Maxima and Minima | Engineering Mathematics - Engineering Mathematics PDF Download
Definition of Maxima and Minima
- The function f is said to have a maximum value in I, if there exists a point c in such that f(c) > f(x), for all x I. The value f(c) is called the maximum value of f(x) in I and the point c is called a point of maximum value of f(x) in I.
- The function f is said to have a minimum value in I, if there exists a point c in I such that f(c) < f(x), for all x I. The value f(c), in this case, is called the minimum value of f(x) in I and the point c, in this case is called a point of minimum value of
f(x) in I. - The function f is said to have an extreme value in I if there exists a point c in I such that f(c) is either maximum value or a minimum value of f(x) in I.
- The number f(c) in this case, is called an extreme value of f(x) in I and the point c is called an extreme point.
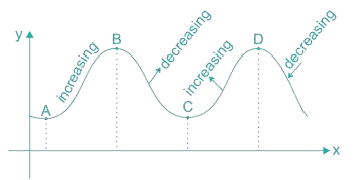 Here Point A, C are Local Minima and B, D are Local Maxima.
Here Point A, C are Local Minima and B, D are Local Maxima.
Notes
- Concave Downwards indicates Maxima of the function i.e.
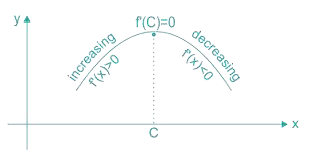
- Concave Upwards indicates Minima of the function i.e.
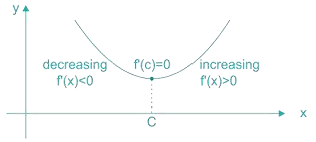
- If f ‘(x) does not change sign as x increases through c, then c is neither a point of Local maxima nor a point of local minima. In fact, such a point is called point of inflection. So the condition for point of inflection is f ‘’(x) = 0
- Similarly the necessary condition for the existing of either Maxima or Minima is f ‘(x) = 0.
Example 1: Find all the points of local maxima and local minima of the function f given by f(x) = 2x3 - 6x2 + 6x + 5
Solution: Given that f(x) = 2x3 - 6x2 + 6x + 5
f ‘(x) = 6x2 - 12x + 6 = 6(x - 1)2
f ‘(x) = 0 at x = 1
Observe that f ‘(x) > 0 for all x R and in particular f ‘(x) > 0, for values close to 1 and to the left and right of 1.
Hence x = 1 is a point of inflection.
Definition of Local Maxima and Minima
Let f be a function defined on an interval I and c I. Let f be twice differentiable at c.
Then
- x = c is a point of local maxima if f ‘(c) = 0 and f ‘'(c) < 0. Then the value f(c) is local maximum value of f(x).
- x = c is a point of local minima if f ‘(c) = 0 and f ‘'(c) > 0. In this case, f(c) is local minimum value of f(x).
Example 2: Find local maximum and local minimum values of the function f given by
f(x) = 3x4 + 4x3 - 12x2 + 12
Solution: f(x) = 3x4 + 4x3 - 12x2 + 12
f ‘(x) = 12x3 + 12x2 – 24x = 12x(x – 1)(x + 2)
f ‘(x) = 0 at
x = 0, x = 1 and x = –2
f ‘'(x) = 36x2 + 24x – 24
f ‘'(0) = –24 < 0
f ‘'(1) = 36 > 0
f ‘'(–2) = 144 – 48 – 24 = 72 > 0
x = 0 is a point of local maxima and local maximum value of f(x) at x = 0 is f(0) = 12 while x = 1 and x = –2 are local minimum points.
Local minimum values are f(1) = 7 and f(–2) = 20
Absolute Maxima and Absolute Minima
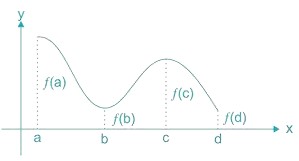
- The graph gives a continuous function defined on a closed interval [a, d]. Observe that the function f has a local minima at x = b and local minimum vales is f(b), the function also has a local maxima at x = c and local maximum values is f(c).
- Also form the graph, it is evident that f has absolute maximum value f(a) and absolute minimum value f(d). Further note that absolute maximum (minimum) value of f(x) is different from local maximum (minimum) value of f(x).
- This absolute maximum value is nothing but global maxima and absolute minimum value is nothing but global minima.
Method to Find Global Maxima and Minima
Step 1: Find the all critical points of the function f(x) in the interval i.e. find points x where either f ‘(x) = 0 or f is not differentiable.Step 2: Take the end points of the interval.
Step 3: At all these points (listed in step 1 and step 2) calculate the values of f(x).
Step 4: Identity the maximum and minimum values of f(x) out of the values will be the absolute maximum (greatest) value of f(x) and the minimum (least) value of f(x).
Example 3: Find the absolute maximum and minimum values of a function f(x) given by f(x) = 2x3 – 15x2 + 36x + 1 in the interval [1, 5]
Solution: f '(x) = 6x2 – 30x + 36 = 6(x – 3)(x – 2)
f '(x) = 0 gives x = 2, x = 3
We shall evaluate the f(x) at x = 2 and x = 3 and at the end points.
f (1) = 24
f(2) = 29
f(3) = 28
f(5) = 56
So absolute maximum value is 56 at x = 5
Absolute minimum value is 24 at x = 1
PYQs: Competitive Exams
Q. Find the maximum value of the following function:
f(x)=−3x2+6x+5
Solution:
We need to find the maximum value of the quadratic function f(x)=−3x2+6x+5.
Step 1: Differentiate the function to find the critical points.
The first derivative of f(x) is:
f′(x)=−6x+6
Step 2: Set the derivative equal to zero to find the critical points.
−6x+6=0
Solving for x, we get:
x=1
Step 3: Check if this critical point is a maximum or minimum by using the second derivative.
The second derivative of f(x) is:
f′′(x)=−6
Since f′′(x)=−6, which is negative, this indicates that the function has a maximum at x=1.
Step 4: Calculate the maximum value by substituting x=1 into the original function.
f(1)=−3(1)2+6(1)+5=−3+6+5=8
Final Answer:
The maximum value of the function is 8.
|
65 videos|129 docs|94 tests
|
FAQs on Maxima and Minima - Engineering Mathematics - Engineering Mathematics
| 1. What are maxima and minima in calculus? |  |
| 2. How do you determine if a critical point is a maximum or minimum? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between absolute and local maxima/minima? |  |
| 4. Can a function have more than one maximum or minimum? |  |
| 5. What role do derivatives play in finding maxima and minima? |  |
















