MCQ & Extra Questions: Beyond Earth | Science Olympiad Class 6 PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: What is the primary component of a comet's nucleus?
a) Rock
b) Metal
c) Ice and Dust
d) Gas
Ans: c) Ice and Dust
The primary component of a comet's nucleus is ice and dust. Comets are made up of frozen gases mixed with dust and rocky material. When they approach the Sun, the ice vaporizes, forming a glowing coma and tail.
Q2: Which constellation is known as the hunter?
a) Ursa Major
b) Orion
c) Cassiopeia
d) Canis Major
Ans: b) Orion
Orion is known as the hunter, with its three prominent stars forming the belt of the hunter.
Q3: Which star is the brightest in the night sky?
a) Betelgeuse
b) Pole Star
c) Sirius
d) Alpha Centauri
Ans: c) Sirius
Sirius, located in the constellation Canis Major, is the brightest star visible in the night sky.
 Sirius
Sirius
Q4: What do we call the group of objects including the Sun, planets, moons, asteroids, and comets?
a) Milky Way
b) Solar System
c) Galaxy
d) Universe
Ans: b) Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun, its eight planets, their moons, and various smaller objects like asteroids and comets.
Q5: Which planet is closest to the Sun?
a) Venus
b) Earth
c) Mercury
d) Mars
Ans: c) Mercury
Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun and has the shortest orbit among all the planets in the Solar System.
