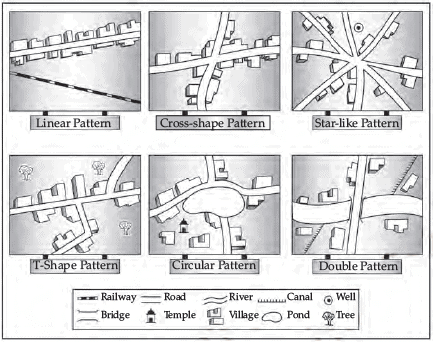
Q. 1. Name any five types of rural settlement patterns developed in different parts of the world. Write their typical features.
OR
Describe any five patterns of rural settlements in the world on the basis of forms or shapes.
OR
Explain any five patterns of rural settlements in the world with the help of suitable diagrams.
OR
Classify rural settlements pattern on the basis of forms or shapes.
Ans. Rural Settlement types on the basis of forms or shapes:
(a) Linear pattern
(b) Rectangular pattern
(c) Circular pattern
(d) Star-like pattern
(e) T-shaped, Y-shaped or Cross-shaped pattern
(f) Double village pattern
(Explain any five points and draw a suitable diagram)
(Detailed Answers:
(a) Linear pattern:
(i) In such settlements, houses are located along a road, railway line, river or a canal edge.
(ii) These types of settlements have two parallel rows of houses facing each other.
(b) Rectangular pattern:
(i) In such pattern, roads cut each other at right angle. These pattern can be seen in plain areas.
(ii) Such villages develop at the meeting place of two roads.
(c) Circular pattern:
(i) When the houses are constructed along a bank of a pond or a lake, the settlement takes the shape of circle and is known as circular pattern.

(d) Star-like pattern:
(i) In this pattern, several roads converge star-shaped settlements develop by houses build along the roads radiating from a common centre.
(e) T-shaped pattern, Y-shaped pattern, cruciform settlements:
(i) Such pattern develops at tri-junction of roads (T), while Y-shaped settlements emerge at the places where two roads converge on the third one and houses are built along these roads.
Cruciform settlements develop on the cross-roads and houses extend in all the four directions.
(ii) Villages and towns confined between two rivers at their junction or confluence or between bifurcations of two roads eventually results in a T-shaped pattern.
(f) Double village pattern:
(i) These settlements extend on both sides of a river where there is a bridge or a ferry.
Q. 2. Explain any five factors responsible for the location of rural settlements in the world.
OR
Explain any five factors that affect the location of rural settlements of the world.
Ans. The following factors are responsible for the location of rural settlements in the world:
(i) Water Supply: Usually rural settlements are located near water bodies such as rivers, lakes, and springs where water can be easily obtained. Most water-based ‘wet point’ settlements have many advantages such as water for drinking, cooking and washing. Rivers and lakes can be used to irrigate farm land.
(ii) Land: People choose to settle near fertile lands suitable for agriculture. In Europe, villages grew up near rolling country avoiding swampy, low lying-land while people in South-east Asia chose to live near low-lying river valleys and coastal plains suited for wet rice cultivation.
(iii) Upland: Upland which is not prone to flooding was chosen to prevent damage to houses and loss of life. Thus, in low-lying river basins people chose to settle on terraces and levees which are “dry points.”
(iv) Building Material: The availability of building materials—wood, stone near settlements is another advantage. Early villages were built in forest clearings where wood was plentiful.
(v) Defence: During the times of political instability, war, hostility of neighbouring groups—villages were built on defensive hills and islands.
Q. 3. Classify the human settlements of the world into two types by their shape. Explain any two features of each type.
OR
What is settlement? Classify settlements of the world on the basis of their shapes into two categories. Mention any three characteristics of each.
OR
What are rural settlements? What are the two types of rural settlements in the world? How are they different from each other? Give three points of distinction.
Ans. A human settlement is defined as a place inhabited more or less permanently. It includes buildings in which they live or use and paths and streets over which they travel. It also includes the temporary camps of the hunters and herders. It may consist of only a few dwelling units called hamlets or a huge cluster of buildings called urban cities. Settlements can also be classified on the basis of shape and pattern into:
(i) Compact settlements:
(a) In such settlements, the houses are built very near to each other.
