MCQ & Extra Questions: The Living Organisms - Characteristics & Habitats | Biology for Grade 9 PDF Download
Extra Questions
Q1: What is Adaptation?
Ans: Adaptation is defined as the presence of particular characteristics or characteristics that enable an organism to survive in its environment. Adaptations vary from animal to animal. A fish, for example, has gills that allow it to breathe underwater.
Q2: What are the different kinds of habitats?
Ans: Habitats are places where animals live, and they can be categorized into terrestrial (on land) and aquatic (in water) habitats. Terrestrial habitats include rainforests, grasslands, deserts, and mountains. Aquatic habitats encompass ponds, lakes, rivers, seas, and oceans. Each habitat has unique abiotic components that influence its biotic composition.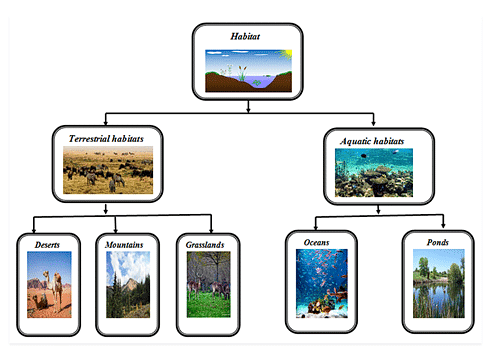
Q3: How body structure of camel helps it to survive in desert condition?
Ans: Camels have long legs which help to keep their body away from the heat of the sand. They secrete small amount of urine, their dung is dry and they do not sweat so they lose little water from their bodies.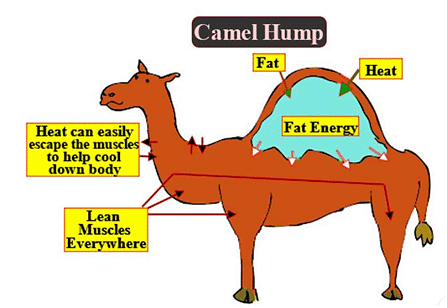
Q4: What is the difference between biotic and abiotic components of habitat?
Ans: The living things such as plants and animals in a habitat are called its biotic components. Non-living things such as soil, water, air are abiotic components of a habitat.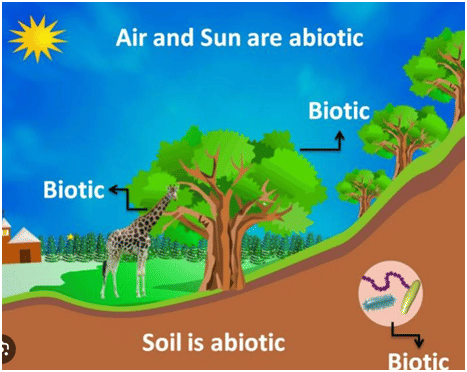
Q5: Frogs can live both on land and in water, name the adaptations seen in these animals.
Ans: Frogs have strong back legs that help them in leaping and catching their prey. They have webbed feet which help them to swim in water.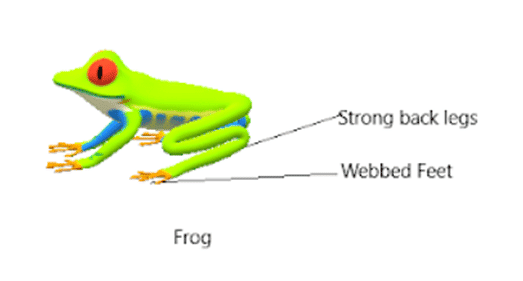
Q6: How is a lion adapted to live in the grassland?
Ans: The light brown colour of the lion helps it to hide in dry grasslands.
Q7: Explain the term ‘respiration’.
Ans: The process of breathing in oxygen and breathing out carbon dioxide accompanied with oxidation of food and energy release is termed as respiration.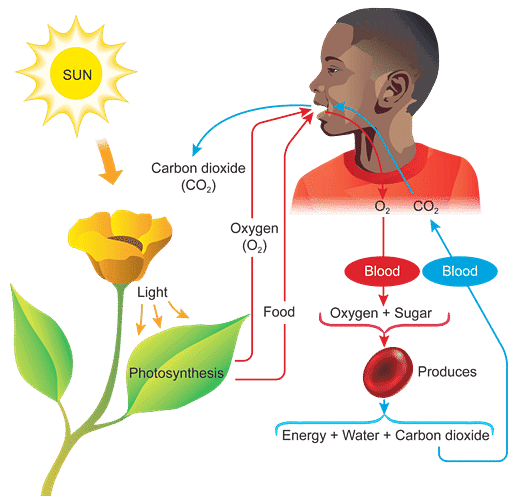
Q8: What is the difference between roots of terrestrial plants and aquatic plants?
Ans: In terrestrial plants roots play role in absorption of water and minerals from the soil. Whereas in aquatic plants roots are reduced in size and their main function is to hold the plant in place.
