Microkernel & Monolithic Kernel | Operating System - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Microkernel in Operating Systems
Kernel is the core part of an operating system which manages system resources. It also acts like a bridge between application and hardware of the computer. It is one of the first programs loaded on start-up (after the Bootloader).
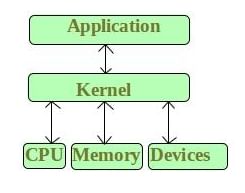
Kernel mode and User mode of CPU operationThe CPU can execute certain instruction only when it is in the kernel mode. These instruction are called privilege instruction. They allow implementation of special operation whose execution by the user program could interface with the functioning of operating system or activity of another user program. For example, instruction for managing memory protection.
- The operating system puts the CPU in kernel mode when it is executing in the kernel so, that kernel can execute some special operation.
- The operating system puts the CPU in user mode when a user program is in execution so, that user program cannot interface with the operating system program.
- User-level instruction does not require special privilege. Example are ADD,PUSH,etc.
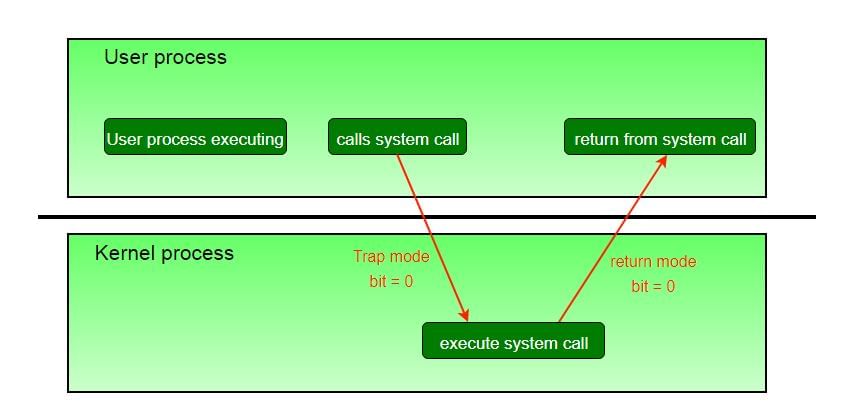
The concept of modes can be extended beyond two, requiring more than a single mode bit CPUs that support virtualization use one of these extra bits to indicate when the virtual machine manager, VMM, is in control of the system. The VMM has more privileges than ordinary user programs, but not so many as the full kernel.
System calls are typically implemented in the form of software interrupts, which causes the hardware’s interrupt handler to transfer control over to an appropriate interrupt handler, which is part of the operating system, switching the mode bit to kernel mode in the process. The interrupt handler checks exactly which interrupt was generated, checks additional parameters ( generally passed through registers ) if appropriate, and then calls the appropriate kernel service routine to handle the service requested by the system call.
User programs’ attempts to execute illegal instructions ( privileged or non-existent instructions ), or to access forbidden memory areas, also generate software interrupts, which are trapped by the interrupt handler and control is transferred to the OS, which issues an appropriate error message, possibly dumps data to a log ( core ) file for later analysis, and then terminates the offending program.
What is Microkernel?
Microkernel is one of the classification of the kernel. Being a kernel it manages all system resources. But in a microkernel, the user services and kernel services are implemented in different address space. The user services are kept in user address space, and kernel services are kept under kernel address space, thus also reduces the size of kernel and size of operating system as well.
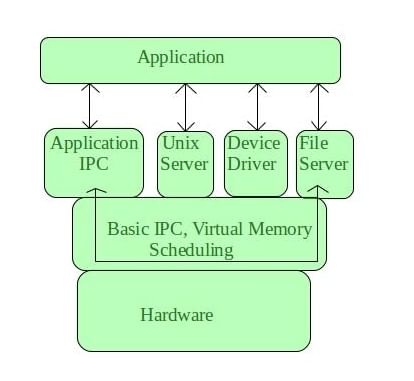
It provides minimal services of process and memory management. The communication between client program/application and services running in user address space is established through message passing, reducing the speed of execution microkernel. The Operating System remains unaffected as user services and kernel services are isolated so if any user service fails it does not affect kernel service. Thus it adds to one of the advantages in a microkernel. It is easily extendable i.e. if any new services are to be added they are added to user address space and hence requires no modification in kernel space. It is also portable, secure and reliable.
Microkernel Architecture
Since kernel is the core part of the operating system, so it is meant for handling the most important services only. Thus in this architecture only the most important services are inside kernel and rest of the OS services are present inside system application program. Thus users are able to interact with those not-so important services within the system application. And the microkernel is solely responsible for the most important services of operating system they are named as follows:
- Inter process-Communication
- Memory Management
- CPU-Scheduling
Advantages of Microkernel
- The architecture of this kernel is small and isolated hence it can function better.
- Expansion of the system is easier, it is simply added in the system application without disturbing the kernel.
Monolithic Kernel and key differences from Microkernel
Apart from microkernel, Monolithic Kernel is another classification of Kernel. Like microkernel this one also manages system resources between application and hardware, but user services and kernel services are implemented under same address space. It increases the size of the kernel, thus increases size of operating system as well.
This kernel provides CPU scheduling, memory management, file management and other operating system functions through system calls. As both services are implemented under same address space, this makes operating system execution faster.
Below is the diagrammatic representation of Monolithic Kernel:
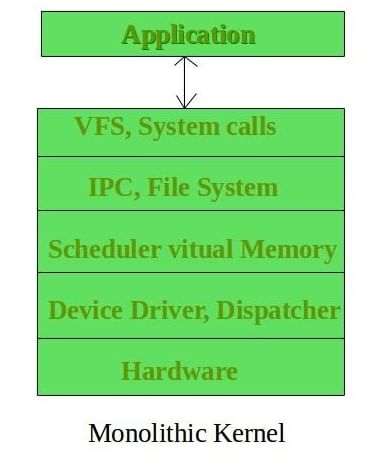
If any service fails the entire system crashes, and it is one of the drawbacks of this kernel. The entire operating system needs modification if user adds a new service.
Advantages of Monolithic Kernel
- One of the major advantage of having monolithic kernel is that it provides CPU scheduling, memory management, file management and other operating system functions through system calls.
- The other one is that it is a single large process running entirely in a single address space.
- It is a single static binary file. Example of some Monolithic Kernel based OSs are: Unix, Linux, Open VMS, XTS-400, z/TPF.
Disadvantages of Monolithic Kernel
- One of the major disadvantage of monolithic kernel is that, if anyone service fails it leads to entire system failure.
- If user has to add any new service. User needs to modify entire operating system.
Key differences between Monolithic Kernel and Microkernel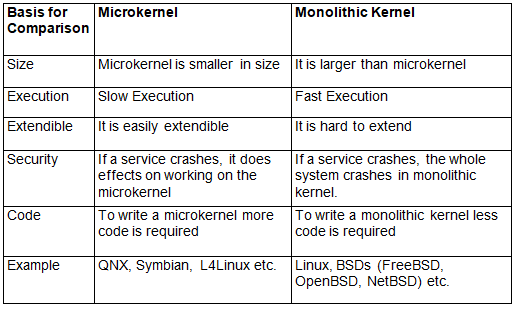
Difference between User Level thread and Kernel Level thread
|
10 videos|99 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Microkernel & Monolithic Kernel - Operating System - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What is a microkernel in operating systems? |  |
| 2. How does a microkernel differ from a monolithic kernel? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of using a microkernel architecture? |  |
| 4. Are there any disadvantages of using a microkernel architecture? |  |
| 5. Which operating systems use a microkernel architecture? |  |


