(b) These settlements are usually found near river valleys and plains.
(c) The people living in such settlements share close bonds and common occupations.
(ii) Dispersed settlements:
(a) In such settlements the houses are built far away from each other.
(b) The main attraction of these settlements are the religious places such as a church or a temple which binds the settlement together.
(c) Such types of settlements are found at hills, plateau and highlands.
Q. 4. Compare the cities of developed and developing countries of the world. Explain various functions of urban centres.
Ans. Majority of the cities in the developed countries are well-planned and have well laid out shapes whereas, the cities of the developing countries are not well laid out; they grow haphazardly. The cities in the developed countries have easy access to basic amenities such as clean drinking water, sewerage, electricity, health care services, public transport, etc., whereas, those in developing countries are deprived of such facilities. Moreover, the cities in the developed countries are pollution free as compared to cities in the developing countries which are marked by population congestion.
On the basis of the functions, the towns and cities can be classified into the following categories: Administrative towns : National capitals, which house the administrative offices of central governments, such as New Delhi, Canberra, Beijing, Addis Ababa, Washington D.C., London, etc. are called administrative towns. Provincial (sub-national) towns can also have administrative functions, for example, Victoria (British Columbia), Albany (New York), Chennai (Tamil Nadu).
Trading and commercial towns : Agricultural market towns such as Winnipeg and Kansas city; banking and financial centres like Frankfurt and Amsterdam; large inland centres like Manchester and St Louis; and transport nodes such as, Lahore, Baghdad and Agra have been important trading centres.
Cultural towns: Places of pilgrimage, such as Jerusalem, Mecca, Jagannath Puri and Varanasi, etc., are considered cultural towns. These urban centres are of great religious importance.
Additional functions which the cities perform are health and recreation (Miami and Panaji), industrial (Pittsburgh and Jamshedpur), mining and quarrying (Broken Hill and Dhanbad) and transport (Singapore and Mughal Sarai).
Q. 5. Describe any five patterns of rural settlements of the world, on the basis of their shape.
Ans. Patterns of rural settlements:
(i) On the basis of setting: The main types are:
(a) Plain villages
(b) Plateau villages
(c) Coastal villages
(d) Forest villages
(e) Desert villages
(ii) On the basis of functions, There may be:
(a) Farming villages
(b) Fishermen’s villages
(c) Pastoral villages
(iii) On the basis of forms and shapes of the settlements:
(a) Linear pattern: In such settlements houses are located along a road, railway line, river, edge of a canal, etc.
(b) Rectangular pattern: Such patterns are common in the plains or wide inter montane valleys. The roads cut each other at right angles.
(c) Circular pattern: Circular villages develop around lakes, tanks.
(d) T-shaped settlements: These settlements are formed near the tri-junctions of the roads.
(e) Star-like pattern: Such settlements are developed by the houses built along the roads. Several roads converge here.
(f) Double village: Such settlements extend on both sides of a river where there is a bridge or a ferry.
Q. 6. What are rural and urban settlements? Mention their characteristics.
Ans. Rural settlements are dominated by primary activities such as agriculture, animal husbandry, fishing, etc. The settlements size is relatively small.
Usually rural settlements are located near water bodies such as rivers, lakes, and springs where water can be easily obtained.
The following are the characteristics of rural settlements in the world:
(i) Water Supply: Usually rural settlements are located near water bodies such as rivers, lakes, and springs where water can be easily obtained. Most water-based ‘wet point’ settlements have many advantages such as water for drinking, cooking and washing. Rivers and lakes can be used to irrigate farm land.
(ii) Land: People choose to settle near fertile lands suitable for agriculture. In Europe villages grew up near rolling country avoiding swampy, low lying land while people in South-east Asia chose to live near low lying river valleys and coastal plains suited for wet rice cultivation.
(iii) Upland: Upland which is not prone to flooding was chosen to prevent damage to houses and loss of life. Thus, in low lying river basins people chose to settle on terraces and levees which are “dry points.”
(iv) Building Material: The availability of building materials—wood, stone near settlements is another advantage. Early villages were built in forest clearings where wood was plentiful.
