Matrix-Match Type Questions: Carbohydrates, Amino Acids, Polymers & Miscellaneous | JEE Advanced | 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE PDF Download
Each question contains statements given in two columns, which have to be matched. The statements in Column-I are labelled A, B, C and D, while the statements in Column-II are labelled p, q, r, s and t. Any given statement in Column-I can have correct matching with ONE OR MORE statement(s) in Column-II. The appropriate bubbles corresponding to the answers to these questions have to be darkened as illustrated in the following example :
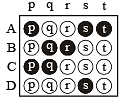
If the correct matches are A-p, s and t; B-q and r; C-p and q; and D-s then the correct darkening of bubbles will look like the given.
Q.1. Match the chemical substances in Column I with type of polymers/type of bonds in Column II. (2007)
Column I Column II
(A) cellulose (p) Natural polymer
(B) nylon-6, 6 (q) Synthetic polymer
(C) protein (r) Amide linkage
(D) sucrose (s) Glycoside linkage
Ans.
Sol. (A) : (p) an d(s) Cellulose is a natural polymer and has a C1 – C4 b-glycosidic linkage.
(B) : (q) and (r) Nylon -6, 6 is a syn thetic polymer of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid and has amide linkages.
(C) : (p) and (r) Proteins are natural polymers of a amino acids joined by amide linkages (peptide bonds).
(D) : (s) Sucrose is a disaccharide of a-D glucose and b-D-fructose and has an a, b-glycosidic linkage.
Q.2. Match the reaction in Column I with appropriate options in Column II. (2010)
| Column-I | Column-II |
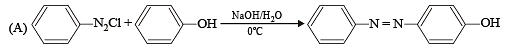 | (p) Racemic mixture |
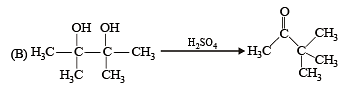 | (q) Addition reaction |
 | (r) Substitution reaction |
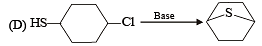 | (s) Coupling reaction |
(t) Carbocation intermediate
Ans. (A) - r,s ; (B) - t ; (C) - p,q ; (D) - r
Sol. (A) – (r), (s) ; (B) – (t) ; (C) – (p), (q) ; (D) – (r)
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
FAQs on Matrix-Match Type Questions: Carbohydrates, Amino Acids, Polymers & Miscellaneous - JEE Advanced - 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE
| 1. What are carbohydrates and why are they important for the body? |  |
| 2. How are amino acids different from carbohydrates? |  |
| 3. What are polymers? How are they related to carbohydrates and amino acids? |  |
| 4. Can you provide examples of carbohydrates and their functions in the body? |  |
| 5. What are some miscellaneous facts about carbohydrates and amino acids? |  |
|
347 docs|185 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|












