MCQ & Extra Questions: A Journey through States of Water | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Extra Questions
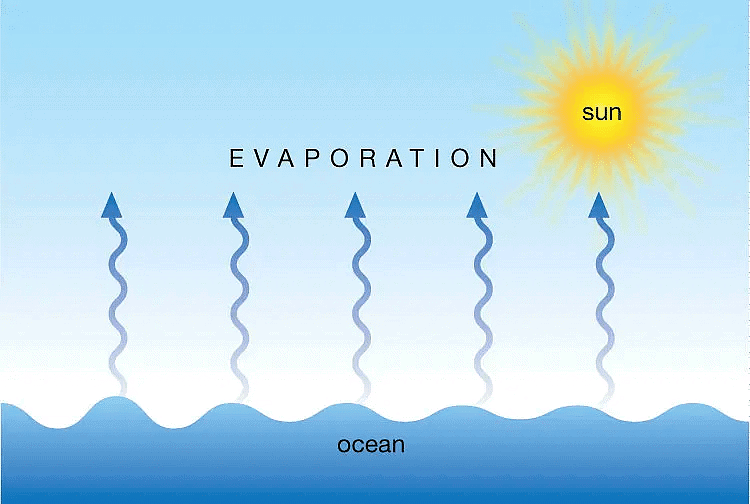
Q1: What is evaporation?
- Evaporation is the process where water changes into vapour. This happens continuously, even at room temperature.
- It occurs when water molecules gain enough energy to escape into the air.
- Examples include:
- Drying of wet clothes
- Water disappearing from puddles
- Sweat evaporating from our skin
Q2: What causes the cooling effect in an earthen pot?
The cooling effect in an earthen pot is caused by water seeping through the surface of the pot and evaporating. This evaporation process imparts a cooling effect on the water inside the pot.
Q3: What happens to the shape of ice when it is placed in different containers?
- Ice retains its shape regardless of the container it is placed in.
- It does not flow or spread like water.
- In contrast, water takes the shape of its container and can flow freely.
Q5: What is condensation?
- Condensation is when water vapour in the air turns into liquid water.
- This occurs when the vapour touches a cold surface, forming tiny droplets.
- These droplets can gather to create clouds or fall as rain, hail, or snow.
Q6: How does water change its state from solid to liquid and from liquid to gas?
- Water changes from solid (ice) to liquid (water) when heat is added.
- It transforms from liquid to gas (water vapour) with further heating.
- To convert water back to ice, it must be placed in a cold environment, like a freezer.
- When ice is removed from the freezer, it melts back into water.
Q7: Why do clothes dry faster on a windy day?
- Clothes dry faster on windy days due to the movement of air.
- This increases evaporation rates, allowing water to leave the fabric more quickly.
- Wind helps to carry away the moisture, making the drying process more efficient.
Q8: What causes the water droplets to appear on the outer surface of a cold glass tumbler?
- Water droplets form on a cold glass tumbler due to a process called condensation.
- This occurs when water vapour in the air cools down and changes into liquid.
- The cold surface of the glass causes the warm air around it to lose heat, leading to the formation of tiny droplets.
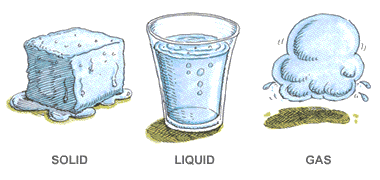
Q9: What are the three states of water? Describe them briefly.
Water exists in three states:
- Solid (Ice): Retains its shape and does not flow.
- Liquid (Water): Takes the shape of its container and flows freely.
- Gas (Water Vapour): Fills the available space and is often invisible.
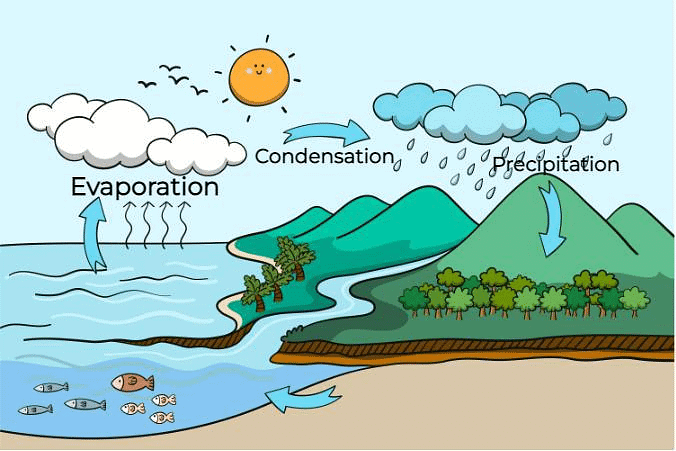
Q10: How does the water cycle work?
