Microsoft Office | Computer Awareness and Proficiency - SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Microsoft Word |

|
| Microsoft Excel |

|
| Microsoft PowerPoint |

|
| Microsoft Access |

|
| Microsoft Outlook |

|
Microsoft Office (MS-Office), developed by Microsoft in 1988, is a suite of software designed primarily for office tasks. To access any MS-Office program, you can use the Start button.
MS-Office includes five main applications:
- MS-Word (Word Processing Software)
- MS-Excel (Spreadsheet Software)
- MS-PowerPoint (Presentation Software)
- MS-Access (Database Management Software)
- MS-Outlook (E-mail Client)
Microsoft Word
 MS-Word is a popular word processing application used for creating and editing various types of documents, such as posters, reports, letters, brochures, and web pages. Documents are typically smaller than 45 KB. To start MS-Word, you can use one of these methods:
MS-Word is a popular word processing application used for creating and editing various types of documents, such as posters, reports, letters, brochures, and web pages. Documents are typically smaller than 45 KB. To start MS-Word, you can use one of these methods:
- Click the Start button, then select Run. In the Run dialog box, type
winwordand press Enter. - Click Start → All Programs → Microsoft Office → Microsoft Word 2010.
By default, a new document in MS-Word is named Document1.docx, where .docx is the file extension for MS-Word documents.
Components of Microsoft Word
Title Bar: Displays the application and file names. It has three control buttons: Minimize (reduces the window but keeps the application active), Restore (resizes the window to its original size), and Close (closes the window).
Standard Toolbar: Shows icons for common functions like Open, Print, Save, etc.
Ribbon: A set of tool panels organized into tabs at the top of the screen, each providing different tools and commands:
- Home Tab: Includes Clipboard, Font, Paragraph, Styles, and Editing.
- Insert Tab: Contains options for Pages, Tables, Illustrations, Links, Header & Footer, Text, and Symbols.
- Page Layout Tab: Features Themes, Page Setup, Page Background, Paragraph, and Arrange.
- References Tab: Provides Table of Contents, Footnotes, Citations & Bibliography, Captions, Index, and Table of Authorities.
- Mailings Tab: Offers Create, Start Mail Merge, Write & Insert Fields, Preview Results, and Finish.
- Review Tab: Includes Proofing, Language, Comments, Tracking, Changes, Compare, and Protect.
- View Tab: Contains Document Views, Show, Zoom, Window, and Macros
Ruler: Appears at the top of the document window and helps format horizontal or vertical alignment. It includes:
- Horizontal Ruler: Indicates document width and sets left and right margins.
- Vertical Ruler: Indicates document height and sets top and bottom margins.
Status Bar: Displays information such as page number, current page, template, column number, and line number.
Work Area: The main area where you type text, also known as the workplace.
Cursor: Also called the insertion pointer, it shows where text or other items will be placed when typed or inserted.
Features of Microsoft Word
- Text Editing: Allows for editing, adding, and deleting text, including cut, copy, and paste functions.
- Format Text: Provides options to modify text appearance with various styles like bold, italic, and underline.
- Indentation: Controls the distance between text and page margins with positive, hanging, and negative indentation options.
- Page Orientation: Offers two views for printed text: Portrait (vertical) and Landscape (horizontal).
- Find & Replace: Enables users to replace text throughout the document with alternative text.
- Spell Check: Automatically checks for spelling errors and offers suggestions for corrections.
- Thesaurus: Provides synonyms for words to enhance vocabulary.
- Bullets and Numbering: Used to create and manage lists with bullet points or numbers.
- Graphics: Allows insertion of drawings and images to enhance documents.
- Object Linking and Embedding (OLE): Facilitates sharing information between programs through embedded objects like charts, equations, and multimedia.
Scroll Bars: Enable navigation within the document:
- Horizontal Scroll Bar: Located above the status bar, moves left and right.
- Vertical Scroll Bar: Located along the right side, moves up and down.
Save a Document: To save a document, use one of these methods:
- Click Save from the File menu.
- Select the Save button on the Standard toolbar.
- Press Ctrl + S on your keyboard.
Tit-Bits
- MS-Word debuted in 1983 as Multi-Tool Word for Xenix Systems.
- In MS-Word, paragraphs are typically aligned to the left by default.
