MCQ (Solution) - Sound | Science Class 8 PDF Download
Q1: What is the primary cause of sound production?
(a) Heat
(b) Light
(c) Vibration
(d) Electricity
Correct Answer is Option (c)
- The primary cause of sound production is vibration.
- When an object vibrates, it causes the air particles around it to move back and forth, creating sound waves that travel to our ears.
- For example, when you pluck a guitar string, it vibrates and produces sound.
- Without vibration, no sound can be created.
Vibration of Air Particles
Q2: What is the role of the larynx in sound production by humans?
(a) Filtering sound
(b) Controlling amplitude
(c) Producing sound
(d) Enhancing pitch
Correct Answer is Option (c)
- The larynx, also known as the voice box, plays a crucial role in sound production in humans.
- It contains the vocal cords, which vibrate when air passes through them, producing sound.
- The tension and length of the vocal cords determine the pitch and tone of the sound.
- Hence, the primary function of the larynx is to produce sound.
Larynx
Q3: In which medium does sound travel the fastest?
(a) Solids
(b) Liquids
(c) Gases
(d) Vacuum
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- Sound travels the fastest in solids because the particles in solids are packed very closely together.
- This makes it easier for vibrations (which create sound) to pass from one particle to the next.
- In comparison, particles in liquids and gases are farther apart, so sound travels more slowly.
- In a vacuum, there are no particles, so sound cannot travel at all.
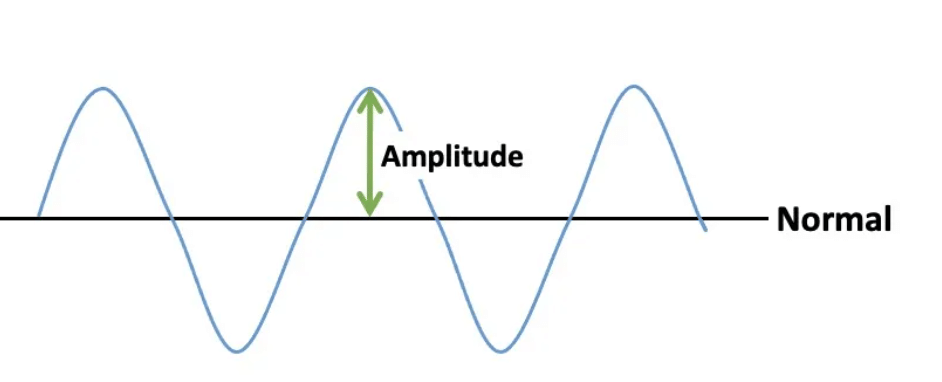
Q4: What characteristic determines the loudness of a sound wave?
(a) Amplitude
(b) Frequency
(c) Time period
(d) Propagation speed
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- The loudness of a sound wave depends on its amplitude.
- Amplitude is how big the wave is or how far the particles of the medium move from their resting position.
- A larger amplitude means the sound is louder, while a smaller amplitude means the sound is softer.
Q5: What is the unit of frequency?
(a) Watts
(b) Hertz
(c) Decibels
(d) Newton
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- The unit used to measure frequency is called hertz (Hz).
- One hertz means one cycle happening in one second.
- It is named after Heinrich Hertz, a German scientist who greatly advanced the study of electromagnetism and waves.
Q6:What is the range of audible sound for humans?
(a) 5 Hz to 50,000 Hz
(b) 10 Hz to 100,000 Hz
(c) 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz
(d) 15 Hz to 30,000 Hz
Correct Answer is Option (c)
- The range of audible sound for humans typically falls between 20 hertz (Hz) and 20,000 Hz.
The lower limit of 20 Hz represents the lower threshold of human hearing, while the upper limit of 20,000 Hz represents the higher threshold.
Q7: The minimum distance from a sound-reflecting surface required to hear an echo is:
(a) 10 meters
(b) 17 meters
(c) 20 meters
(d) 34 meters
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- An echo is heard when sound reflects off a surface and comes back to our ears.
- For the echo to be clear and distinct, the reflected sound must take enough time to reach our ears after the original sound.
- This happens only if the surface is at least 17 meters away.
- If the distance is less, the reflected sound mixes with the original sound, and no distinct echo is heard.
Q8: What health problems can be caused by noise pollution?
(a) Improved sleep
(b) Enhanced concentration
(c) Hypertension
(d) Increased hearing ability
Correct Answer is Option (c)
- Noise pollution has been associated with an increased risk of hypertension, and several mechanisms may contribute to this relationship.
- Prolonged exposure to high levels of noise can activate the body's stress response, leading to physiological changes that may contribute to hypertension.
Hypertension Disorder
Q9: Infrasound can be produced by –
(a) whales
(b) dolphins
(c) bats
(d) porpoise
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- Infrasound refers to sound waves with frequencies below the range of human hearing, typically less than 20 Hz.
- Whales are known to produce infrasound for communication over long distances in the ocean.
- Other animals, like dolphins, bats, and porpoises, use high-frequency sounds (ultrasound) for echolocation, which is the opposite of infrasound.
- Hence, the correct answer is whales.
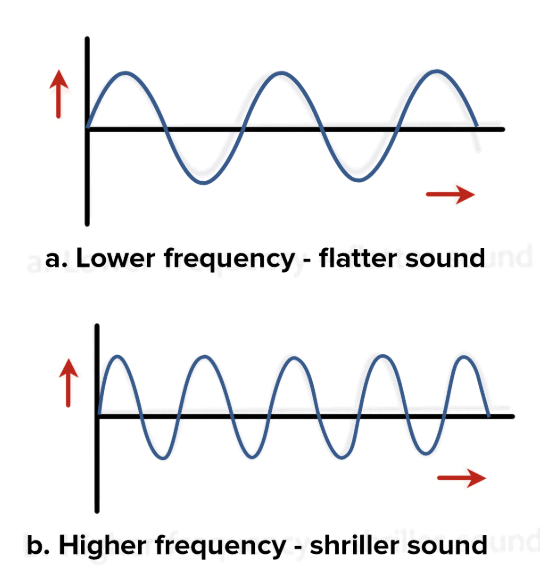
Q10: What does the frequency of a sound wave determine?
(a) Loudness
(b) Pitch
(c) Time period
(d) Propagation speed
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- The frequency of a sound wave determines its pitch.
- Frequency is the number of vibrations or waves produced in one second.
- A higher frequency means a higher pitch (like the sound of a whistle), and a lower frequency means a lower pitch (like the sound of a drum).
- So, the pitch of a sound depends on how fast the vibrations are occurring.
|
90 videos|415 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ (Solution) - Sound - Science Class 8
| 1. What is sound and how is it produced? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of sound waves? |  |
| 3. How does sound travel through different mediums? |  |
| 4. What is the relationship between frequency and pitch in sound? |  |
| 5. What factors affect the loudness of sound? |  |