Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 2
| Table of contents |

|
| Microorganisms |

|
| Where do Microorganisms Live? |

|
| Microorganisms and Us |

|
| Harmful Microorganisms |

|
| Food Preservation |

|
| Nitrogen Fixation |

|
| Nitrogen Cycle |

|
Introduction
We’re surrounded by more than just the plants and animals we can see—there are also tiny living organisms called microorganisms or microbes. Ever noticed how moist bread in the rainy season develops greyish-white patches? If you look closely with a magnifying glass, you’ll spot tiny black dots. But what are these, and where do they come from? Let's explore the hidden world of microbes!

Microorganisms
Microorganisms, also known as microbes, are tiny living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye and can only be observed with a microscope. They can be found in water, soil, air, and even the human body. Microorganisms can exist as single-celled organisms or as colonies of cells.
- Microorganisms are classified into four major groups. These groups are: bacteria, fungi, protozoa and some algae.
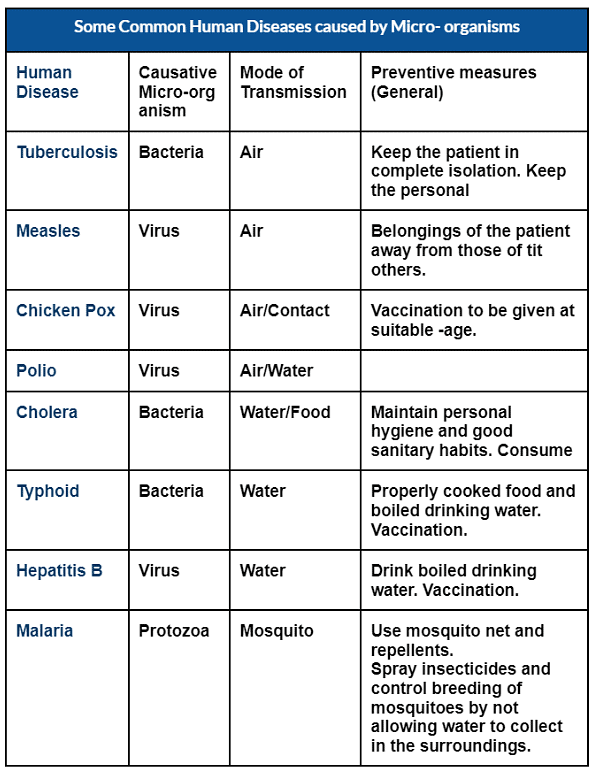
- Diseases like dysentery and malaria are caused by protozoa(protozoans)
- Typhoid and Tuberculosis (TB) are bacterial diseases
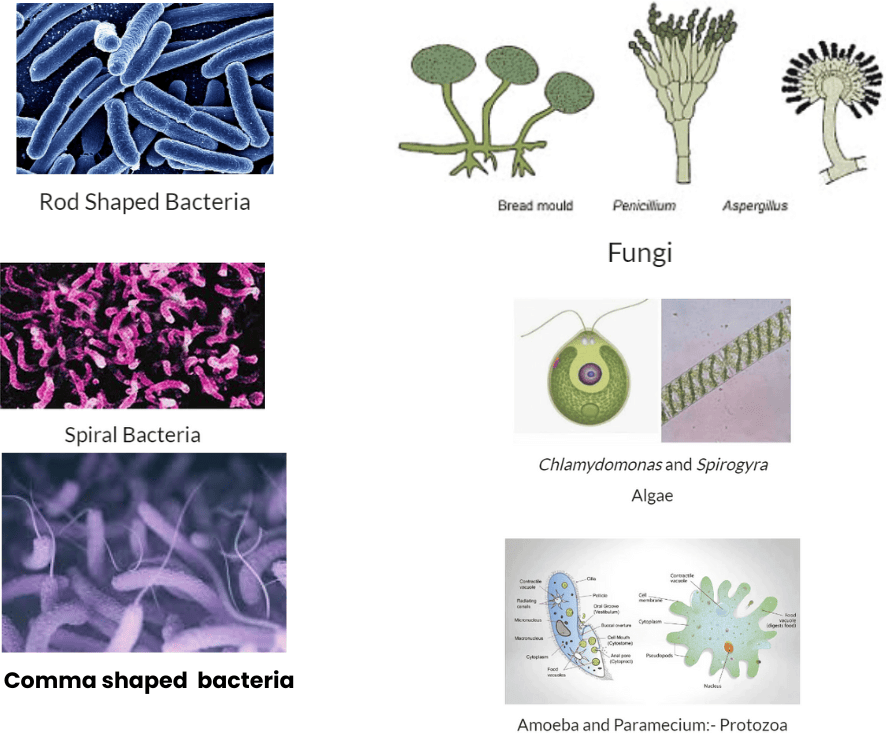 Microbes:- Bacteria, Fungi, algae, Protozoa
Microbes:- Bacteria, Fungi, algae, Protozoa
Viruses
Viruses are also microscopic. They, however, reproduce only inside the cells of the host organism, which may be a bacterium, plant or animal.