- MS-Word includes a collection of predefined errors related to typing, spelling, capitalization, and grammar that Auto-correct can identify and fix.
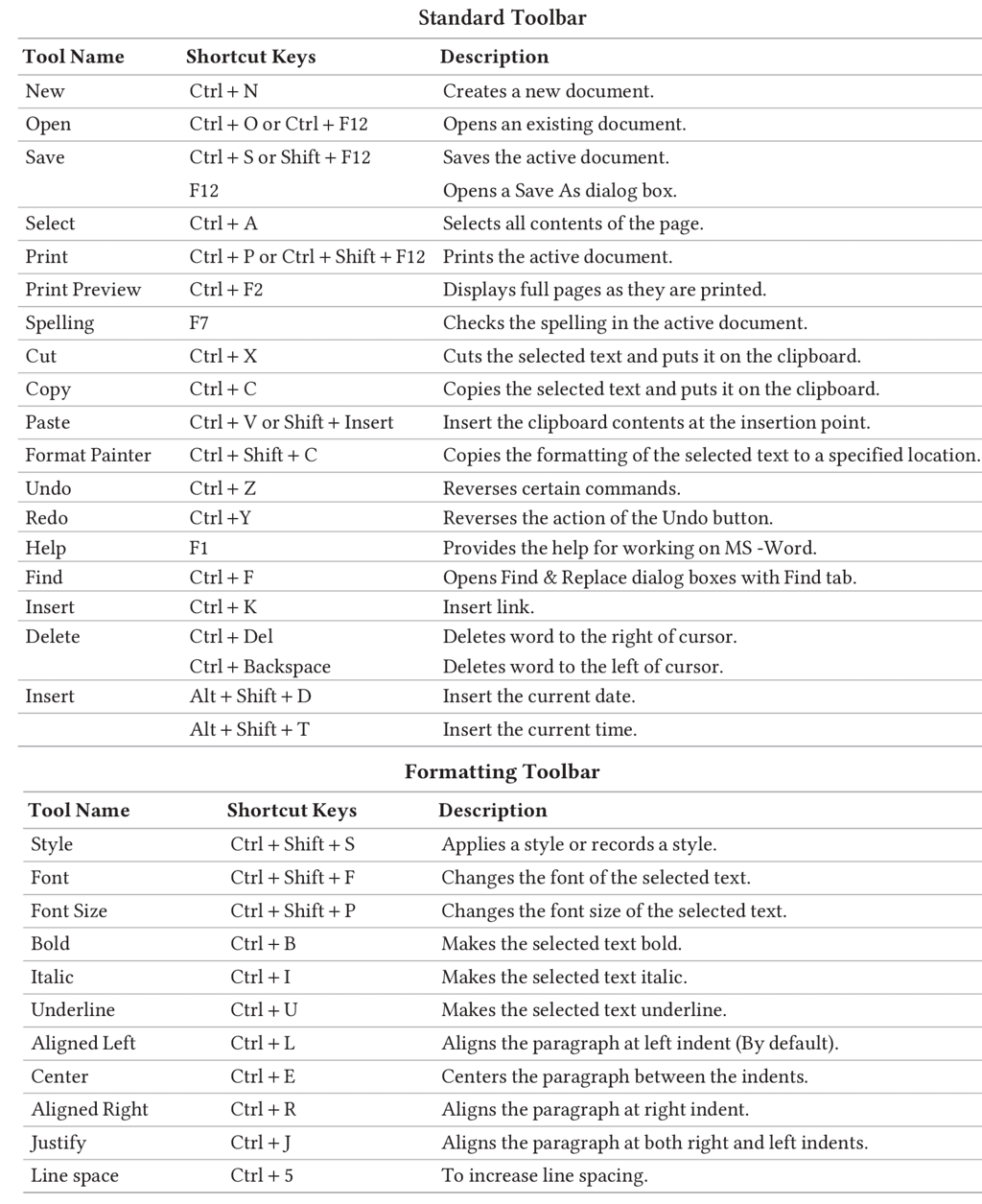
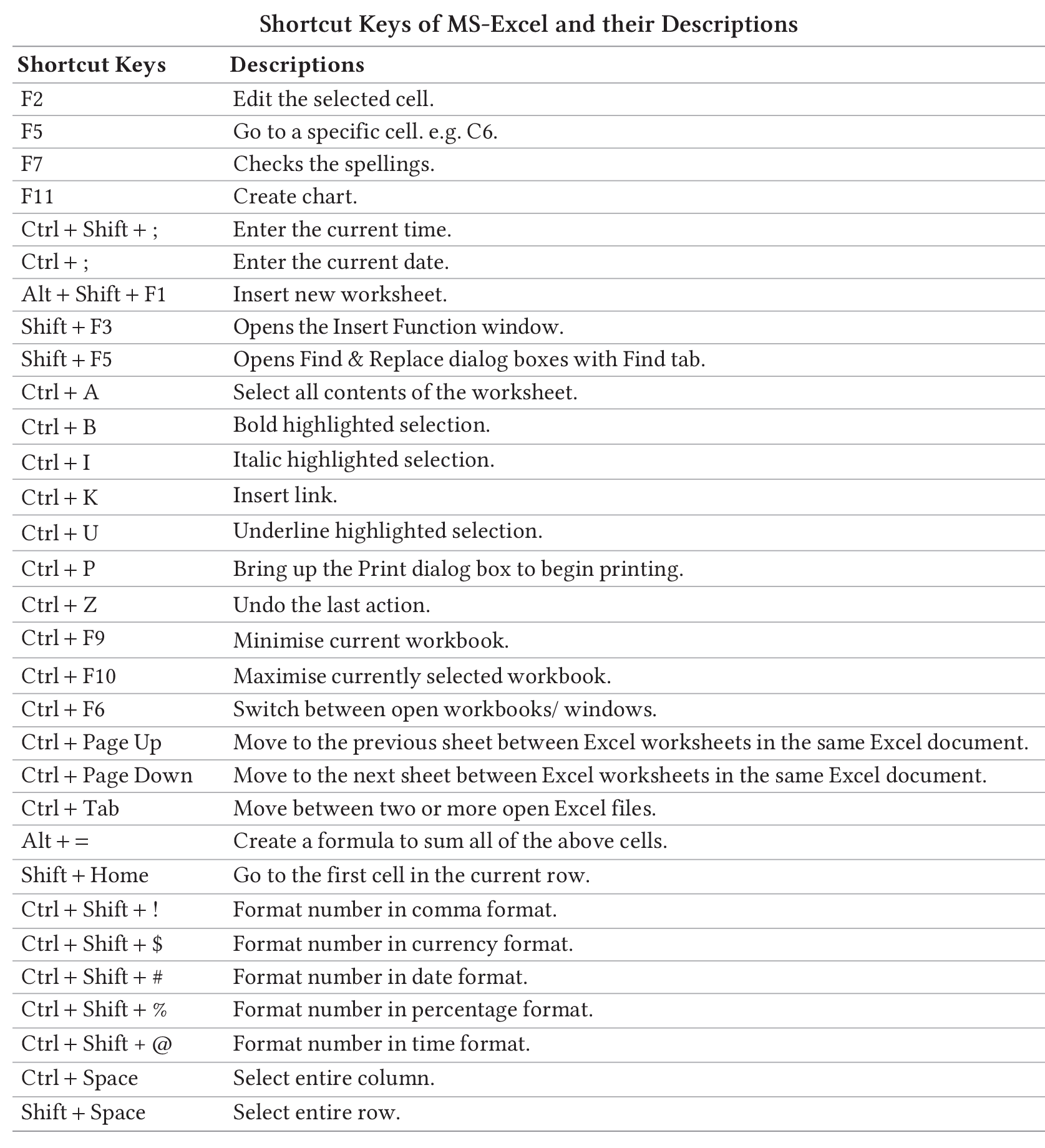
Shortcut Keys of MS-Word and their Descriptions
Microsoft Excel

- A spreadsheet is a matrix of rows and columns, similar to an accounting ledger.
- Electronic spreadsheets, like Microsoft Excel, are used for analyzing, managing, and sharing information, often for accounting purposes, mathematical calculations, budgeting, and billing.
- These programs also offer tools for creating graphs, inserting pictures, and analyzing data.
- Examples of other spreadsheet software include Corel Quattro Pro, VisiCalc, Lotus-1-2-3, and Apple Numbers.