(v) Defence: During the times of political instability, war, hostility of neighbouring groups, villages were built on defensive hills and islands. The definition of urban settlements varies from one country to another. Urban settlement is a human settlement with high population density and infrastructure of build environment.
Some of the characteristics of urban settlements are :
(i) Population size: It is an important criterion used by most of the countries to define urban areas. The lower limit of the population size for a settlement to be designated as urban is 1,500 in Colombia, 2,000 in Argentina and Portugal, 2,500 in USA, etc.
(ii) Occupational structure: In come countries, such as India, the major economic activities in addition to the size of the population is designating a settlement as urban are also taken as a criterion.
(iii) Administration: The administration setup is a criterion for classifying a settlement as urban in some countries. For example, in India, a settlement of any size is considered urban, if it has a municipality, Cantonment Board or Notified Area Council.
(iv) Location: Location of urban centres is examined with reference to their function. For example, the sitting requirements of a holiday resort are quite different from that of an industrial town, a military centre or seaport. Location of earlier urban settlements were based on the availability of water, building materials and fertile land. Today while these considerations remain valid, modern technology plays a significant role in locating urban settlements far away from the source of these materials.
Q. 7. Explain factors which affect the location of rural settlements in the world.
Ans. Factors: (i) Water Supply: Rural settlements are located near water bodies such as river, lakes and springs where water can be easily obtained.
(ii) Land: Fertile lands suitable for agriculture are the most suitable
(iii) Upland: People settles on upland because it is not prone to flooding to prevent damage to houses and loss of life. In low lying river basin, people chose to settle on terraces and levees which are dry points.
(iv) Building Material: People settle at places where building materials such as wood or stones are available.
(v) Defence: Villages and forts were built on hills and islands. So that people may defend themselves in case of war or attack by the enemy.
Planned Settlement: Sometimes planned settlements are constructed by government by providing shelter, water and other infrastructure to the village people.
Q. 8. Classify urban settlements on the basis of size, functions and services available into five categories and explain an important characteristic of each type.
Ans. Depending on the size, functions and the service available, urban settlements are designated as towns, city, million city, conurbation and megalopolis.
(i) Towns: Population size in town is higher than the village. Functions such as manufacturing, retail and wholesale trade and professional services exist in towns.
(ii) City: A city may be regarded as a leading town. Cities are much larger than towns and have a greater number of economic functions. They tend to have transport terminals, major financial institutions and regional administrative offices. When the population crosses one million mark it is designated as a million city.
(iii) Million City: The city having more than million population is known as million city. The number of these types of cities in the world have been increasing as never before.
(iv) Conurbation: The term ‘conurbation’ was introduced by Patrick Geddes in 1915 and applied to a large area of urban development resulted from the merging of originally separate towns or cities. Greater London, Greater Mumbai, Manchester, Chicago are some of the examples.
(v) Megalopolis: This Greek word meaning ‘great city’ was popularised by Jean Gottmann(1957) and signifies ‘super metropolitan’ region extending union of conurbations. The urban landscape stretching from Boston in the North to Washington in the South of USA is the best examples of megalopolis.
Q. 9. Shortage of housing and growth of slums—major problems of urban settlements in developing countries. Explain.
OR
Discuss the problems associated with urban settlements in developing countries.
Ans. Shortage of housing and growth of slums—major problems of urban settlements:
(i) People flock to cities to avail of employment opportunities and civic amenities.
(ii) Urban settlement creates severe congestion.
(iii) There is shortage of houses.
(iv) Growth of slums is a common feature.
(v) People live in sub-standard hutments and shanties.
(vi) The unplanned growth of urban settlements defaces the beauty of the cities.
(vii) In most million plus cities in India, one in four inhabitants lives in illegal settlements. (viii) In the Asia Pacific countries, around 60 per cent of the urban population lives in squatter settlements.
Detailed Answer:
(i) People flock to cities to avail of employment opportunities and civic amenities: People from rural areas move to urban areas in search of greener pastures. This huge gush or inflow of migrants leads to lack of accommodation.
(ii) Urban settlement creates severe congestion: The inflow of migrants leads severe accommodation crunch and this forces the mushrooming up of illegal construction without any proper planning.
