Q. 1. What is soil erosion? Explain the formation and distribution of Ravine in India?
Ans. SOIL EROSION Causes of soil erosion—So long a cause of soil erosion balance exists between the processes of soil formation and soil erosion, there is no problem. When the balance is disturbed, the soil erosion becomes a menace. Indiscriminate felling of trees, careless overgrazing of pasture lands, unscientific drainage operations and improper land use are some of the important causes which upset this balance. Soil erosion has been a problem in West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra. Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Delhi, Rajasthan and many other parts of India. Excessive grazing by cattle on the slopes of hills cause rapid soil erosion. Potato cultivation in Meghalaya and in the Nilgiri hills, clearing of forests in the Himalayas and on the Western Ghats, and jhuming by the tribal population in different parts of the country have resulted in considerable depletion of the soils.
Ravines.
(1) Ravines are wide spread in the Chambal basin. They cover over 6 lakh hectares of land in Gwalior, Morena and Bhind districts of Madhya Pradesh, and Agra, Etawah and Jalaun districts of Uttar Pradesh.
(2) In Tamil Nadu, ravines are common in South Arcot, North Arcot, Kanniyakumari, Tiruchirapalli, Chingleput, Salem and Coimbatore districts.
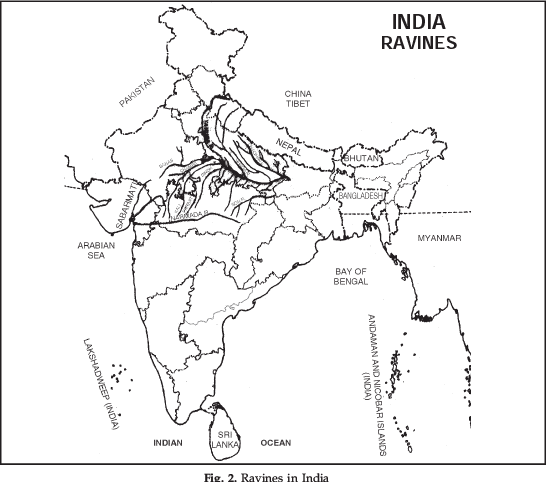
(3) In West Bengal numerous gullies and ravines exist in the upper catchment areas of the Kangsabati river in Purulia district. The country is losing about 8,000 hectares to ravines every year.
III Effects of Soil Erosion.
(1) It is estimated that over 80,000 hectares of cultivated land of India have already been lost and a much larger area is rendered less productive by soil erosion every year.
(2) Soil erosion is a national menace for the Indian agriculture and its bad effects are seen in other spheres also.
(3) Eroded materials are carried down to rivers and they lower down their carrying capacity, and cause frequent floods and damage to agricultural lands.
(4) The bed of the Kaveri river in Tiruchirapalli and Tanjavur districts of Tamil Nadu, for example, has gradually risen and many of the old irrigation sluices and drainage inlets have got blocked. The shallowing of the Brahmaputra causes flood every year.
(5) Silting of tanks is another serious consequence of soil erosion. A large number of tanks in different parts of the country get silted every year.
Types of Soil Erosion. The two most active agents of soil erosion in India are wind and running water. Wind erosion is common in arid and semiarid areas of Gujarat, Rajasthan and Haryana. Light soils are more susceptible to wind erosion than heavier soils. Sands removed by wind spread over adjoining cultivated lands and destroy their fertility. Water erosion which is more serious and occurs extensively in different parts of India takes place mainly in the form of sheet and gully erosion. Sheet erosion takes place on level lands after heavy shower and the soil removal is not easily noticeable. Gully erosion is common on steep slopes. Gullies deepen with rainfall, cut the agricultural lands into small fragments and make them unfit for cultivation. Several factors contribute to soil deterioration.
For example, when the forests are cut, the supply of humus to the soil stops, and the capacity of running water to remove its top layer grows. If drainage system is disturbed, water logging or loss of soil moisture takes place; and if it is overused, it loses its fertility. The removal of the soil by running water in wet areas and wind in dry areas is referred to as soil erosion and the removal of its organic and mineral content is referred to as soil exhaustion. Soil degradation results from its misuse.
Q. 2. What is Soil Erosion? In what different ways does it occur?
Ans. Soil Erosion. It is the destruction and removal of top soil by running water, wind, etc. Soil erosion has become a serious problem in many areas. Soil formation is a slow process and takes thousands of years to develop soil, but it may be removed in a matter of a few years. Soil erosion results from the following causes :
Causes of Soil Erosion :
(1) Steep slopes. Steep slopes affect the rapidity of running water. On steep slopes, intensity of soilerosion increases.
(2) Torrential rainfall. Heavy rainfall loosens the soil particles and scoops out the soil forming gullies and ravines. This gives rise to a dissected surface called badland as in Chambal Valley of India.
(3) Strong winds. Winds and dust storms blow away soil in dry areas. This process is known as deflation.
(4) Over-grazing. Due to over-grazing, the vegetation becomes too thin to protect the soil. Rain and wind can easily erode the loose soil.
(5) Over-cropping. Crop rotation maintains soil fertility. But over-cropping and shifting cultivation renders soil infertile.
(6) Deforestation. Deforestation means the removal of forest cover and it exposes the area to soil-erosion. Reckless cutting of trees has resulted in soil erosion by chos along the Siwalik hills. Human misuse of the land through wrong farming practices, deforestation, etc. leads to the removal of soil cover.
Q. 3. Which types of soils are derived from Deccan Lavas? Describe three important characteristics of these soils.
Ans. Black soils or Regur soils are derived from Deccan Lavas. These are called cotton soils also. The three important characteristic of these soils are : Black soils are mainly found over the Deccan Lava tract including Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh. These soils have been formed due to weathering of lava rocks. These soils cover an area of about 5 lakh sq. km. These soils are rich in lime, iron, magnesia and alumina. But these lack in phosphorous, nitrogen and organic matter. These are called ‘Regur Soils’. These soils are most suitable for cotton cultivation and are known as ‘Black Cotton Soils’.






















