Magnetic Field & The Earth's Magnetic Field | Physics for Grade 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Magnetic Fields |

|
| Force of Attraction |

|
| Representing Magnetic Fields |

|
| The Earth's Magnetic Field |

|
Magnetic Fields
- All magnets are surrounded by a magnetic field
- A magnetic field is defined as:
- The region around a magnet where a force acts on another magnet or on a magnetic material (such as iron, steel, cobalt and nickel)
Magnetic Field Lines
- Magnetic field lines are used to represent the strength and direction of a magnetic field
- The direction of the magnetic field is shown using arrows
- The strength of the magnetic field is shown by the spacing of the magnetic field lines
- If the magnetic field lines are close together then the magnetic field will be strong
- If the magnetic field lines are far apart then the magnetic field will be weak
- There are some rules which must be followed when drawing magnetic field lines. Magnetic field lines:
- Always go from north to south (indicated by an arrow midway along the line)
- Must never touch or cross other field lines
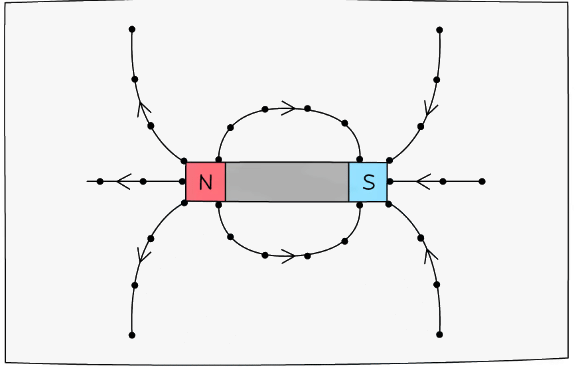
Magnetic Field around a Bar Magnet
- The magnetic field is strongest at the poles
- This is where the magnetic field lines are closest together
- The magnetic field becomes weaker as the distance from the magnet increases
- This is because the magnetic field lines are getting further apart
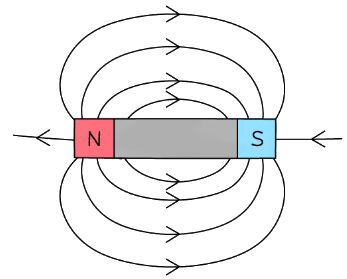 The magnetic field around a bar magnet
The magnetic field around a bar magnet
- Two bar magnets can repel or attract, the field lines will look slightly different for each:
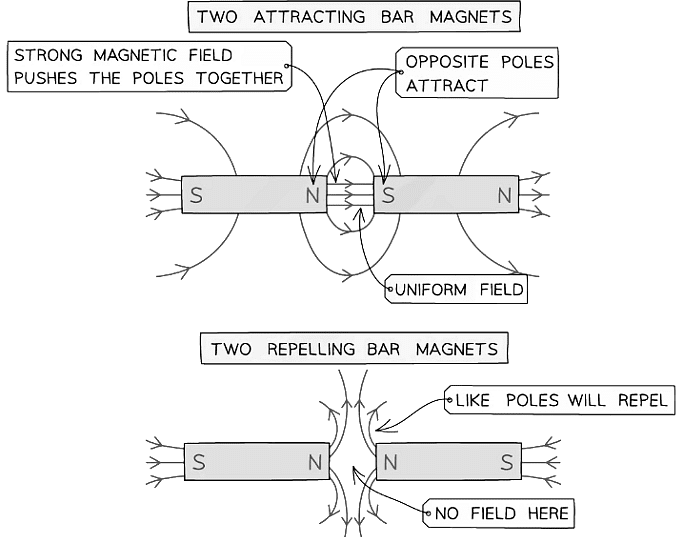 Magnetic field lines for attracting and repelling bar magnets
Magnetic field lines for attracting and repelling bar magnets
- Therefore, the magnetic field lines around different configurations of two bar magnets would look like:
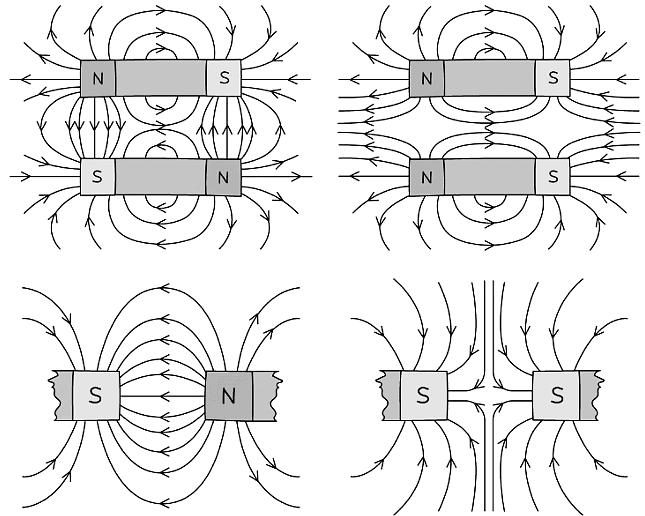 Magnetic field lines between two bar magnets
Magnetic field lines between two bar magnets
Exam Tip
If you are asked to draw the magnetic field around a bar magnet remember to indicate both the direction of the magnetic field and the strength of the magnetic field.