(iii) There is shortage of houses: Due to the inflow of huge migration rush there crops up shortage of proper housing and planning.
(iv) Growth of slums is a common feature: Growth of unplanned and haphazard construction with lack of proper sanitation and hygiene facilities crops up at the outskirts of the cities.
(v) People live in substandard hutments and shanties: The substandard hutments and shanties are called slums.
(vi) The unplanned growth of urban settlements defaces the beauty of the cities: The slums led to spread to diseases and filth all over.
(vii) In most million plus cities in India, one in four inhabitants lives in illegal settlements: One of the biggest examples of this is the slums of Dharavi, Mumbai.
(viii) In the Asia Pacific countries, around 60 per cent of the urban population lives in squatter settlements: These settlements lack in basic hygiene and sanitation facilities and are prone to outbreack of diseases.
Q. 10. Explain any two socio-cultural and any three environmental problems of urban settlements of the world.
Ans. Socio-cultural problems: (i) Inadequate social infrastructure and basic facilities is due to lack of financial resources and overpopulation in the cities.
(ii) The available educational and health facilities remain beyond the reach of the urban poor.
(iii) Cities suffer from poor health conditions.
(iv) Lack of employment and education tends to aggravate the crime rates.
(v) Male selective migration to the urban areas distorts the sex-ratio in these cities. (Any two)
Environmental problems:
(i) The large urban population in developing countries uses and disposes off a huge quantity of water and all types of waste materials.
(ii) Many cities of the developing countries do not provide the minimum required quality of drinkable water and water used for industrial and domestic use.
(iii) An improper sewerage system creates unhealthy conditions.
(iv) Massive use of traditional fuel in the domestic as well as the industrial sector severely pollutes the air.
(v) The domestic and industrial wastes are either let into the general sewerage or dumped without treatment at unspecified locations.
(vi) Huge concrete structures of buildings create heat in city environment.
Q. 11. How are rural settlements facing different types of problems in the developing countries? Explain any five major problems.
OR
Analyse any five problems of rural settlements of developing countries in the world.
OR
Explain any five problems of rural settlements in the developing countries of the world.
OR
What are the problems of rural settlements in developing countries?
Ans. Problems faced by the developing countries:
(i) House shortage: Since most cities in developing countries are unplanned, it creates severe congestion. Shortage of housing, vertical expansion and growth of slums are characteristic features of modern cities of developing countries.
(ii) Economic problems: The decreasing employment opportunities in the rural as well as smaller urban areas of the developing countries consistently push the population to the urban areas. The enormous migrant population generates a pool of unskilled and semi-skilled labour force, which is already saturated in urban areas.
(iii) Socio-cultural problems: Cities in the developing countries suffer from several social ills. Insufficient financial resources fail to create adequate social infrastructure catering to the basic needs of the huge population.
(iv) Poor education and health facilities: The available educational and health facilities remain beyond the reach of the urban poor. Health indices also, present a gloomy picture in cities of developing countries. Lack of employment and education tends to aggravate the crime rates.
(v) Environmental problems: The large urban population in developing countries not only uses but also disposes off a huge quantity of water and all types of waste materials. An improper sewerage system creates unhealthy conditions. Massive use of traditional fuel in the domestic as well as the industrial sector severely pollutes the air. The domestic and industrial wastes are either let into the general sewerages or dumped without treatment at unspecified locations.
Q. 12. Explain the nature of rural settlements. Describe any four problems related to rural settlements of the world.
Ans. Rural settlements are most closely and directly related to land. People are generally engaged in primary activities such as agriculture, animal husbandry, fishing etc. The settlement size is relatively small. The problems related to the rural settlements of the world are mentioned below:
Water Supply: Water supply is not adequate. People, particularly in mountainous and arid regions have to walk long distances to fetch drinking water.
Waterborne diseases: Cholera and jaundice are the common diseases which break out in villages.
Drought and Floods: The countries of South Asia face conditions of drought and floods very often. Crop cultivation sequences, in the absence of irrigation, also suffer.
Health Problems: The general absence of toilets garbage disposal facilities causes health-related problems. (Any other relevant point)