- Common ailments like cold, influenza (flu) and most coughs are caused by viruses.
- Serious diseases like polio and chicken pox are also caused by viruses.
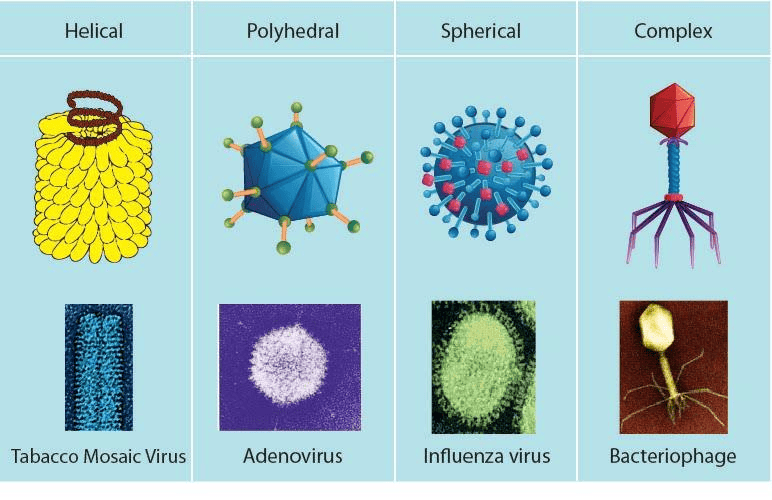 Viruses
Viruses
Where do Microorganisms Live?
Microorganisms may be single celled (bacteria, some algae and protozoa) or multi-cellular (algae and fungi) can survive under all types of environment, ranging from ice-cold climate to hot springs and deserts to marshy lands.- They are also found inside the bodies of other organisms including humans.
- Growth of some microorganisms depends on other organisms while other organisms exist freely.
- Microorganisms like amoeba can live alone, while fungi and bacteria may live in colonies.
Microorganisms and Us
Microorganisms play an important role in our lives. Some of them are beneficial in many ways whereas some others are harmful and cause diseases.
 Fig: Viruses
Fig: Viruses
Friendly Microorganisms
Friendly microorganisms, also known as beneficial microbes, are microorganisms that live in our body or environment and provide us with health benefits. They aid in digestion, boost the immune system, and help in nutrient absorption, among other functions.
Microorganisms are used for various purposes.
(i) Making of Curd and Bread
Curd and Bacteria
- Curd is formed with the help of microorganisms, particularly the bacterium Lactobacillus.
- Lactobacillus multiplies in milk and converts it into curd.
- Bacteria play a role in the production of cheese, pickles, and other food items.
- Curd is an important ingredient in rava (sooji) idlis and bhaturas.
