MCQ & Extra Questions: Diversity in the Living World | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Extra Questions
Q1: What is biodiversity?
Biodiversity refers to the variety of all forms of life on Earth, including different plants, animals, microorganisms, and the ecosystems they form.
Q2: How do plants adapt to survive in deserts?
Plants in deserts often have fleshy stems to store water and may have spines instead of leaves to reduce water loss.
Q3: What is the importance of grouping plants and animals?
Grouping makes it easier to understand and study plants and animals on the basis of their similarities and differences.
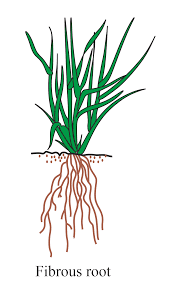
Q4: What are fibrous roots?
Fibrous roots are a type of root system where many thin roots spread out from the base of the stem, common in plants with parallel venation.
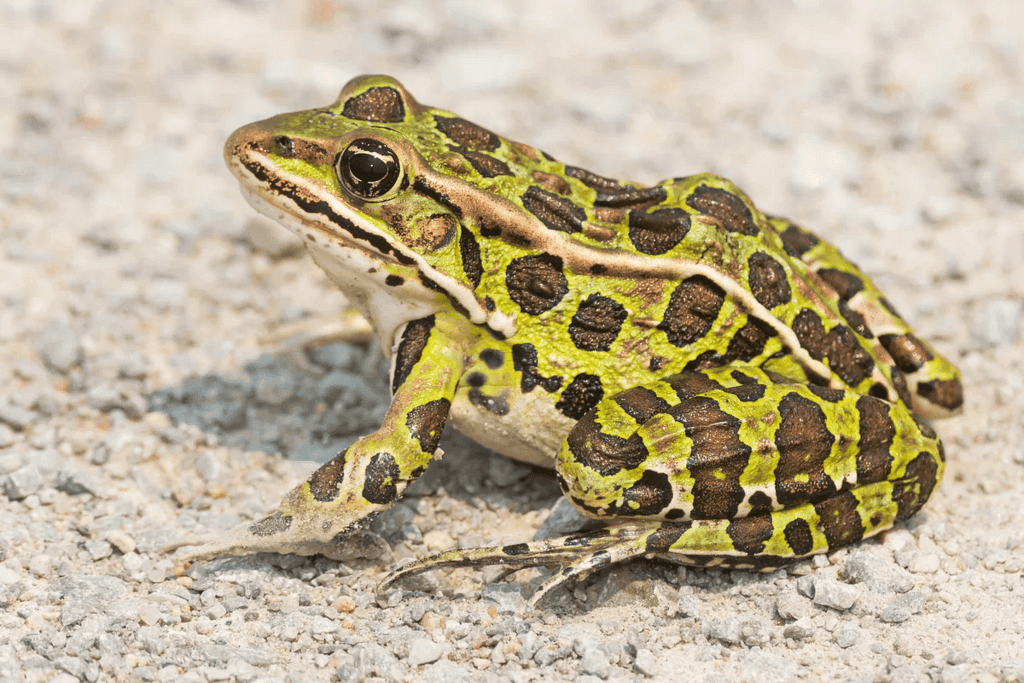
Q5: Give an example of an aquatic habitat and an organism that lives there.
An example of an aquatic habitat is a pond, and a fish is an organism that lives there.
Q6: What is the difference between terrestrial and aquatic habitats?
Terrestrial habitats are those found on land, while aquatic habitats are found in water bodies like ponds, lakes, and oceans.
Q7: What type of venation is found in the leaves of monocots?
Monocots typically have parallel venation in their leaves. In monocotyledonous (monocot) plants, the veins in the leaves run parallel to each other, forming a pattern where the veins are aligned along the length of the leaf. This is in contrast to dicotyledonous (dicot) plants, which typically have a reticulate (net-like) venation pattern where the veins form a branching network.
Q9: What is a habitat?
A habitat is the natural environment where a plant or animal lives and obtains its food, water, shelter, and other survival needs.
Q10: How do amphibians differ from other animals in terms of habitat?
Amphibians can live both on land and in water, unlike most other animals that are specialized for one type of habitat.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: What feature is commonly observed in desert plants?
a) Broad leaves
b) Thick, fleshy stems
c) Thin roots
d) Soft stems
Ans: b) Thick, fleshy stems
Desert plants have thick, fleshy stems to store water and survive the arid conditions.
 Q2: Which of the following is an example of a terrestrial habitat?
Q2: Which of the following is an example of a terrestrial habitat?
a) River
b) Lake
c) Forest
d) Ocean
Ans: c) Forest
A forest is a terrestrial habitat, where plants and animals live on land.
Q3: What type of root system is commonly found in monocots?
a) Taproot system
b) Fibrous root system
c) Adventitious root system
d) Prop root system
Ans: b) Fibrous root system
Monocots typically have a fibrous root system, with many thin roots spreading out from the stem base.
Q4: Which of the following animals is considered an amphibian?
a) Whale
b) Frog
c) Elephant
d) Eagle
Ans: b) Frog
Frogs are amphibians, meaning they can live both on land and in water.
Q5: What is the role of a habitat for a plant or animal?
a) Provides only water
b) Provides only food
c) Provides food, water, shelter, and other survival needs
d) Provides only shelter
Ans: c) Provides food, water, shelter, and other survival needs
A habitat provides all the essential needs for survival, including food, water, and shelter.
Q6: Which type of venation is commonly associated with dicots?
a) Parallel venation
b) Reticulate venation
c) Spiral venation
d) Random venation
Ans: b) Reticulate venation
Dicots typically exhibit reticulate venation, where the veins form a network-like pattern.
Q7: What adaptation helps camels survive in cold deserts?
a) Long legs
b) Thin fur
c) Short legs and two humps
d) Broad leaves
Ans: c) Short legs and two humps
While “two humps” is accurate for Bactrian camels, a better answer would emphasize thick fur or fat storage. Among the options, c) Short legs and two humps is the closest, but it’s not ideal. If the intent was to highlight Bactrian camel adaptations, thick fur should have been included (e.g., “thick fur and two humps”).
Q9: What is a common feature of plants found in mountainous regions?
a) Large, flat leaves
b) Conical shape and sloping branches
c) Shallow roots
d) Thin stems
Ans: b) Conical shape and sloping branches
Plants in mountainous regions often have conical shapes and sloping branches to let snow slide off easily.
Q10: What type of roots does a mustard plant have?
a) Fibrous roots
b) Taproots
c) No roots
d) Aerial roots
Ans: b) Taproots
Mustard plants have a taproot system. In this type of root system, there is one main root, known as the taproot, that grows straight down into the soil. From this main root, smaller secondary roots branch out. Taproots help the plant access water and nutrients from deeper layers of the soil and provide strong anchorage to the plant.
|
69 videos|289 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ & Extra Questions: Diversity in the Living World - Science for Class 6
| 1. What is biodiversity? |  |
| 2. Why is biodiversity important? |  |
| 3. How can we protect biodiversity? |  |
| 4. What are the threats to biodiversity? |  |
| 5. How can individuals contribute to preserving biodiversity? |  |