To start MS-Excel, you can use one of the following methods:
- Click the Start button, select Run, type
Excelin the text box, and press Enter. - Click Start → All Programs → Microsoft Office → Microsoft Excel 2010.
This will open MS-Excel with a new blank spreadsheet named Book1.xlsx by default, where .xls and .xlsx are the file extensions for Excel spreadsheets.
Components of Microsoft Excel
- Title Bar: Displays the application and file names. It includes three control buttons: Minimize (reduces the window size), Maximize (resizes the window to full screen), and Close (closes the window).
- Ribbon: Contains a set of command panels organized into tabs.
- Tabs: The ribbon is divided into seven tabs:
- Home Tab: Features Clipboard, Font, Alignment, Number, Styles, Cells, and Editing.
- Insert Tab: Includes Tables, Illustrations, Charts, Sparklines, Filter Links, Text, and Symbols.
- Page Layout Tab: Contains Themes, Page Setup, Scale to Fit, Sheet Options, and Arrange.
- Formulas Tab: Offers Function Library, Defined Names, Formula Auditing, and Calculation.
- Data Tab: Includes Get External Data, Connections, Sort & Filter, Data Tools, and Outline.
- Review Tab: Contains Proofing, Language, Comments, and Changes.
- View Tab: Provides Workbook Views, Show, Zoom, Window, and Macros.
- Status Bar: Shows information about the active worksheet, including page number, view shortcuts, and zoom slider.
- Formula Bar: Located below the ribbon, it is used to enter and edit data. It includes:
- Name Box: Displays references or the location of the active cell.
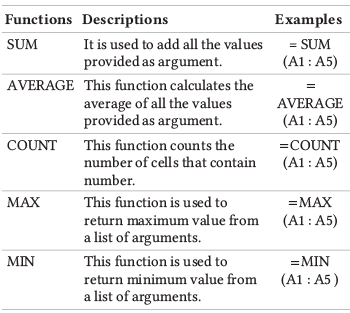
- Functions: Predefined formulas that perform calculations using specific values called arguments.
There are different types of functions
Basic Terms of Spreadsheet
- Spreadsheet: A software tool for entering, calculating, manipulating, and analyzing numbers.
- Cell: The intersection of a row and column, used to store data such as numbers (constants), formulas (mathematical equations), or text (labels).
- Sheet/Worksheet: A collection of cells organized in a tabular format.
- Workbook: A document containing one or more worksheets. By default, a new workbook includes three worksheets.
- Row: Identified by numbers (e.g., 1, 2, 3, …).
- Column: Identified by letters (e.g., A, B, C, …, AA, AB, …).
- Active Cell: The cell currently being worked on.
- Cell Pointer: A boundary that indicates which cell is active.
- Formula: An equation that calculates a value, starting with an equal sign (
=). - Cell Address: Specifies the intersection of a row and column with a letter and number.
Charts
Charts provide a graphical representation of worksheet data. Types of charts include:
- Area Chart: Emphasizes the magnitude of change over time.
- Column Chart: Displays data changes over time or compares items.
- Bar Chart: Compares individual items with categories organized vertically and values horizontally.
- Line Chart: Shows trends over time with data points connected by lines.
- Pie Chart: Represents the proportional size of items within a single data series.
- XY (Scatter) Chart: Displays relationships between numeric values or plots pairs of values.
Components of a Chart
- Chart Area: The total area surrounding the chart.
- Plot Area: The region where data is plotted, bounded by axes in 2D charts or walls and floor in 3D charts.
- Chart Title: Descriptive text to help identify the chart.
- Axis Title: Titles for the X, Y, and Z axes.
- Data Series: Rows or columns of numbers plotted in the chart.
- Gridlines: Horizontal and vertical lines to improve readability.
- Legend: Identifies various data series in the chart.
- Data Label: Provides additional information about data markers.
- Data Table: A range of cells used for testing and analyzing outcomes.
Tit-Bits
- $ Sign locks the cells in place.
- Stacked Bar Column illustrates how parts relate to the whole.
- Chart Wizard helps make charts in MS-Excel.
- Embedded Chart is a chart on an existing sheet.
Microsoft PowerPoint
- presentation: A presentation involves visually showing and explaining the contents of a topic to an audience or learner.
