Methods of Research (Brief) - Research Aptitude Notes
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Methods of Research? |

|
| Methods of Research |

|
| Historical Research Method |

|
| Descriptive Research Method |

|
| Experimental Method of Research |

|
What are Methods of Research?
Methods of research are systematic approaches used to collect, analyze, and interpret data, encompassing techniques such as controlled experiments to determine causality, surveys for gathering quantitative or qualitative data from large populations.
These methods encompass the tools and procedures utilized by researchers to investigate and address their research inquiries effectively.
 Research MethodsPrimary Aim: to resolve a particular issue or query by establishing a connection between the known data and the unidentified components of the problem.
Research MethodsPrimary Aim: to resolve a particular issue or query by establishing a connection between the known data and the unidentified components of the problem.
- Research methods are crucial as they provide a systematic approach to gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data, thereby facilitating the generation of reliable and valid results.
- Researchers rely on these methodologies to structure their investigations and ensure that their findings are methodologically sound and credible.
- Significance: Ensures a systematic and methodical approach to research, leading to credible outcomes.
Methods of Research
However, keeping this in view, research methods can be put into the following categories:
- Historical Research Method
- Descriptive Research Method
- Experimental Method of Research
- Action Research
- Quantitative Research Method
- Qualitative Research Method
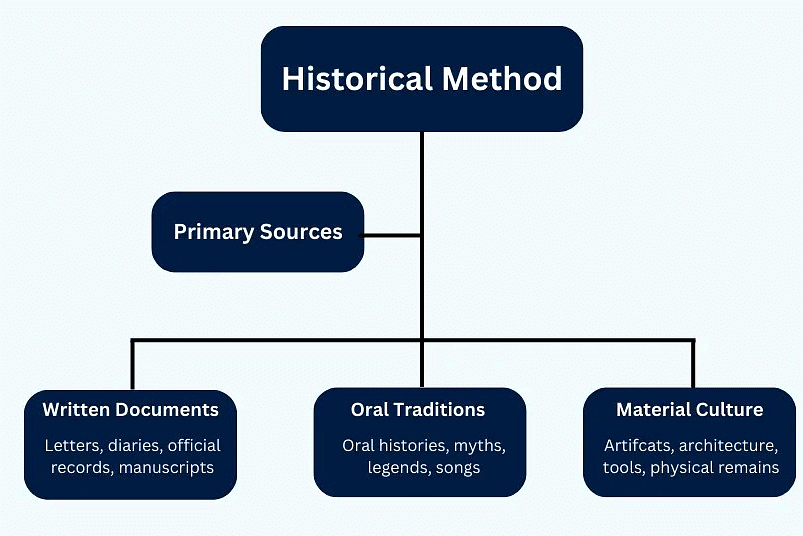
Historical Research Method
Historical research involves the collection and objective evaluation of data related to past occurrences to test hypotheses regarding causes, effects, or trends of events. This aids in explaining present events and anticipating future ones.
Key Elements:
- It delves into causality between events.
- Records achievements of individuals and organizations.
- Enhances comprehension of current issues.
- Seeks to interpret events shaping our world.
Steps of Historical Research:
- Identify an idea, topic, or research question.
- Conduct a background literature review.
- Refine research ideas and questions.
- Determine the use of historical method.
- Identify primary and secondary data sources.
- Evaluate the authenticity and accuracy of source materials.
- Analyze data and develop a narrative exposition of findings.
Objectives of Historical Research:
- Discover unknown events.
- Study cause-and-effect relationships.
- Evaluate accomplishments of individuals, institutions, and organizations.
- Provide understanding of immediate concerns.
- Understand events shaping specific situations.
Methods of Historical Research:
- Archival Data: Primary sources like official documents found in archives, museums, etc.
- Secondary Sources: Works of other historians.
- Running Records: Documentaries by private or non-profit organizations.
- Recollections: Sources like autobiographies, diaries, or memoirs.
Example: In historical research, a scholar studying the American Civil War might analyze letters from soldiers (primary source) and books written by historians (secondary source) to understand the conflict's impact on society.
Descriptive Research Method
It is a research method that aims to depict the characteristics of the population or phenomenon under study. Focuses on the "what" of the research subject rather than the "why," emphasizing description over causality.