- Bacteria and yeast aid in the fermentation of rice idlis and dosa batter.
Yeast and Fermentation
- Yeast reproduces quickly and produces carbon dioxide during respiration.
- The gas bubbles created by yeast increase the volume of dough.
- This process is used in the baking industry for making breads, pastries, and cakes.
(ii) Commercial Uses of Microorganisms
Microorganisms, particularly yeasts and bacteria, are extensively utilized in various industries for their ability to produce valuable substances.
Here are the key commercial applications:
- Production of Alcohol: Yeast is primarily used for the large-scale production of alcohol and wine.
- Fermentation: The process of converting sugar into alcohol is known as fermentation. During fermentation, yeast consumes natural sugars, producing alcohol and carbon dioxide.
- Historical Significance: The process of fermentation was discovered by Louis Pasteur in 1857, marking a significant advancement in microbiology.
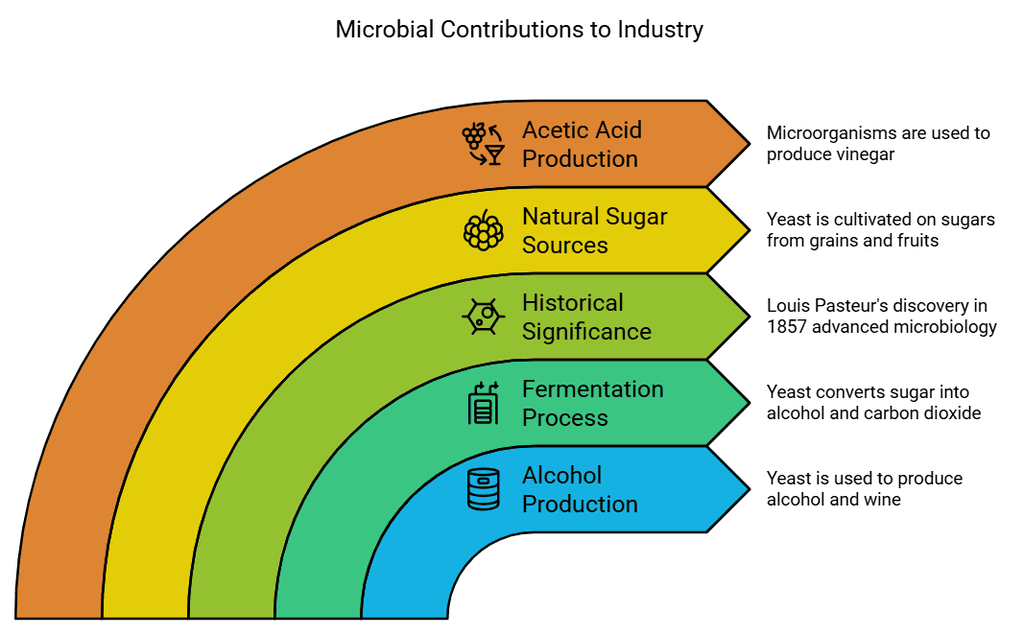
- Sources of Natural Sugars: For fermentation, yeast is cultivated on natural sugars derived from various sources, including:
Grains: Barley, wheat, and rice.
Fruits: Crushed fruit juices provide sugars essential for fermentation. - Production of Acetic Acid (Vinegar): Microorganisms also play a role in the production of acetic acid, which is the main component of vinegar.
 Production of alcohol with the help of yeast
Production of alcohol with the help of yeast
(iii) Medicinal Uses of Microorganisms
Microorganisms play a crucial role in the field of medicine, particularly in the development of antibiotics.
Here are the key points regarding their medicinal applications:
- Antibiotics and Their Discovery: When we become ill, doctors often prescribe antibiotics, which are derived from microorganisms.
- Discovery of Penicillin: In 1929, Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin while studying disease-causing bacteria. He noticed that a green mold in his culture plate inhibited bacterial growth and even killed some bacteria. This mold was later developed into the antibiotic penicillin.
