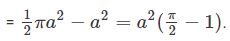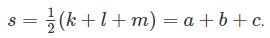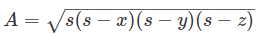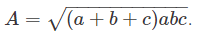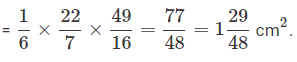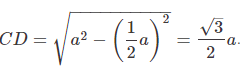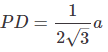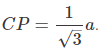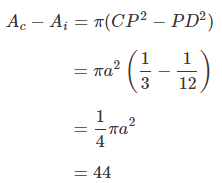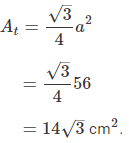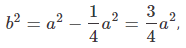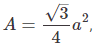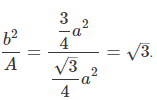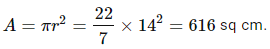Mensuration - Practice Questions | SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year PDF Download
Que1: The area of a rectangle is thrice that of a square. The length of the rectangle is 20 cm and the breadth 3/2 times the length of a side of the square. The side length of the square (in cm) is,
a) 10
b) 20
c) 60
d) 30
Ans: a
Let the side length of the square be x cm.
The area of the square is: x2 cm2The area of the rectangle is three times the area of the square:
Area of rectangle = 3x2 cm2
The length of the rectangle is given as 20 cm, and the breadth of the rectangle is (3/2) times the side length of the square:
Breadth of rectangle = (3/2)x cm
The area of the rectangle is also given by:
Area of rectangle = Length × Breadth
Substituting the values:
3x2 = 20 × (3/2)x
Simplify:
3x2 = 30x
Divide through by x (assuming x ≠ 0):
3x = 30
Solve for x:
x = 10 cm
Thus, the side length of the square is 10 cm.
Que2: The perimeter of a rhombus is 40 cm and its height is 5 cm. Its area in (cm2) is,
a) 45
b) 60
c) 55
d) 50
Ans: d
The perimeter of the rhombus is given as 40 cm.
The perimeter of a rhombus is calculated as: 4 × sideSubstitute the value:
4 × side = 40
Solve for the side length: side = 40 ÷ 4 = 10 cm
The formula for the area of a rhombus is:
Area = Base × Height
Substitute the values:
Area = 10 × 5 = 50 cm2
Thus, the area of the rhombus is 50 cm2.
Que3: The sum of the length, breadth, and height of a rectangular parallelepiped is 24 cm and the length of the diagonal is 15 cm. Then its total surface area is,
a) 351 cm2
b) 256 cm2
c) 265 cm2
d) 315 cm2
Ans: a
Let the length, breadth, and height of the rectangular parallelepiped be l, b, and h, respectively.
The sum of the dimensions is given as:l + b + h = 24 (1)
The length of the diagonal is given as 15 cm, and the formula for the diagonal of a rectangular parallelepiped is:
Diagonal = √(l2 + b2 + h2)
Substituting the diagonal value:
15 = √(l2 + b2 + h2)
Squaring both sides:
l2 + b2 + h2 = 225 (2)
The total surface area of the rectangular parallelepiped is given by:
Total Surface Area = 2(lb + bh + hl)
Using the identity:
(l + b + h)2 = l2 + b2 + h2 + 2(lb + bh + hl)
Substitute the values from equations (1) and (2):
242 = 225 + 2(lb + bh + hl)
576 = 225 + 2(lb + bh + hl)
351 = 2(lb + bh + hl)
lb + bh + hl = 175.5
Now, calculate the total surface area:
Total Surface Area = 2(lb + bh + hl) = 2 × 175.5 = 351 cm2
Que4: In the figure given below two shaded regions are formed in a circle of radius a.
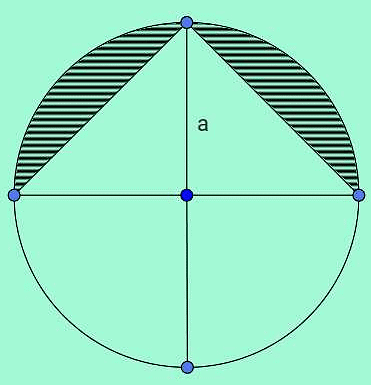
The area of the shaded region is,
a) 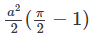
b) a2 (π -1)
c)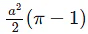
d)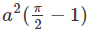
Ans: d
The triangle formed by the horizontal diameter is a right triangle (as all diameters subtend a 90° angle at the periphery) with two inclined sides equal and the vertical radius as the perpendicular bisector of the base.
Area of this triangle = 1/2 x a x 2a = a2
Area of the semi-circle = 1/2πa2
So, area of the shaded region
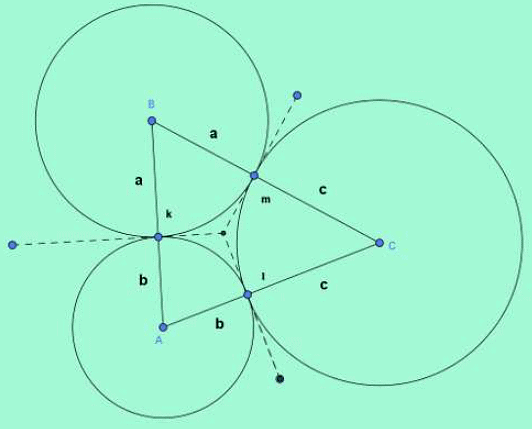
Que5: Three circles of radii a, b and c touch each other externally. The area of the triangle formed by the three centres is,
a) ab+bc+ca
b) 
c) 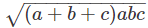
d) none of the above
Ans: c
The following figure represents the solution.