The water cycle works through a continuous process of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation. Here’s how it works:
- Evaporation: Water from the ocean, lake, and other water bodies evaporates into the atmosphere as water vapour.
- Condensation: The water vapour cools and condenses to form clouds.
- Precipitation: Water returns to the Earth's surface as rain, hail, or snow.
- Collection: The precipitation collects in rivers, and groundwater, and eventually flows back to the ocean, where the cycle begins again.
This circulation of water helps maintain the balance and availability of water on Earth.
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: What is the process called when water changes from a liquid to a gas?
a) Freezing
b) Condensation
c) Melting
d) Evaporation
Ans: d) Evaporation
Evaporation is the process in which water changes from a liquid to a gas. Key points include:
This process is essential in the water cycle, where water vapour eventually condenses to form clouds.
- Occurs when water absorbs heat.
- Can happen at any temperature, even at room temperature.
- Examples include drying wet clothes and sweat evaporating from skin.
Q2: Which state of water takes the shape of the container it is in?
a) Solid
b) Liquid
c) Gas
d) Plasma
Ans: b) Liquid
Liquid water takes the shape of its container while keeping a constant volume. Key points include:
- Liquid flows and adapts to the shape of the container.
- It does not have a fixed shape.
- Unlike ice (solid), which retains its shape, liquid water spreads out.
Q3: What happens to water when it is placed in a freezer?
a) It evaporates
b) It condenses
c) It melts
d) It freezes
Ans: d) It freezes
- When water is placed in a freezer, it turns into ice.
- This process changes water from a liquid to a solid state.
- If the ice is removed from the freezer, it will melt back into water.
Q5: Which of the following is NOT a state of water?
a) Solid
b) Liquid
c) Gas
d) Plasma
Ans: d) Plasma
Water exists in three main states:
Plasma is not a state of water.
- Solid: Ice retains its shape.
- Liquid: Water flows and takes the shape of its container.
- Gas: Water vapour spreads out in the air.
Q6: What forms when water vapour condenses in the atmosphere?
a) Ice
b) Clouds
c) Salt
d) Dust
Ans: b) Clouds
Clouds form when water vapour in the air condenses into tiny droplets. This process occurs around dust particles present in the atmosphere. Here’s how it works:
- As air rises, it cools down.
- When the air cools sufficiently, water vapour condenses into droplets.
- These droplets cluster together to create clouds.
- Eventually, larger droplets may fall as rain, hail, or snow.
Q7: Which factor does NOT directly affect the rate of evaporation?
a) Humidity
b) Temperature
c) Surface area
d) Color of water
Ans: d) Color of water
However, it is not affected by the colour of water.
- The rate of evaporationis influenced by:
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Surface area
Q8: What do you observe when you pour water on a clean surface?
a) It evaporates instantly
b) It forms a puddle
c) It solidifies
d) It changes colour
Ans: b) It forms a puddle
- When you pour water on a clean surface, it forms a puddle.
- The water spreads out depending on the surface's properties.
Q9: When water in a puddle disappears, what is the most likely cause?
a) Seeping into the ground
b) Chemical reaction
c) Evaporation
d) Absorption by plants
Ans: c) Evaporation
- The most likely cause of a puddle disappearing is evaporation.
- During evaporation, water changes into vapour due to heat.
- This vapour then escapes into the air.
Q10: Why does water evaporate faster from a wide plate compared to a small cap?
a) The plate has more water
b) The plate is exposed to more sunlight
c) The plate has a larger exposed surface area
d) The cap is warmer
Ans: c) The plate has a larger exposed surface area
- Water evaporates faster from a wide plate because it has a larger surface area exposed to air.
- This increased exposure allows more water to change into vapour at the same time.
|
67 videos|289 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ & Extra Questions: A Journey through States of Water - Science for Class 6
| 1. What are the three states of water? |  |
| 2. How does water change from one state to another? |  |
| 3. What factors influence the state of water? |  |
| 4. Can water exist in all three states at the same time? |  |
| 5. How does the state of water affect its density? |  |