- Function of Antibiotics: Antibiotics are medicines produced from bacteria and fungi that kill or inhibit the growth of disease-causing microorganisms.
- Common antibiotics include:
1. Streptomycin
2. Tetracycline
3. Erythromycin
These medications are effective against various bacterial infections but are ineffective against viral infections, such as colds and flu. - Cautions with Antibiotic Use: Antibiotics should only be taken under the guidance of a qualified doctor to ensure proper usage.
- Misuse of antibiotics can lead to:
Reduced effectiveness of the medication when truly needed in the future.
Elimination of beneficial bacteria in the body, disrupting natural flora. - Applications in Agriculture: Antibiotics are also added to the feed of livestock and poultry to prevent microbial infections in animals. Additionally, microorganisms are utilized in controlling various plant diseases, contributing to agricultural health.
(iv) What are Vaccines?
Vaccines are biological preparations that help the immune system recognize and fight disease-causing microbes.
Immune Response
- When disease-causing microbes invade the body, the immune system produces antibodies to combat these invaders.
- Once the body has fought off the infection, it retains a memory of how to combat that specific microbe if it re-enters in the future.
Mechanism of Vaccination
- Vaccines often contain dead or weakened forms of pathogens (disease-causing microbes).
- When injected into a healthy individual, these inactive microbes stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies.
- The antibodies remain in the body, providing long-term protection against future infections from the same pathogen.
Preventable Diseases
- Vaccination can prevent several serious diseases, including:
- Cholera
- Tuberculosis
- Smallpox
- Hepatitis
Edward Jenner discovered the vaccine for smallpox in 1798.
(v) Increasing Soil Fertility
- Some bacterias and blue-green algae are able to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere to enrich soil with nitrogen and increase its fertility.
- These microbes are commonly called biological nitrogen fixers.
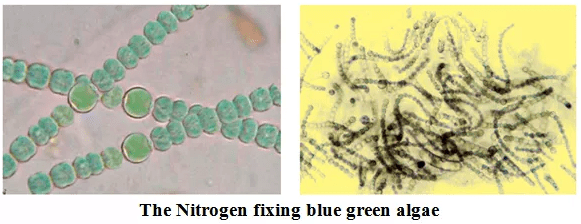
(vi) Cleaning the Environment
- Microbes are responsible to decompose the plant waste and turn into manure and the nutrients released during this process can be utilized again by plants.
- Dead organic matter, such as decaying plants and animals, is often found on the ground.
- Microorganisms decompose this organic waste and convert it into simpler substances.
- These substances are then utilized by other plants and animals.
- Microorganisms can be used to break down harmful and smelly substances, contributing to environmental cleanup.
Harmful Microorganisms
- Microorganisms are harmful in many ways. Some of the microorganisms cause diseases in human beings, plants and animals. Such disease-causing microorganisms are called pathogens.
- Some microorganisms spoil food, clothing and leather.
1. Disease-causing Microorganisms in Humans
Pathogens can enter the human body through:
- Air: Breathing contaminated air.
- Water: Drinking contaminated water.
- Food: Consuming contaminated food.
- Direct Contact: Touching an infected person or surfaces.
Communicable Diseases: Diseases that can spread from an infected person to a healthy person via air, water, food, or physical contact are known as communicable diseases.
Examples:
- Cholera
- Common Cold
- Chicken Pox
- Tuberculosis
Transmission Mechanism: For instance, when a person with a common cold sneezes, fine droplets containing thousands of viruses are released into the air. A healthy person may inhale these droplets, leading to infection.
 Female Aedes mosquito
Female Aedes mosquito
Carriers of Disease:
Certain insects and animals can carry disease-causing microbes:
Housefly:
- Flies land on garbage and animal waste, picking up pathogens. When they touch uncovered food, they can transfer these pathogens to humans.