Q6: Which constellation contains the Pleiades star cluster?
a) Orion
b) Taurus
c) Ursa Major
d) Cassiopeia
Ans: b) Taurus
The Pleiades star cluster is located within the constellation Taurus and is often referred to as the 'Seven Sisters', making it a prominent feature of Taurus.
Q7: Which planet is known as the "Red Planet"?
a) Mars
b) Venus
c) Mercury
d) Saturn
Ans: a) Mars
Mars is known as the "Red Planet" due to its reddish appearance, which is caused by iron oxide (rust) on its surface.
Q8: Which term is used for objects like Pluto that are smaller than planets and lie beyond Neptune?
a) Moons
b) Satellites
c) Asteroids
d) Dwarf Planets
Ans: d) Dwarf Planets
Pluto and similar objects that are smaller than planets and lie beyond Neptune are classified as dwarf planets according to the redefined definition by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 2006.
Q9: What is the name of Earth’s natural satellite?
a) Mars
b) Sun
c) Moon
d) Pluto
Ans: c) Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite, orbiting our planet and affecting tides and other natural phenomena.
Q10: Which constellation contains the Big Dipper?
a) Ursa Major
b) Orion
c) Ursa Minor
d) Cassiopeia
Ans: a) Ursa Major
The Big Dipper is a part of the constellation Ursa Major, also known as the Great Bear.
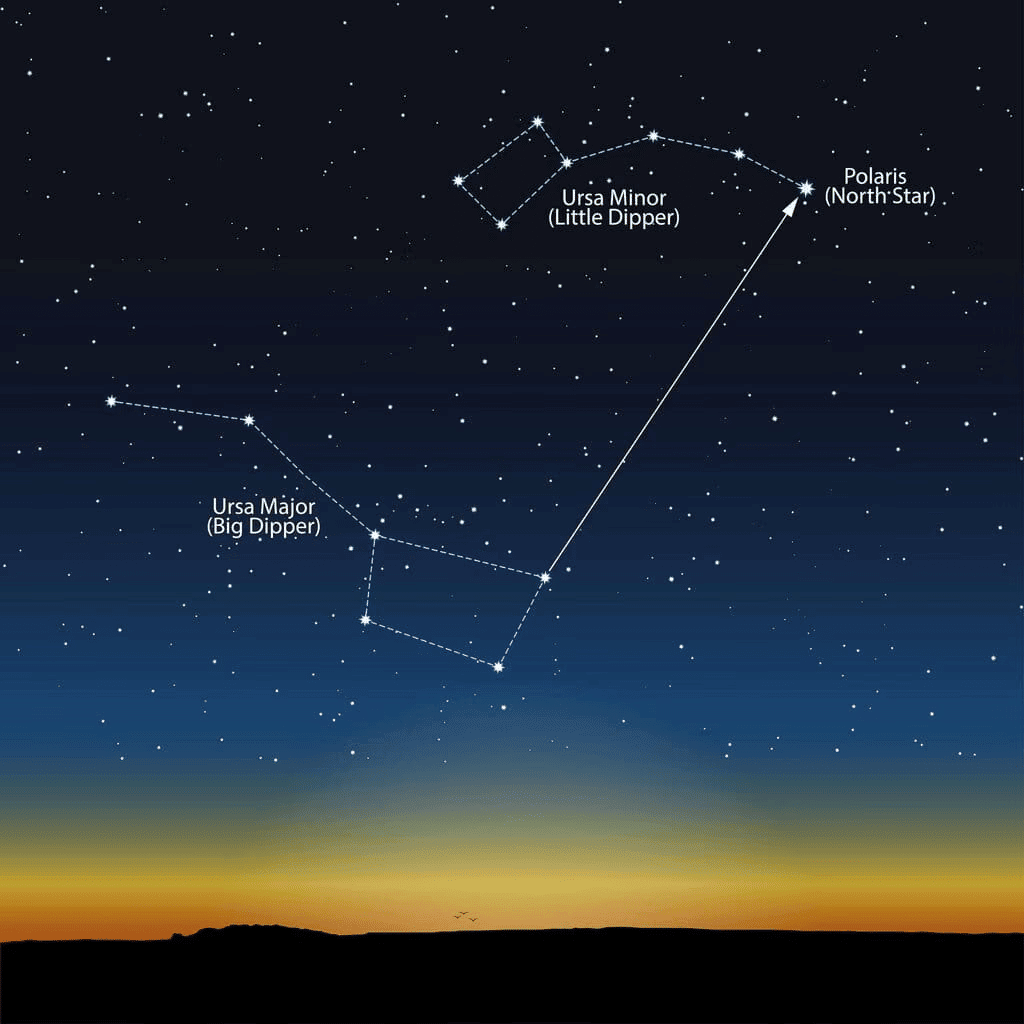 Constellation
Constellation
Extra Questions
