MCQ (Solution) - Understanding Marginalisation | Social Studies (SST) Class 8 PDF Download
Q1: What does it mean to be socially marginalized?
(a) Living in urban areas
(b) Being excluded or pushed to the sidelines in society
(c) Having a high socio-economic status
(d) Practicing tribal religions
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Social marginalization refers to the process where individuals or groups are pushed to the edges of society, leading to their exclusion.
- It often affects those who are different in terms of culture, language, or social status.
- Marginalised individuals may feel discriminated against or ridiculed in social settings.
- This exclusion can result in a lack of access to resources and opportunities.
- Communities may become isolated, leading to feelings of powerlessness and disadvantage.
Socially marginalized
Q2: Who are Adivasis?
(a) Urban settlers in India
(b) Communities living in close association with forests
(c) Nomads in the desert regions of India
(d) Followers of mainstream religions in India
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Adivasis are communities often referred to as the original inhabitants of India. They have a close relationship with forests and make up about 8% of the country's population.
- There are over 500 different Adivasi groups across India.
- Adivasis are primarily found in states such as Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, and Odisha.
- They have their own languages, which are often very different from mainstream Indian languages.
- Adivasi communities are known for their rich cultural traditions, including worship practices that involve sacred groves.
- They have historically been influenced by various religions, including Buddhism and Christianity.
Adivasis
Q3: In which states of India are Adivasis particularly numerous?
(a) Punjab and Haryana
(b) Kerala and Tamil Nadu
(c) Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, and others
(d) Uttar Pradesh and Bihar
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Adivasis are particularly numerous in states like Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, and various northeastern states.
Q4: What is a common stereotype associated with Adivasis?
(a) They lack advancement.
(b) They are exotic, primitive and backward.
(c) They are resistant to change.
(d) All of the above.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
- Adivasis are often shown in very stereotypical ways, typically dressed in colorful costumes, wearing headgear, and performing dances.
- Despite these portrayals, we know very little about the real lives of Adivasis.
- This lack of understanding can lead people to view them as exotic, primitive, and backward.
- Adivasis are often blamed for not progressing, as many believe they are resistant to change or new ideas.
Q5: Why have Adivasis been forced to migrate to cities in recent years?
(a) Cultural preferences
(b) Economic changes, forest policies, and political force
(c) Lack of educational opportunities
(d) Adequate employment opportunities in rural areas
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Adivasis have been forced to migrate to cities in recent years due to several factors:
This migration often results in low-wage jobs and a cycle of poverty, with many Adivasis facing significant challenges in urban settings.
- Economic changes: Traditional livelihoods have diminished, pushing Adivasis to seek work in urban areas.
- Forest policies: Restrictions on forest access have deprived them of resources and income.
- Political pressure: State and private interests have displaced communities, leading to urban migration.
Q6: What does the term "minority" commonly refer to?
(a) Large communities in relation to the population
(b) Numerically small communities in relation to the population
(c) Urban populations
(d) Nomadic communities
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The term minority typically refers to communities that are numerically smaller compared to the larger population. However, its meaning extends beyond just numbers and includes:
- Power dynamics: Minorities often have less influence in societal and political matters.
- Access to resources: They may face challenges in obtaining essential resources and opportunities.
- Social and cultural aspects: Minority groups can experience cultural dominance by the majority, leading to marginalisation.
Q7: Why are safeguards necessary for minority communities according to the Indian Constitution?
(a) To avoid discrimination.
(b) To dominate the majority.
(c) To increase their size.
(d) To reduce their rights.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The Indian Constitution recognizes that minority communities may face marginalization, discrimination, and cultural domination due to their smaller size relative to the majority. To prevent such disadvantages, safeguards are implemented to ensure their protection and equal rights in society. This helps promote fairness and inclusivity.Cultural Diversity and Equality
Q8: According to the 2011 Census, what percentage of India's population is Muslim?
(a) 12.5%
(b) 14.2%
(c) 16.4%
(d) 18.1%
Correct Answer is Option (b)
According to the 2011 Census, Muslims constitute 14.2% of India's total population. This community is often viewed as marginalised due to:
The data underscores the need for focused efforts to enhance the community's development and support their progress.
- Lower levels of socio-economic development.
- Limited access to basic amenities.
- Lower literacy rates compared to other groups.
Muslims
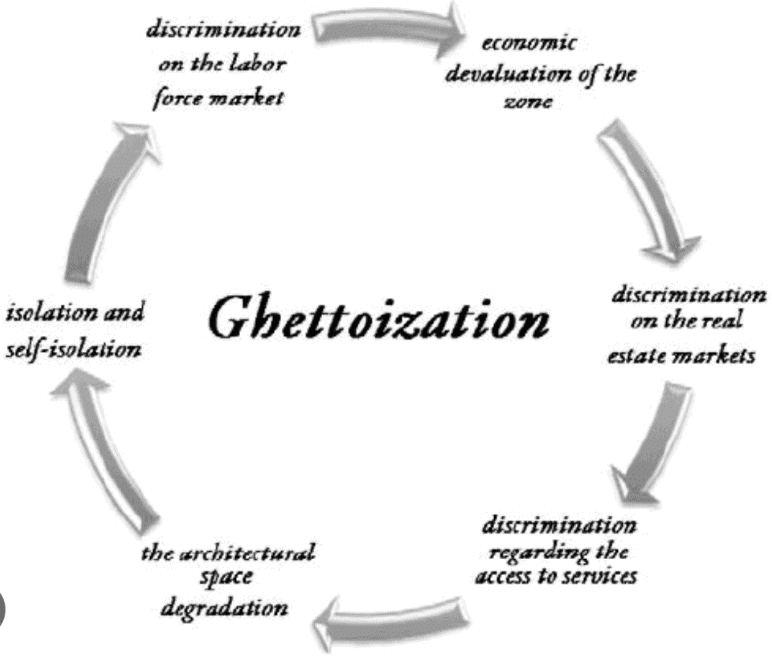
Q9: What does "ghettoisation" refer to?
(a) A process of cultural integration.
(b) A community being isolated and alienated.
(c) A community's economic advancement.
(d) Customary practices like wearing burqa and fez
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Ghettoisation refers to the process of creating a ghetto, which is an area primarily inhabited by a specific community. This phenomenon can arise from various factors, including:
Fear or hostility may drive communities to cluster together for a sense of security. Unfortunately, those in a ghettoised area often have limited options to move, which can lead to feelings of alienation from the wider society.
- Social reasons, such as discrimination or exclusion.
- Cultural factors, where communities prefer to live among those with similar backgrounds.
- Economic challenges that limit mobility and opportunities.
Q10: Why are Muslims often identified differently from others?
(a) Because of their socio-economic status.
(b) Due to their distinct customs and practices.
(c) Due to their economic advancements.
(d) Because of their mainstream lifestyle.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Muslim customs and practices, such as wearing a burqa, sporting a long beard, or wearing a fez, often set them apart from the mainstream. These distinct customs become ways to identify Muslims, and as a result, some people tend to view them as different from the rest of society. This can lead to discrimination or prejudice, as their differences are used as an excuse to treat them as outsiders.
|
87 videos|558 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ (Solution) - Understanding Marginalisation - Social Studies (SST) Class 8
| 1. What is marginalization and how does it affect individuals in society? |  |
| 2. What are some common examples of marginalized groups? |  |
| 3. How can society address and reduce marginalization? |  |
| 4. What role does education play in combating marginalization? |  |
| 5. How can individuals support marginalized communities? |  |