Mosquitoes:
- Female Aedes Mosquito: Carries the dengue virus.
- Female Anopheles Mosquito: Carries the malaria parasite.
2. Disease-causing Microorganisms in Animals
- Several microorganisms not only cause diseases in humans and plants, but also in other animals.
For example, anthrax is a dangerous human and cattle disease caused by a bacterium. Foot and mouth disease of cattle is caused by a virus.
Robert Köch (1876) discovered the bacterium (Bacillus anthracis) which causes anthrax disease.
3. Disease-causing Microorganisms in Plants
- Several microorganisms cause diseases in plants like wheat, rice, potato, sugarcane, orange, apple and others.
- The diseases reduce the yield of crops. They can be controlled by the use of certain chemicals which kill the microbes.
 Some Common Plant Diseases caused by Microorganisms
Some Common Plant Diseases caused by Microorganisms
Food Poisoning
- Food poisoning could be due to the consumption of food spoiled by some microorganisms. Microorganisms that grow on our food sometimes produce toxic substances.
- These make the food poisonous, causing serious illness and even death. So, it is very important that we preserve food to prevent it from being spoiled.
Food Preservation
Microorganisms spoil our food. Spoiled food emits a bad smell and has a bad taste and changes colour.  Fermentation way of preserving foods
Fermentation way of preserving foods
1. Chemical Method
- Salts and edible oils are the common chemicals generally used to check the growth of microorganisms.
- Therefore they are called preservatives. We add salt or acid preservatives to pickles to prevent the attack of microbes. Sodium benzoate and sodium meta-bisulfite are common preservatives.
- These are also used in the jams and squashes to check their spoilage.
(i) Preservation by Common Salt
- Common salt has been used to preserve meat and fish for ages.
- Meat and fish are covered with dry salt to check the growth of bacteria.
- Salting is also used to preserve amla(Indian Gooseberry), raw mangoes, tamarind, etc.
 Tamarind
Tamarind
(ii) Preservation by Sugar
- Jams, jellies and squashes are preserved by sugar.
- Sugar reduces the moisture content which inhibits the growth of bacteria that spoil food.
(iii) Preservation by Oil and Vinegar
- Use of oil and vinegar prevents spoilage of pickles because bacteria cannot live in such an environment.
- Vegetables, fruits, fish and meat are often preserved by this method.
2. Heat and Cold Treatments
- You must have observed your mother boiling milk before it is stored or used. Boiling kills many microorganisms.
- Similarly, we keep our food in the refrigerator. Low temperature inhibits the growth of microbes.
- Pasteurized milk can be consumed without boiling as it is free from harmful microbes. The milk is heated to about 70°C for 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilled and stored. By doing so, it prevents the growth of microbes.
This process was discovered by Louis Pasteur. It is called pasteurization.
3. Storage and Packing
- These days dry fruits and even vegetables are sold in sealed air tight packets to prevent the attack of microbes.
Nitrogen Fixation
- Bacterium Rhizobium, which plays a crucial role in nitrogen fixation for leguminous plants like beans and peas. Rhizobium resides in the root nodules of these plants, forming a symbiotic relationship with them. Additionally, nitrogen fixation can occur through lightning. Despite these processes, the total amount of nitrogen in the atmosphere remains constant.
 Rhizobium
Rhizobium
Nitrogen Cycle
- Our atmosphere has 78% nitrogen gas. Nitrogen is one of the essential constituents of all living organisms as part of proteins, chlorophyll, nucleic acids and vitamins.
- Certain bacteria and blue-green algae present in the soil fix nitrogen from the atmosphere and convert it into compounds of nitrogen.
- Once nitrogen is converted into these usable compounds, it can be utilized by plants from the soil through their root system. Nitrogen is then used for the synthesis of plant proteins and other compounds. Animals feeding on plants get these proteins and other nitrogen compounds.