- Does not make predictions or establish cause-and-effect relationships.
- Utilizes quantitative techniques to gather quantifiable data for statistical analysis.
- Commonly employed in market research to understand and depict demographic segments.
- Variables in descriptive research remain unaffected as it relies on observational methods.
- Researchers do not control the behavior of variables, as they are studied as they naturally occur.
- Typically involves cross-sectional studies, analyzing different sections of the same group simultaneously.
- Data collected through this method can be utilized by other research approaches.
Descriptive research provides a snapshot of a particular phenomenon or population at a specific point in time without manipulating variables. For instance, a study describing the buying patterns of customers in a certain region would fall under descriptive research. Researchers would collect data on what customers buy, how often, and at what price, without delving into why these patterns occur.
Types of Descriptive Research
Descriptive research is categorized into various types based on the approach used during the research process.
1. Descriptive-Survey Research: This type of research involves utilizing surveys to collect data on different subjects. The primary objective is to understand the extent to which various conditions exist among these subjects.

- Example: A researcher aims to assess the qualifications of employed professionals in India. To achieve this, the researcher employs a survey as the research instrument. Each survey item related to qualifications requires a binary Yes/No response.
2. Descriptive-Normative Survey: The descriptive-normative survey is an extension of the descriptive survey, incorporating a normative element.
- Purpose: It involves comparing the study results with a norm or standard to evaluate performance or outcomes.
- Scenario: An organization wants to assess the proficiency of its employees in a specific skill.
- Implementation: The organization administers a skills test to the employees to gauge their competency levels.
- Assessment: The results of the skills test are then compared against an established norm or benchmark to determine the effectiveness of the employees' skills.
- Skill test as evaluation tools : The skill tests serve as the assessment mechanism in this scenario, where the outcomes of these tests are compared against the established norms for each specific role.
3. Descriptive-Status:
This method involves a quantitative description approach that aims to address queries pertaining to real-world situations. For instance, consider a researcher investigating the correlation between the income levels of employees within a company and their job performance.
4. Descriptive-Analysis Method:
This research technique delves into a subject by dissecting it into distinct segments. To illustrate, imagine the creation of a questionnaire designed to scrutinize the job responsibilities of employees earning comparable salaries and working in identical roles.
5. Descriptive-Comparative Research
In descriptive-comparative research, the researcher examines two variables without manipulating them and establishes a formal procedure to determine which variable is superior. For instance, an examination body may seek to identify the more effective method of conducting tests, such as paper-based versus computer-based tests.
Characteristics of Descriptive Research
- Descriptive research employs a quantitative research approach by gathering quantifiable data for statistical analysis of a population sample.
- It can also utilize qualitative research methods to effectively describe the research problem, as descriptive research aims to explain rather than explore or experiment.
- In descriptive research, researchers do not have control over variables as they do in experimental research.
- The findings of descriptive research can be further analyzed and applied in other research methodologies.
Overall, descriptive-comparative research provides valuable insights by comparing variables without manipulation, enabling a better understanding of different methods or approaches.
Experimental Method of Research
The experimental method is a systematic and scientific approach to research where the researcher manipulates variables while controlling and measuring changes in other variables.
- Researchers manipulate stimuli, treatments, or environmental conditions to observe how subjects' conditions or behaviors are affected or changed.
- An experiment involves comparing the effects of a specific treatment with a different treatment or no treatment.
- It is the most systematic method for establishing cause-effect relationships in individuals' behavior.
- The findings from experiments are subject to critical examination and verification.
- One limitation of the experimental method is that human behavior is changeable, and identical behavior may not occur under the same conditions at different times.
- This method can be costly and time-consuming.
Key Elements:
- Systematic and scientific approach to research
- Manipulation of variables
- Control and measurement of changes
- Comparison of treatments
- Establishing cause-effect relationships
- Critical examination of findings
- Limitations: variability in human behavior, cost, and time constraints
Example: In a study investigating the effects of caffeine on memory retention, researchers may manipulate the amount of caffeine given to participants and measure how it impacts their ability to recall information. By comparing the performance of participants who received different doses of caffeine or a placebo, researchers can determine the causal relationship between caffeine intake and memory retention.
|
12 videos|38 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Methods of Research (Brief) - Research Aptitude Notes
| 1. What are the different methods of research? |  |
| 2. How can historical research method be used in research studies? |  |
| 3. What is the purpose of descriptive research method? |  |
| 4. How does experimental method of research differ from other research methods? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to choose the right research method for a study? |  |
