- Presentation graphics software: Software like Microsoft PowerPoint is designed to create professional-looking visual aids for this purpose.
- Slides: This software allows you to create slides and display information through a series of slides.
- Tools: Presentation software offers tools for text editing, graphics insertion, and multimedia effects.
To start MS-PowerPoint, follow these steps:
- Click the Start button → All Programs → Microsoft Office → Microsoft PowerPoint 2010.
By default, a new presentation file is named Presentation1.ppt, where .ppt or .pptx are the file extensions for PowerPoint presentations.
Components of Microsoft PowerPoint
- Title Bar: Displays the name of the currently open file followed by the software name.
- Ribbon: Similar to Word and Excel, with tabs for various functions. Unique tabs in PowerPoint include Animations and Slide Show.
- Slide: Located in the center of the window, where you create and add content to your presentation slides.
- Slide Pane: Shows all the slides in the presentation.
- Slide View Tab: Provides a thumbnail view of all slides.
- Outline View Tab: Displays the text from the presentation in an outline format.
- Notes Section: Allows you to create notes for each slide, which can be printed and used during the actual presentation.
- Status Bar: Shows the number of the currently displayed slide.
PowerPoint Views
- Normal View: The primary editing view where you design and create your presentation. This is the main screen where you work on your slides.
- Slide Sorter View: Displays slides as thumbnails, making it easier to sort and organize their sequence.
- Notes Page View: Shows the notes for the current slide below the slide itself. These notes can be printed and used during the presentation.
- Slide Show View: Used to deliver the presentation to an audience. It takes up the full screen for a professional display. Press the Esc key to exit this view.
- Master View: Includes Slide View, Handout View, and Notes View. It allows you to set up the overall presentation layout, including background colors, font effects, and placeholder sizes and positions.
Tit-Bits
- Trigger is an object or item that acts when we click the mouse during a slide presentation.
- MS-PowerPoint can zoom in up to a maximum of 400%.
- In MS-PowerPoint, you can insert various image and sound file types like .gif, .bmp, .png, .jpg, .giv, .wav, .mid. etc.
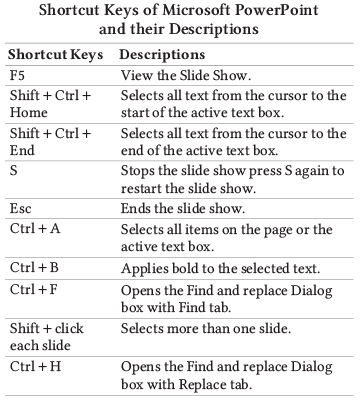
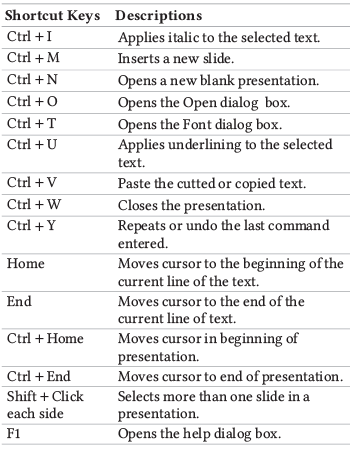
Microsoft Access
- A database is a collection of logically related and similar data, organized in a way that allows for easy retrieval of information when needed.
- Microsoft Access is a software application designed to create and manage databases.
- It is a Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) that helps organize and manage data efficiently.
Microsoft Outlook
- Microsoft Outlook is an email client and personal information manager included in the Microsoft Office suite.
- For Windows mobile devices, Outlook offers synchronization capabilities, allowing users to access their email data on their smartphones.
- MS-Outlook can integrate with Microsoft Exchange Server and Microsoft SharePoint Server, enabling features such as shared mailboxes, calendars, public folders, SharePoint lists, and meeting schedules for multiple users within an organization.
|
48 videos|22 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Microsoft Office - Computer Awareness and Proficiency - SSC CGL
| 1. What are the main components of Microsoft Office? |  |
| 2. How can Microsoft Excel be used in a professional setting? |  |
| 3. What is the purpose of Microsoft Access? |  |
| 4. How can Microsoft PowerPoint help in creating effective presentations? |  |
| 5. How can Microsoft Outlook assist in managing email and schedules efficiently? |  |





