You can do this by:
- Adding arrows pointing away from the north pole and towards the south pole
- Making sure the magnetic field lines are further apart as the distance from the magnet increases
Force of Attraction
- An attractive force can be experienced between:
- The opposite poles of two different permanent magnets (due to the law of magnetism)
- A magnet and a magnetic material (due to induced magnetism)
- A magnet will always induce the opposite pole in the closet end of a magnetic material
Uniform Magnetic Field
- A uniform magnetic field will be produced in the gaps between opposite poles
- Note: Outside that gap the field will not be uniform
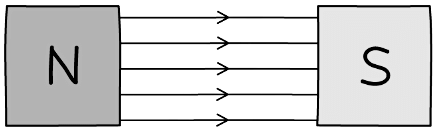
- A uniform magnetic field is one that has the same strength and direction at all points
- To show that the magnetic field has the same strength at all points there must be equal spacing between all magnetic field lines
- To show that the magnetic field is acting in the same direction at all points there must be an arrow on each magnetic field line going from the north pole to the south pole
- The magnetic field lines are the same distance apart between the gaps of the poles to indicate that the field strength is the same at every point between the poles
Exam Tip
When drawing a uniform field, stick to the field directly between the two poles – don’t worry about what is going on around the sides.
- Start by drawing a single straight line (use a pencil and ruler) in the middle – make sure you indicate its direction
- Next draw two lines at the top and bottom of the gap
- Finally, you can add two further lines halfway between the others
Representing Magnetic Fields
Direction of a Magnetic Field
- The direction of the magnetic field at any point is given by the direction of the force that would act on another north pole placed at that point
- The direction of a magnetic field line is from the north pole of a magnet to the south pole of a magnet
- This is because a north pole would be repelled by the north pole of a magnet and attracted to the south pole of a magnet
Plotting Magnetic Fields
- The shape and direction of a magnetic field may be investigated using plotting compasses
- A plotting compass is like a small bar magnet, with a north and south pole
- The arrow of the plotting compass represents the north pole
Investigating the Shape and Direction of a Magnetic Field
Step 1:- Place the magnet on top of a piece of paper
- Draw a dot at one end of the magnet (near its corner)