Q1: What is the primary purpose of constellations in modern astronomy?
Constellations help in identifying and locating stars and other celestial objects.
Q2: What is a galaxy?
A galaxy is a large system of stars, gas, and dust bound together by gravity.
Q3: What is the pattern formed by a group of stars in the night sky?
Constellation.
Q4: Which planet is often referred to as Earth’s twin because of its similar size and proximity?
Venus is often called Earth’s twin due to its similar size, mass, and proximity to Earth, although its surface conditions are very different.
Q5: How many planets are there in our Solar System?
Eight.
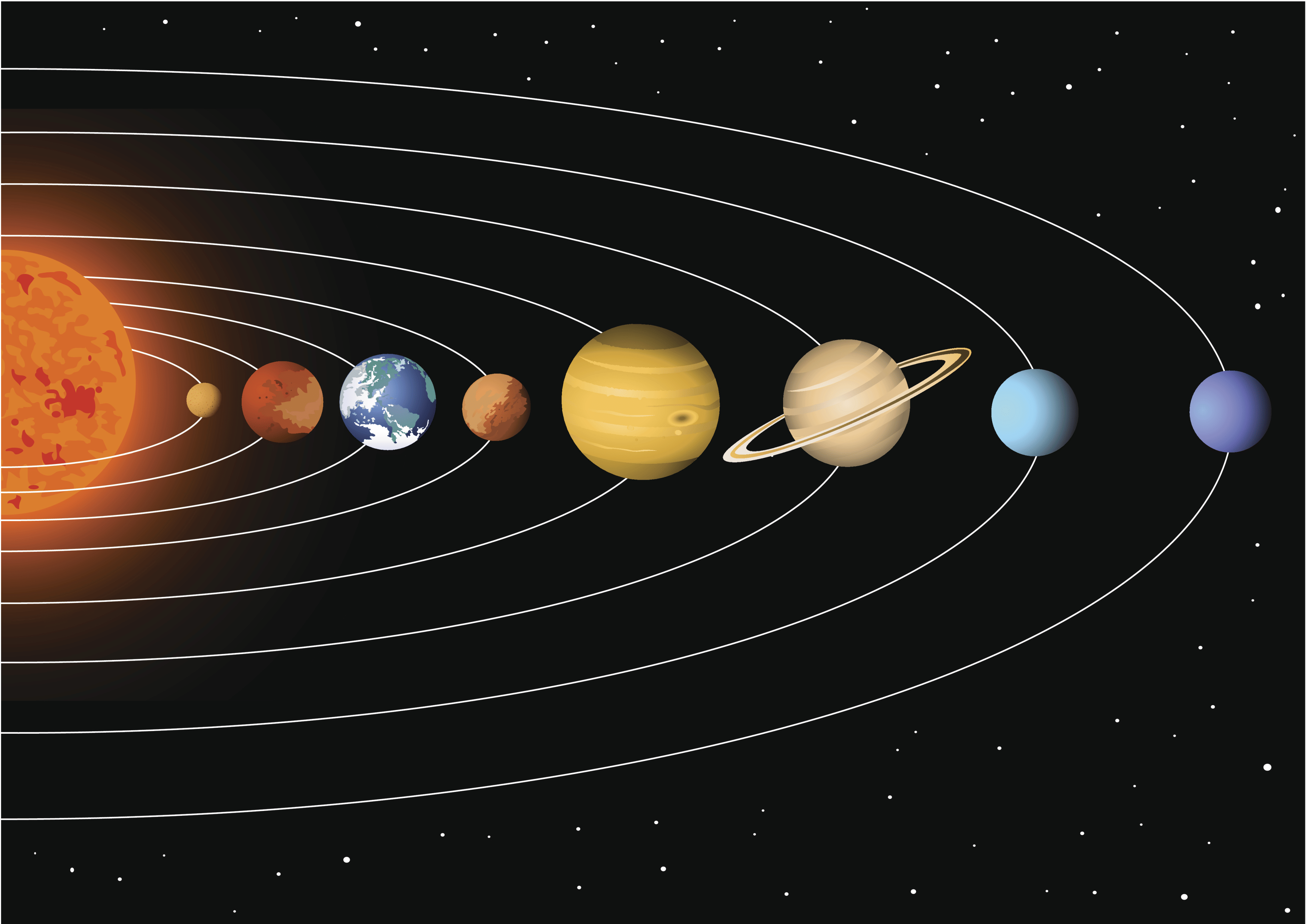 Solar System
Solar System
Q6: Why is Venus known as the Evening Star or the Morning Star?
Venus is called the Evening Star or the Morning Star because it is often visible at dawn or dusk, shining brightly either in the western sky after sunset or in the eastern sky before sunrise.
Q7: Explain why the Pole Star is important for navigation.
The Pole Star is important for navigation because it remains nearly stationary in the sky, indicating the direction of true north.
Q8: What is the significance of the Milky Way Galaxy in our understanding of the universe?
The Milky Way Galaxy is significant because it is our home galaxy, containing our Solar System. Studying the Milky Way helps us understand the structure, formation, and evolution of galaxies.
