MCQ & Extra Questions: Exploring Magnets | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Extra Questions
Q1: What are magnetic materials?
Magnetic materials are those that are attracted towards a magnet, such as iron, nickel, and cobalt.
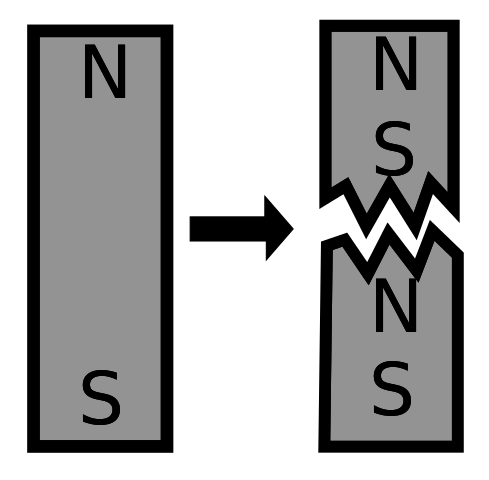
Q2: What happens when a magnet is broken into smaller pieces?
When a magnet is broken into smaller pieces, each piece becomes a new magnet with its own North and South poles.
Q3: How can you identify the North and South poles of a bar magnet using another magnet?
You can bring one end of a known magnet near the unmarked magnet. If it repels, it indicates the like poles (North-North or South-South), helping identify the poles.
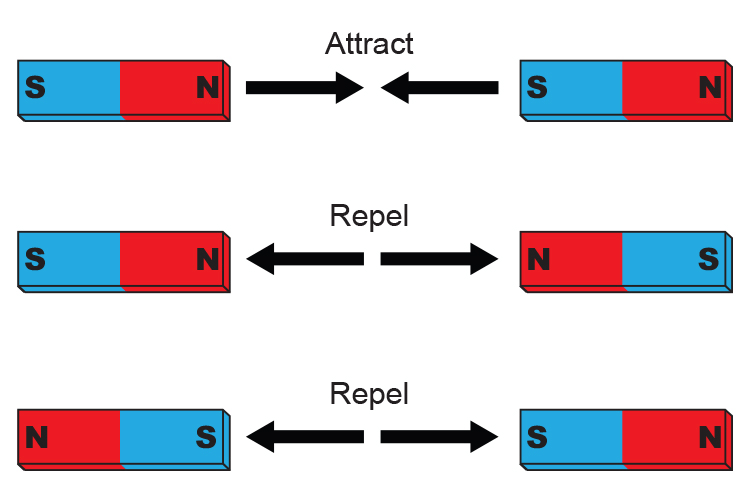
Q5: Why do like poles of two magnets repel each other?
Like poles of two magnets repel each other due to the similar magnetic field lines that exert a repulsive force.
Q6: What materials can block the magnetic effect between a magnet and a compass needle?
Non-magnetic materials like wood, plastic, and glass do not block the magnetic effect.
Q7: What is a magnetic compass made of?
A magnetic compass consists of a needle-shaped magnet mounted on a pin that can rotate freely, indicating directions.
Q8: How does a freely suspended magnet behave?
A freely suspended magnet always aligns itself in the North-South direction due to the Earth’s magnetic field.
Q9: What is the significance of the poles on a magnet?
The poles are where the magnetic force is strongest, with maximum attraction or repulsion occurring at these points.
Q10: What are non-magnetic materials?
Non-magnetic materials are those that are not attracted to magnets, such as plastic, wood, and glass.
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Which of the following materials is magnetic?
a) Wood
b) Plastic
c) Iron
d) Glass
Ans: c) Iron
Iron is a magnetic material, meaning it is attracted to magnets.
Q2: What happens when you bring the North pole of one magnet close to the South pole of another magnet?
a) They repel each other
b) They attract each other
c) They cancel each other’s magnetic fields
d) They break apart
Ans: b) They attract each other
Unlike poles of magnets attract each other.
Q3: What kind of magnets were used by sailors in the olden days?
a) Artificial magnets
b) Lodestones
c) Electromagnets
d) Temporary magnets
Ans: b) Lodestones
Sailors in the olden days used natural magnets called lodestones for navigation. Lodestones are naturally magnetized pieces of the mineral magnetite, which align themselves with the Earth's magnetic field, helping sailors find directions before the invention of the modern magnetic compass.
Q4: Which of these metals is NOT magnetic?
a) Iron
b) Nickel
c) Cobalt
d) Copper
Ans: d) Copper
Among the given options, iron, nickel, and cobalt are magnetic metals, meaning they can be attracted to a magnet. Copper, on the other hand, is not magnetic. It does not interact with magnets in the same way, making it a non-magnetic metal.
Q5: What was the ancient Indian navigation device similar to the modern magnetic compass called?
a) Sundial
b) Matsya-yantra
c) Chakra
d) Yantra-mantra
Ans: b) Matsya-yantra
The Matsya-yantra was an ancient Indian navigation device that worked similarly to the modern magnetic compass. It was used by Indian sailors to find directions while navigating on the seas, long before the magnetic compass was commonly used in Europe.
Q6: When a piece of wood is placed between a magnet and a compass needle, what is observed?
a) The needle deflects more
b) The needle deflects less
c) There is no appreciable change in the deflection
d) The needle stops deflecting
Ans: c) There is no appreciable change in the deflection
Wood is a non-magnetic material, so when it is placed between a magnet and a compass needle, it does not interfere with the magnetic field. Therefore, there is no appreciable change in the deflection of the needle, and it continues to point in the direction of the magnetic field.
Q7: Which shape of magnet is commonly used in a magnetic compass?
a) Bar magnet
b) Ring magnet
c) Horseshoe magnet
d) Needle-shaped magnet
Ans: d) Needle-shaped magnet
A magnetic compass typically uses a needle-shaped magnet to indicate directions.
Q9: Which pole of the Earth’s magnet is near the geographic North Pole?
a) North pole
b) South pole
c) East pole
d) West pole
Ans: b) South pole
The Earth's magnetic South pole is near the geographic North Pole.
Q10: What is the purpose of the dial in a magnetic compass?
a) To measure the strength of the magnet
b) To indicate the directions
c) To measure the distance travelled
d) To store the magnet
Ans: b) To indicate the directions
The dial in a magnetic compass is marked with the cardinal directions (North, South, East, and West). It rotates with the magnetized needle and helps the user determine the direction they are facing by aligning the needle with the dial markings.
|
67 videos|289 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ & Extra Questions: Exploring Magnets - Science for Class 6
| 1. What are the different types of magnets? |  |
| 2. How do magnets work? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between a north pole and a south pole of a magnet? |  |
| 4. How can you demagnetize a magnet? |  |
| 5. What are some common uses of magnets in everyday life? |  |