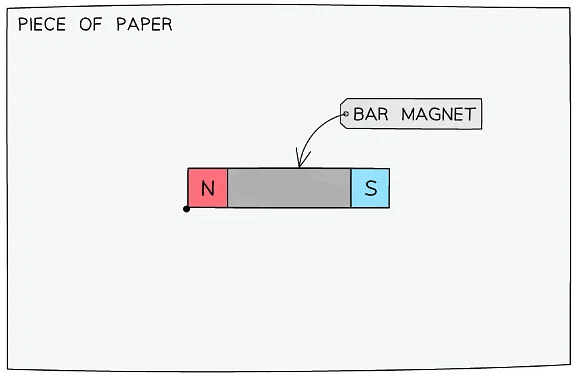
Step 2:
- Place a plotting compass next to the dot, so that one end of the needle of the compass points away from the dot
- Use a pencil to draw a new dot at the other side of the compass needle
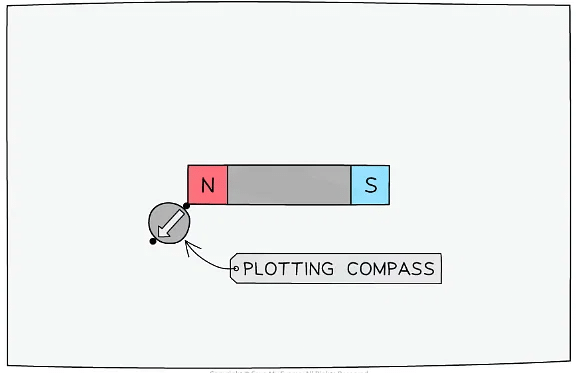
Step 3:
- Move the compass so that it points away from the new dot, and repeat the process above
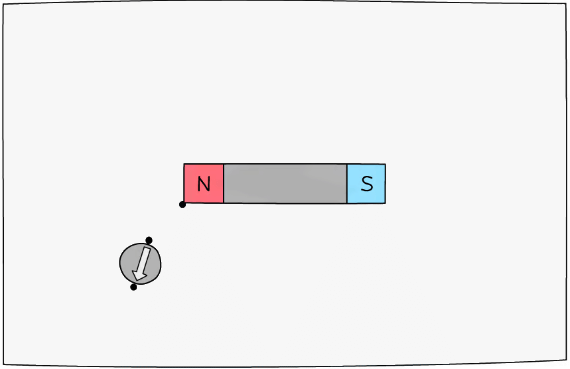
Step 4:
- Keep repeating the previous process until there is a chain of dots going from one end of the magnet to the other
- Then remove the compass, and link the dots using a smooth curve – this will be the magnetic field line
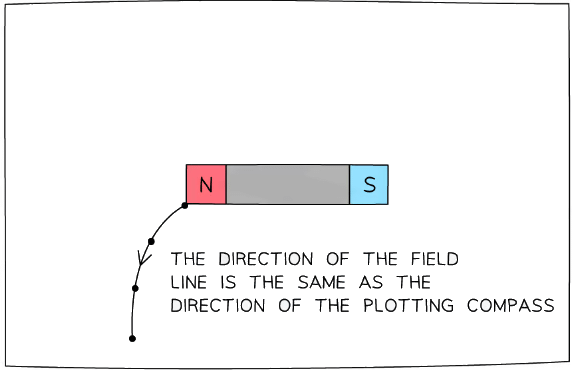
Step 5:
- Repeat the whole process several times to create several other magnetic field lines
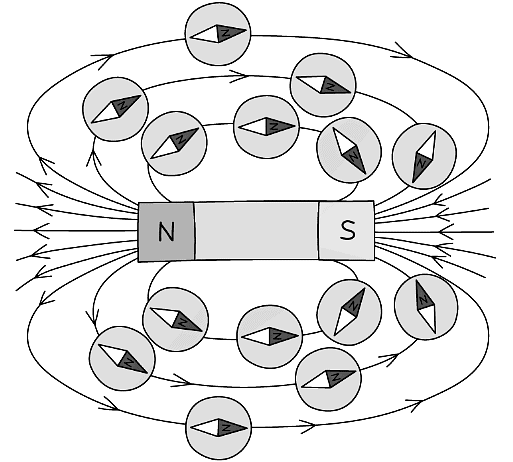 Compasses around a bar magnet show the direction of the magnetic field from north to south
Compasses around a bar magnet show the direction of the magnetic field from north to south
Exam Tip
Remember that the direction of the field line at a point is the same as the direction of the force a north pole would experience at that point
The Earth's Magnetic Field
- On Earth, in the absence of any magnet or magnetic materials, a magnetic compass will always point north
- This is evidence that the core of the Earth is magnetic and creates its own magnetic field
- The Earth's magnetic field is similar to that of a bar magnet
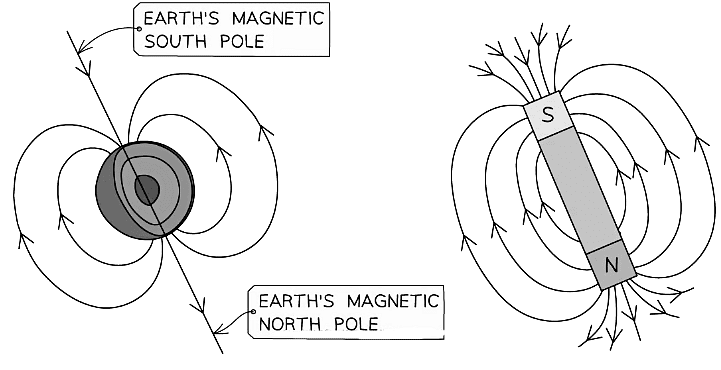 Comparison between the Earth’s Magnetic Field and a Bar Magnet
Comparison between the Earth’s Magnetic Field and a Bar Magnet
- On Earth, the north arrow on a magnetic compass will point towards the geographic North Pole (in the Arctic Ocean)
- This is because the geographic North Pole is a magnetic south pole (the magnetic field lines point into the pole)
- The north pole of the magnetic compass is attracted to the Earth's magnetic south pole
- The geographic South Pole (in Antarctica) is a magnetic north pole (the magnetic field lines point out of the pole)
- The north pole of the magnetic compass is repelled from the Earth's magnetic north pole
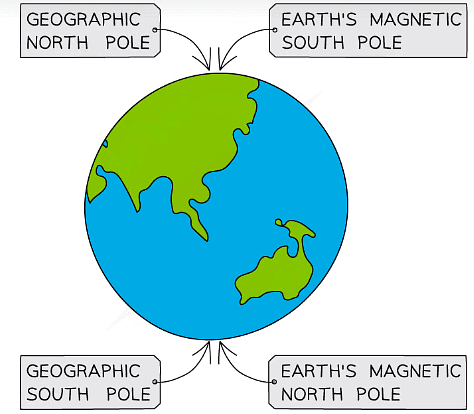 Geographic and Magnetic Poles of the Earth
Geographic and Magnetic Poles of the Earth
Exam Tip
The Earth’s north pole actually acts like the south pole of a magnet: That’s why the north pole of a magnet is attracted to it.
|
122 videos|150 docs|40 tests
|




