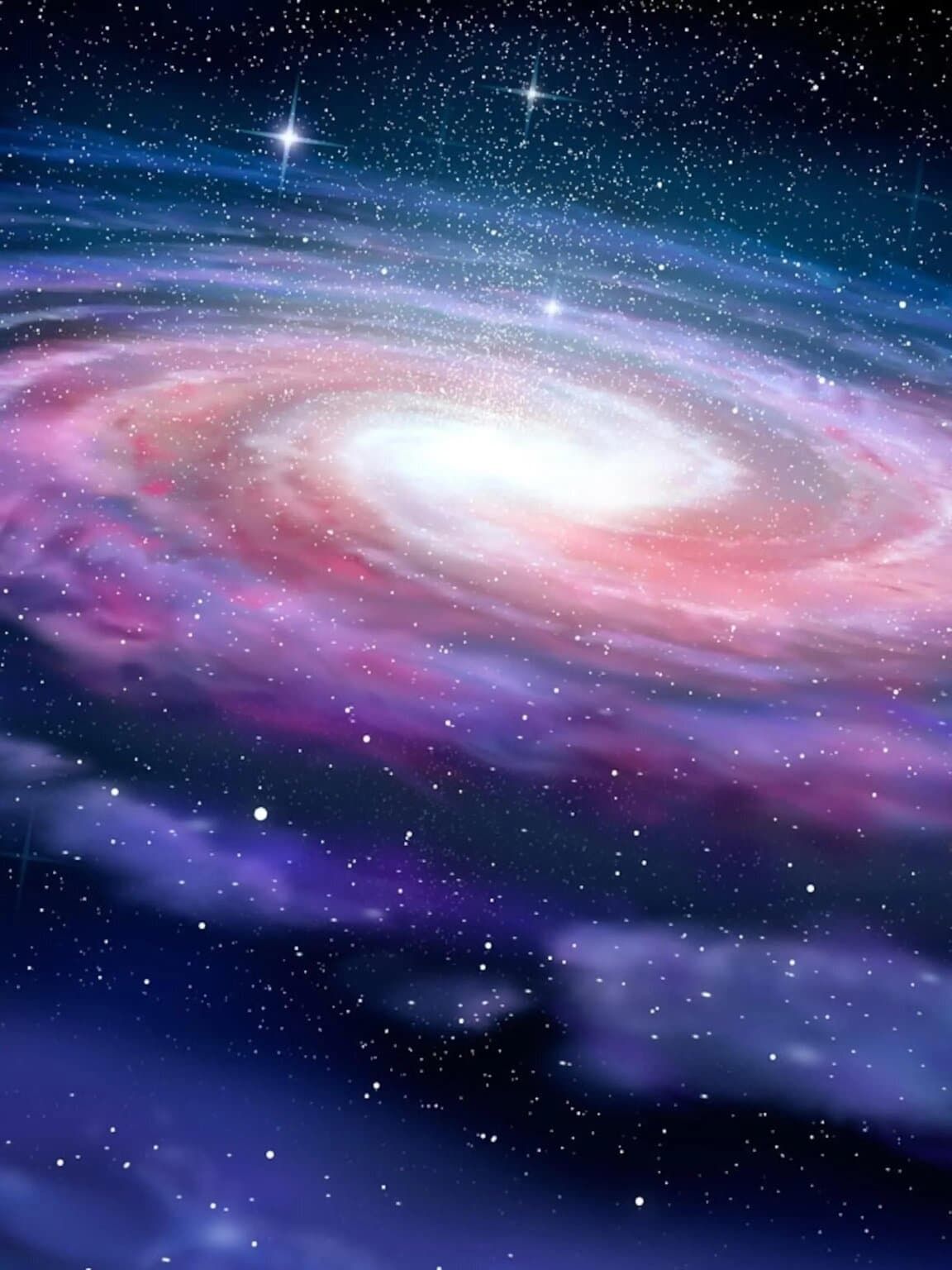 Milky Way Galaxy
Milky Way Galaxy
Q9: How do comets differ from asteroids?
Comets are composed of ice, dust, and rocky material and often have a visible coma or tail when they come close to the Sun. Asteroids, on the other hand, are made mostly of rock and metal and do not develop tails.
Q10: Describe the importance of the Sun in the Solar System.
The Sun is crucial in the Solar System as it is the primary source of energy, providing the heat and light necessary for life on Earth. It also governs the orbits of the planets and other objects through its gravitational pull.
|
69 videos|150 docs|104 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ & Extra Questions: Beyond Earth - Science Olympiad Class 6
| 1. What are some potential benefits of exploring and colonizing planets beyond Earth? |  |
| 2. How do scientists plan to overcome the challenges of living on other planets? |  |
| 3. What are some of the potential risks associated with colonizing other planets? |  |
| 4. How do space agencies prepare astronauts for long-duration space missions to other planets? |  |
| 5. How can the general public contribute to the exploration and colonization of planets beyond Earth? |  |

















