MCQ & Extra Questions: Motion & Measurement of Distances | Science for Grade 6 PDF Download
Extra Questions
Q1: Define rest and motion.
Ans: An object that does not change its position with time is said to be at rest. An object that changes its position with time is said to be in motion.
Q2: What is circular motion? Give example.
Ans: When an object moves in a circular path, such motion is called circular motion.
For example- The motion of a point marked on the blade of an electric fan is a circular motion.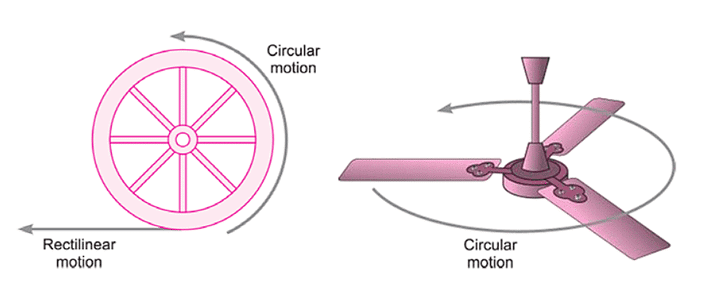
Q3: What is periodic motion? Give example.
Ans: An object that repeats its motion after a fixed interval of time is said to be in periodic motion.
For example- The motion of a pendulum is a periodic motion.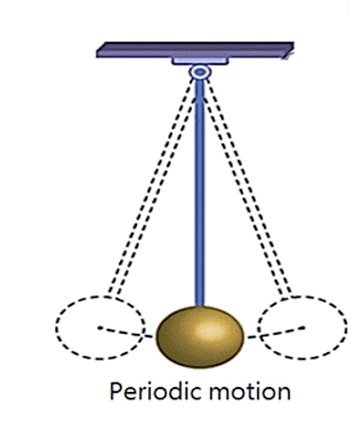
Q4: What is the difference between rectilinear and circular motion?
Ans: When objects move along a straight line such motion is called rectilinear motion. Whereas when an object moves in a circular path, such motion is called circular motion.
Q5: Define Distance.
Ans: Distance is the total length travelled by an object from one point to another, irrespective of the direction.
Q6: Can you measure the length of a pencil with a metre scale?
Ans: No, the length of a pencil cannot be accurately measured with a metre scale. A small scale, such as a plastic ruler marked in centimetres, should be used instead.
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: The standard unit of length in SI system is
(a) Foot
(b) Yard
(c) Centimeter
(d) Metre
Ans: (d)
Sol: The standard unit of length in SI system is metre.
Q2: What device should a tailor use to measure the length of cloth?
(a) Measuring tape
(b) Scale
(c) String
(d) Measuring rod
Ans: (a)
Sol: Measuring tape is used by a tailor to measure the length of cloth.
Q3: One cm is equal to
(a) 1 km
(b) 1 m
(c) 10 mm
(d) 1000 m
Ans: (c)
Sol: One centimetre (cm) is equal to: 10 mm
Q4: One kilometer is equal to
(a) 1000 m
(b) 100 m
(c) 10 m
(d) 1000 cm
Ans: (a)
Sol: One kilometre is equal to 1000 meters.
Q5: Which one is not a/an ancient unit of measurement?
(a) Angul
(b) Meter
(c) Cubit
(d) Girah
Ans: (b)
Sol: Girah, cubit, and angul are ancient units of measurement, whereas the metre is a standard SI unit.
Q6: Change in position of a body with time is called
(a) Displacement
(b) Motion
(c) Speed
(d) Distance
Ans: (b)
Sol: Motion refers to the change in position of a body with respect to time. It is a general term that encompasses various aspects, such as displacement (change in position), speed (rate of change in position), and distance (total path traveled).
|
101 videos|166 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ & Extra Questions: Motion & Measurement of Distances - Science for Grade 6
| 1. What is motion in physics? |  |
| 2. How do we measure distances accurately? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between distance and displacement? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to measure distances in science? |  |
| 5. What units are commonly used to measure distance? |  |

















