NEET PG Exam > NEET PG Notes > Biochemistry > Mind Map: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids -1
Mind Map: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids -1 | Biochemistry - NEET PG PDF Download
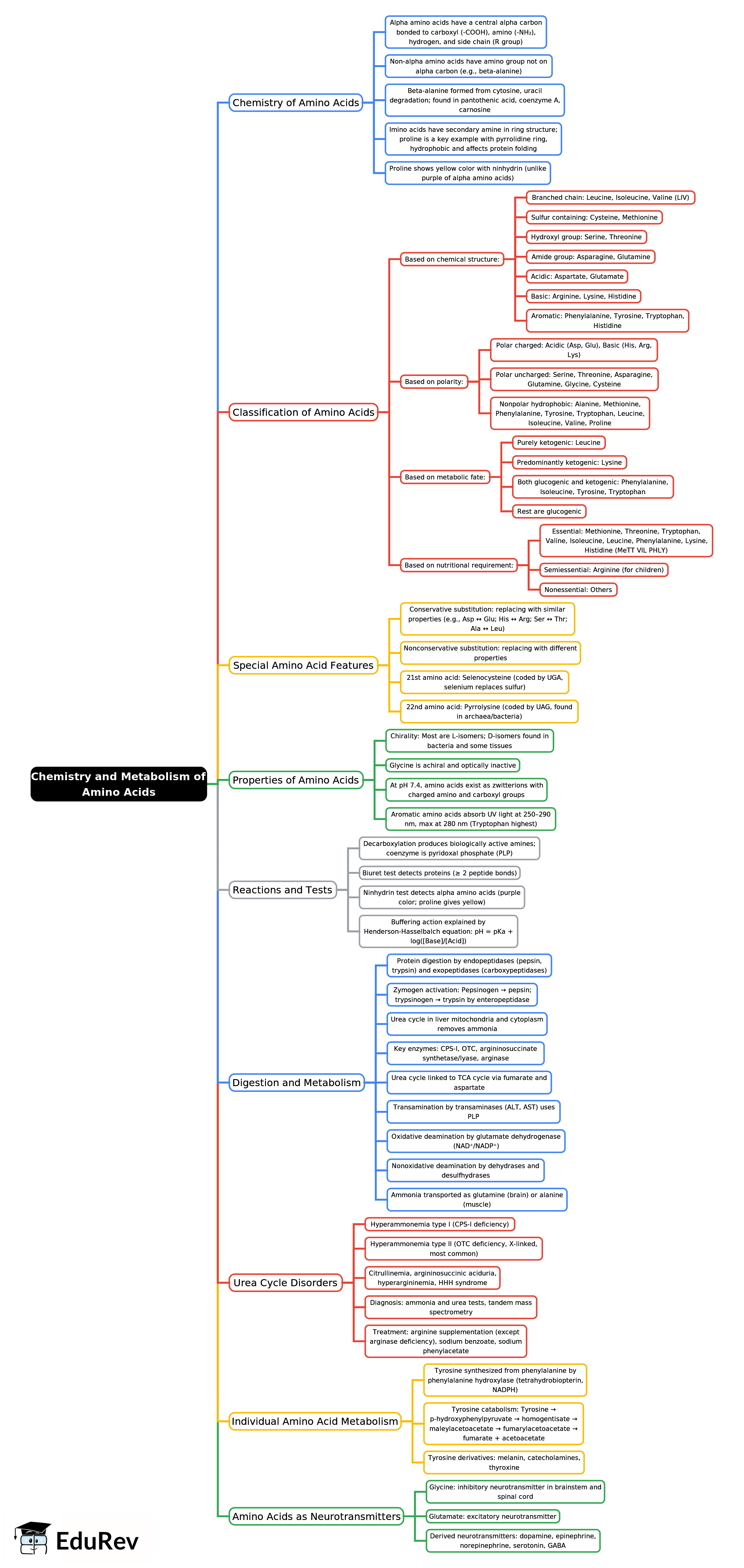
The document Mind Map: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids -1 | Biochemistry - NEET PG is a part of the NEET PG Course Biochemistry.
All you need of NEET PG at this link: NEET PG
|
48 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids -1 - Biochemistry - NEET PG
| 1. What are amino acids and why are they important in metabolism? |  |
Ans. Amino acids are organic compounds that serve as the building blocks of proteins. They contain an amino group (–NH₂), a carboxyl group (–COOH), and a unique side chain (R group) that determines the characteristics of each amino acid. In metabolism, amino acids play crucial roles such as participating in enzymatic reactions, serving as precursors for neurotransmitters and hormones, and participating in the synthesis of various biomolecules. They are essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues.
| 2. How are amino acids classified based on their dietary requirements? |  |
Ans. Amino acids are classified into three categories based on dietary requirements: essential, non-essential, and conditional amino acids. Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained from the diet (e.g., leucine, isoleucine). Non-essential amino acids can be synthesized by the body (e.g., alanine, aspartate). Conditional amino acids are usually non-essential but may become essential during times of stress or illness (e.g., glutamine, arginine).
| 3. What are the primary metabolic pathways involving amino acids? |  |
Ans. The primary metabolic pathways involving amino acids include protein synthesis, transamination, deamination, and the urea cycle. Protein synthesis occurs in ribosomes where amino acids are linked to form proteins. Transamination involves the transfer of an amino group from one amino acid to a keto acid, forming new amino acids. Deamination is the removal of an amino group from an amino acid, leading to the production of ammonia and a corresponding keto acid. The urea cycle converts ammonia to urea for excretion, thus detoxifying ammonia produced from amino acid metabolism.
| 4. What role do amino acids play in neurotransmitter synthesis? |  |
Ans. Amino acids are precursors for several neurotransmitters, which are critical for communication between neurons. For example, the amino acid tryptophan is a precursor for serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood and sleep. Similarly, tyrosine is a precursor for dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine, all of which are important for stress response and mood regulation. The availability of these amino acids can therefore significantly impact mental health and neurological function.
| 5. What are the consequences of amino acid deficiencies in the body? |  |
Ans. Deficiencies in amino acids can lead to a variety of health issues. For instance, insufficient intake of essential amino acids can impair protein synthesis, resulting in muscle wasting, weakened immune function, and delayed wound healing. Specific deficiencies can lead to particular conditions; for example, a lack of tryptophan can contribute to depression due to decreased serotonin levels. In children, amino acid deficiencies can hinder growth and development, while in adults, they can exacerbate chronic illnesses and weaken overall health.
Related Searches





















