Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam > Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Notes > Digital Circuits > Mind Map: Encoders & Decoders
Mind Map: Encoders & Decoders | Digital Circuits - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) PDF Download
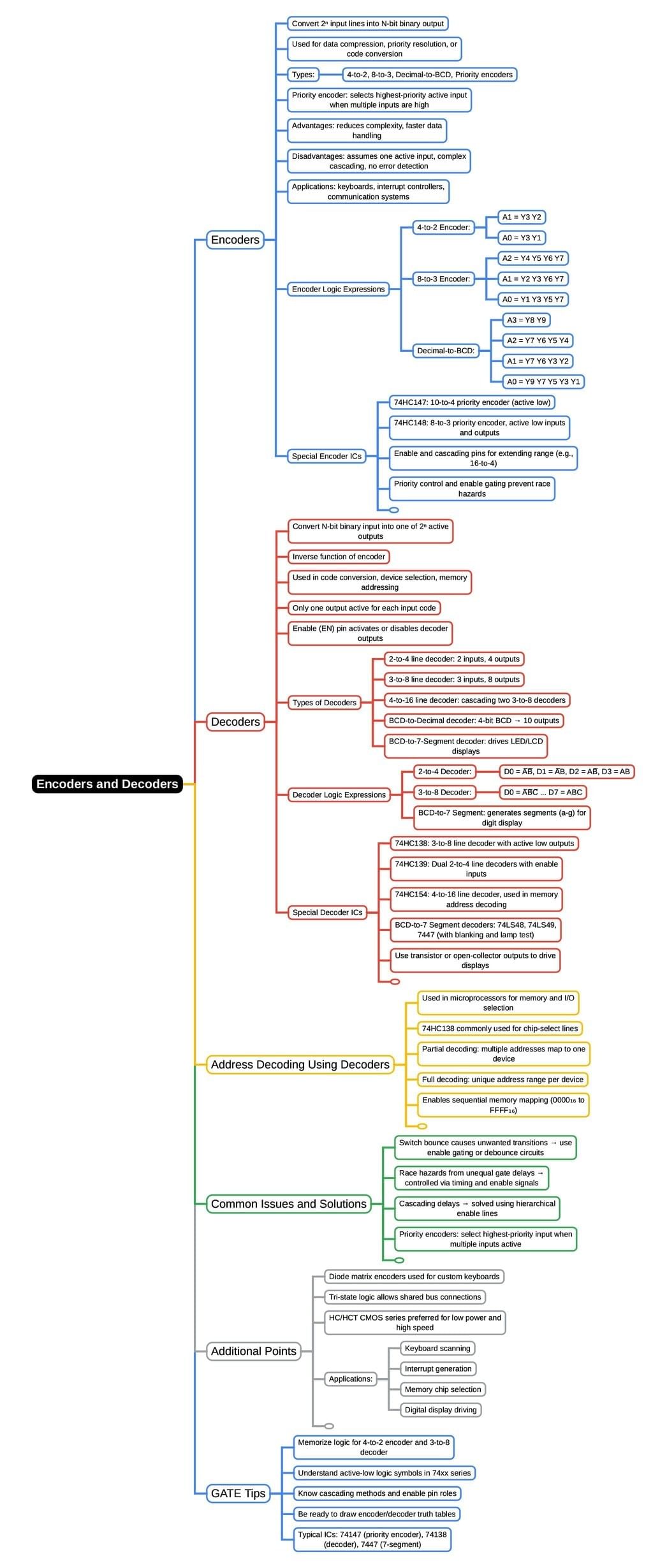
The document Mind Map: Encoders & Decoders | Digital Circuits - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) is a part of the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Course Digital Circuits.
All you need of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) at this link: Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE)
|
75 videos|188 docs|70 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Encoders & Decoders - Digital Circuits - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE)
| 1. What is the basic difference between encoders and decoders in electronics? |  |
Ans. Encoders are devices that convert information from one format to another, often from analog signals to digital codes, while decoders perform the reverse operation, converting coded data back into its original format. Encoders reduce the number of bits needed to represent data, while decoders reconstruct the original information from the encoded data.
| 2. Can you explain the different types of encoders used in communication systems? |  |
Ans. There are several types of encoders used in communication systems, including binary encoders, priority encoders, and rotary encoders. Binary encoders convert multiple input lines into fewer output lines representing the binary value of the active input. Priority encoders determine which input line is highest in priority when multiple inputs are active. Rotary encoders are used to convert the angular position of a shaft into an analog or digital code.
| 3. What are some common applications of decoders in electronic systems? |  |
Ans. Decoders are widely used in various applications, such as memory address decoding in computer architecture, data demultiplexing, and digital display systems. They are crucial in enabling devices to interpret binary-coded information, allowing for tasks such as selecting specific memory locations or displaying information on LED or LCD screens.
| 4. How does a 2-to-4 line decoder function, and what is its truth table? |  |
Ans. A 2-to-4 line decoder takes 2 input lines and decodes them into 4 output lines, where only one output line is activated based on the binary value of the inputs. The truth table for a 2-to-4 decoder is as follows:
| Input A | Input B | Output 0 | Output 1 | Output 2 | Output 3 |
|---------|---------|----------|----------|----------|----------|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 5. What role do encoders and decoders play in digital communication systems? |  |
Ans. In digital communication systems, encoders and decoders are essential for data transmission and reception. Encoders compress and encode data for efficient transmission, minimizing bandwidth usage while maintaining data integrity. Decoders then interpret the received signals, converting them back to the original data format, thus ensuring accurate communication between devices.
Related Searches