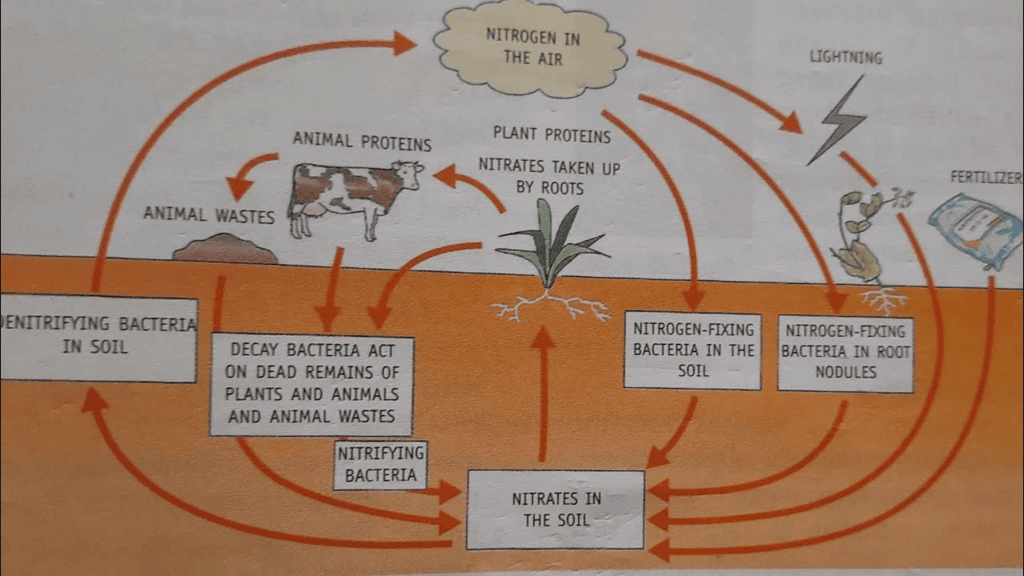
- When plants and animals die, bacteria and fungi present in the soil convert the nitrogenous wastes into nitrogenous compounds to be used by plants again.
- Certain other bacteria convert some part of them to nitrogen gas which goes back into the atmosphere. As a result, the percentage of nitrogen in the atmosphere remains more or less constant.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Related to Microorganisms: Friend or Foe
1. What are microorganisms?
Ans. Microorganisms are tiny living organisms that are invisible to the naked eye, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. They play an important role in our daily life, ranging from the decomposition of organic matter to production of food and medicines.
2. What are the harmful effects of microorganisms?
Ans. Microorganisms can cause various diseases such as typhoid, cholera, tuberculosis, and influenza. They can also spoil food and cause food poisoning. In addition, they can damage crops and cause economic losses.
3. What are the beneficial effects of microorganisms?
Ans. Microorganisms are beneficial in various ways such as producing antibiotics, enzymes, and vitamins. They also help in decomposition of organic matter and soil enrichment. Moreover, they are used in various industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology.
4. How can we control the harmful effects of microorganisms?
Ans. We can control the harmful effects of microorganisms by maintaining proper hygiene, sanitation, and food safety. We can also use antibiotics and vaccines to treat and prevent diseases caused by microorganisms. Additionally, we can use various preservation methods such as canning, refrigeration, and pasteurization to prevent spoilage of food.
5. How can we promote the beneficial effects of microorganisms?
Ans. We can promote the beneficial effects of microorganisms by using them in various industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology. We can also use them for composting and soil enrichment. Moreover, we can promote research on microorganisms to discover new applications and benefits.
|
136 videos|530 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 2
| 1. What are microorganisms and where can they be found? |  |
| 2. How do microorganisms affect human health? |  |
| 3. What is food preservation and how do microorganisms play a role in it? |  |
| 4. What is nitrogen fixation and why is it important? |  |
| 5. Can you explain the nitrogen cycle and its significance? |  |





