Q9: What are blowholes?
Ans: The organs by which dolphin or whales breathe are called blowholes or nostrils.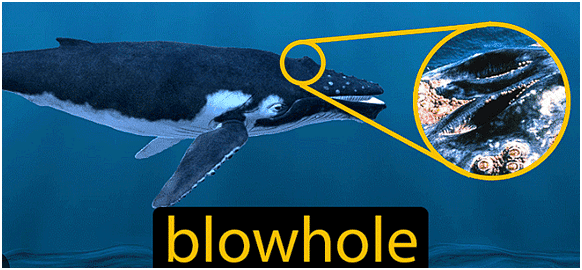
Q10: What is the main function of food?
Ans: Food gives energy to the organism which helps them in growth and development.
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Which of the following is an abiotic component of a habitat?
(a) Lion
(b) Cactus
(c) Rocks
(d) Deer
Ans: (c)
Sol: Abiotic components of a habitat are non-living factors. Rocks fall into this category, providing physical structure and influencing the environment. Lions, Cacti, and Deer are biotic components, as they are living organisms.
Q2: What is the primary purpose of gills in aquatic animals?
(a) To catch prey
(b) To breathe in air
(c) To hold the plant in the soil
(d) To respond to the environment
Ans: (b)
Sol: Gills in aquatic animals serve the purpose of extracting oxygen dissolved in water, allowing the animals to respire underwater. Catching prey, holding plants, and responding to the environment are functions unrelated to gills.
Q3: Which adaptation helps desert plants in conserving water?
(a) Large leaves
(b) Photosynthesis by stems
(c) Absence of roots
(d) Thin ribbon-like leaves
Ans: (b)
Sol: Desert plants, such as the cactus, have adaptations like photosynthesis by stems, as they lack leaves to reduce water loss. Large leaves and thin ribbon-like leaves are not typical adaptations for desert plants.
Q4: Why do mountain goats have strong hooves?
(a) To catch prey
(b) To slip off rainwater
To run on rocky slopes
To respond to the environment
Ans: (c)
Sol: Mountain goats have strong hooves that aid in running on rocky slopes, providing them with stability in their mountainous habitat. Catching prey, slipping off rainwater, and responding to the environment are unrelated functions.
Q5: What is the primary function of the roots of plants in ponds and lakes?
(a) To catch prey
(b) To hold the plant in the soil
(c) To breathe in air
(d) To respond to the environment
Ans: (b)
Sol: In ponds and lakes, plant roots primarily function to anchor the plant in the soil underwater, ensuring stability. Catching prey, breathing in air, and responding to the environment are not the main roles of these roots.
Q6: Which characteristic is specific to living organisms?
(a) Growth
(b) Rocks
(c) Sunlight
(d) Temperature
Ans: (a)
Sol: Growth is a characteristic specific to living organisms. Rocks, sunlight, and temperature are abiotic factors and do not exhibit the attribute of growth.
Q7: Which adaptation helps mountain goats navigate rocky slopes?
(a) Thick fur
(b) Strong hooves
(c) Spiky leaves
(d) Long claws
Ans: (b)
Sol: Mountain goats have strong hooves that provide them with stability and agility on rocky slopes. This adaptation helps them navigate their mountainous habitat, making Option B the correct answer.
Q8: What is the primary function of long claws in lions?
(a) To catch prey
(b) To hold the plant in the soil
(c) To slip off rainwater
(d) To respond to the environment
Ans: (a)
Sol: Long claws in lions are adapted for catching prey, aiding in hunting. Holding plants, slipping off rainwater, and responding to the environment are unrelated functions.
Q9: What is the process of getting rid of wastes by organisms called?
(a) Breathing
(b) Growth
(c) Reproduction
(d) Excretion
Ans: (d)
Sol: Excretion is the process by which organisms eliminate waste products. Breathing, growth, and reproduction are distinct life processes and not synonymous with excretion.
Q10: Why do desert animals like rats and snakes come out only at night?
(a) To catch prey
(b) To avoid predators
(c) To respond to the environment
(d) To slip off rainwater
Ans: (b)
Sol: Desert animals often come out at night to avoid the extreme heat and predators that are more active during the day. Catching prey, responding to the environment, and slipping off rainwater are not the primary reasons for their nocturnal behaviour.
|
50 videos|93 docs|25 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ & Extra Questions: The Living Organisms - Characteristics & Habitats - Biology for Grade 9
| 1. What are the main characteristics of living organisms? |  |
| 2. What are the different habitats in which living organisms can be found? |  |
| 3. How do living organisms obtain energy for their survival? |  |
| 4. What is the importance of adaptation for living organisms in their habitats? |  |
| 5. How do living organisms contribute to the balance of ecosystems? |  |






