The three sides of the triangle are,
k=a+b
l=b+c, and
m=c+a.
The half perimeter of the triangle is then,
Using the relation of area of triangle with its half perimeter, areawhere x, y and z are the three side lengths.
In our case the area of the triangle is then,
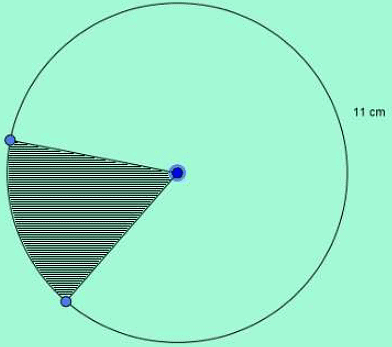
Que6: The circumference of a circle is 11 cm. The area of a sector of the circle subtending an angle of 60° at the periphery (take π = 22/7) is,
a) 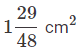
b) 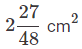
c) 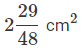
d) 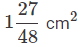
Ans: a
The visualized figure for the problem is as below.
The circumference is,
2πr=11, where r is radius
or, 2×22xr=7×11,
or, r = 4/7 cm
Area subtended by 60º sector is one-sixth of the total area (60º is one-sixth of 360º the whole angle covering the circle).
Thus area of the sector
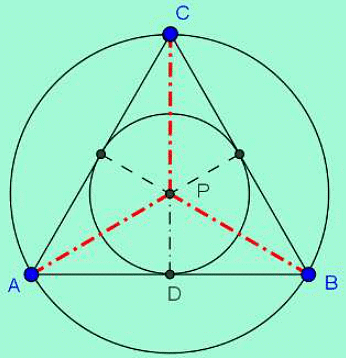
Que7: If the difference between the areas of the circumcircle and incircle of an equilateral triangle is 44 cm2, then the area of the triangle (in cm2, take π=22/7), is,
a) 28 cm2
b) 21 cm2
c) 7√3 cm2
d) 14√3 cm2
Ans: d
The corresponding figure is as below.
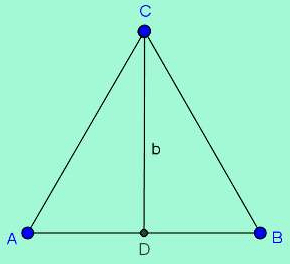
The circumcentre and incentre of the equilateral triangle is the same point P and the perpendicular bisector CD and the other two such bisectors from vertices A and B intersect at P which in this case is also the centroid and CD is a median.Let's assume side length of the triangle as a.
So,
CD being the median, PD is one-third of CD, that is,
Similarly, CP is two-third of CD, that is,
Thus difference in the areas of the circles,Or, a2=56.
The area of the equilateral triangle with side length a is,
Que8: If the area of an equilateral triangle is A and its height is b, the value of b2/A is,
a) 1/3
b) 3
c) √3
d) 1/√3
Ans: c
The following figure depicts the problem situation.If the side length of an equilateral triangle is a, its height is,
And its area is,
So desired expression,
Que9: ABCD is a parallelogram. P and Q are the mid-points of sides BC and CD respectively. If the area of the △ABC is 12 cm2, the area of △APQ is,
a) 9 cm2
b) 12 cm2
c) 10 cm2
d) 8 cm2
Ans: a
The following figure corresponds to visualization of the problem.P being midpoint of BC, it divides the △ABC into two equal parts (height being same, base being half of larger base), that is,
Area of △APC = 1/2 of area of △ABC=6 cm2Similarly, area of △AQC is half of area of △ACD=6 cm2.
So area of quadrilateral APCQ=12 cm2.
Now we only have to find the area of △PCQ and subtract it from this area of the quadrilateral to get the desired area of △APQ.
The other diagonal BD also divides the area of the parallelogram into two equal parts and so, area of the △BCD=12 cm2.
Again BD||PQ and P and Q are the midpoints of the other two sides BC and CD of the △BCD. Thus these two triangles △PCQ and △BCD are similar and each side including the height of the smaller triangle is half its corresponding side and the height of the larger triangle.
This makes the area of the △PCQ = 1/4th of the area of △BCD=3 cm2.
Finally then, the area of △APQ=12−3=9 cm2.
Que10: A wire when bent in the form of a square encloses an area of 484 sq cm. What will be the enclosed area when the same wire is bent into the form of a circle?
a) 616 sq cm
b) 693 sq cm
c) 462 sq cm
d) 539 sq cm
Ans: a
If the side of the square is a cm,
a2=484=222.
So, a=22 cm.
Periphery of the square is then = 4×22=88 cm.
This peripheral length of the wire will then enclose a circular area.
So if the radius of the circular area is r cm,
2πr=88,
Or, r=14 cm.
The area of the circular area is then,
|
1651 videos|1645 docs|920 tests
|
FAQs on Mensuration - Practice Questions - SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year
| 1. What is mensuration in mathematics? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the area of a triangle? |  |
| 3. What is the formula for the volume of a cylinder? |  |
| 4. How do you find the perimeter of a rectangle? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of mensuration problems commonly encountered in exams? |  |