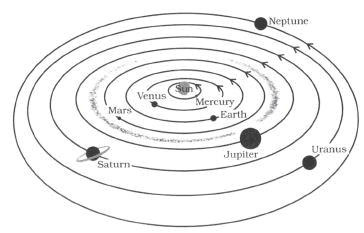
Q. 7. Explain the solar system.
Ans. The sun and the celestial bodies which revolve around it form the solar system. It consists of a large number of bodies such as planets, comets, asteroids and meteors. The gravitational attraction between the sun and these objects keeps them revolving around it. Our earth is also a planet which revolves around the sun. It is also a member of the solar system. There are seven other planets that revolve around the sun. The eight planets are: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
Q. 8. Explain the following terms:
(a) Asteroids
(b) Comets
(c) Meteors
(d) Meteorites.
Ans. (a) Asteroids: There is a gap between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. This gap is occupied by a large number of small objects that revolve around the sun. These small objects are called asteroids.
(b) Comets: Comets are also small bodies which revolve around the sun in highly elliptical orbits. They become visible from the earth only when they come closer to the sun. They are characterised by a small head followed by a long tail.
(c) Meteors: The very small stone like objects are called meteors. They are commonly known as shooting stars, although they are not stars. The meteor occasionally enters the earth’s atmosphere. Due to friction it heats up. It glows and evaporates quickly.
(d) Meteorites: The portion of meteor which does not burn during its fall through the earth’s atmosphere and hits the ground is called a meteorite.

Q. 9. What are planets? Explain them.
Ans. The bodies which revolve around the sun in a certain orbit are called planets. There are following eight planets:
(i) Mercury: The planet Mercury is nearest to the sun. It is the smallest planet of the solar system. It has no satellite of its own.
(ii) Venus: Venus is earth’s nearest planetary neighbour. It is the brightest planet in the night sky. Venus has no moon or satellite of its own.
(iii) Earth: It is the third planet.
The earth is the only planet in the solar system on which life exists. Earth appears blue green due to the reflection of light from water and landmass. It has only one moon.
(iv) Mars: The fourth planet is called Mars. It is called the red planet. Mars has two small satellites.
(v) Jupiter: It is the largest planet of the solar system. It is so large that about 1300 earths can be placed inside this giant planet. It has a large number of satellites.
(vi) Saturn: Beyond Jupiter is Saturn, which appears yellowish in colour. It contains beautiful rings which are not visible with naked eyes.
(vii) Uranus: It is the seventh planet. It is the second outermost planet.
(viii) Neptune: The outermost planet is called Neptune.
Q10: The radius of Jupiter is 11 times the radius of Earth. Calculate the ratio of volumes of Jupiter and the Earth.
Ans. Given that radius of jupiter is 11 times the radius of Earth
Volume of the sphere = 4/3 πr3 where r is radius.
Let RE = radius of Earth
And RJ = Radius of Jupiter
Given RJ =11 * RE
Volume of Jupiter = 4/3 πr3 J = 4/3π (11RE)3 = 1331Re
Therefore, the ratio of volume of jupiter to volume of earth is 1331.
|
80 videos|359 docs|87 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science Question Answers - Stars and the Solar System (Old Syllabus)
| 1. What is a star? |  |
| 2. How are stars formed? |  |
| 3. What is the Solar System? |  |
| 4. How do we measure the distance between stars? |  |
| 5. Can stars die? |  |





















