Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > History Class 9 ICSE > Mind Map: Later Vedic Age
Mind Map: Later Vedic Age | History Class 9 ICSE PDF Download
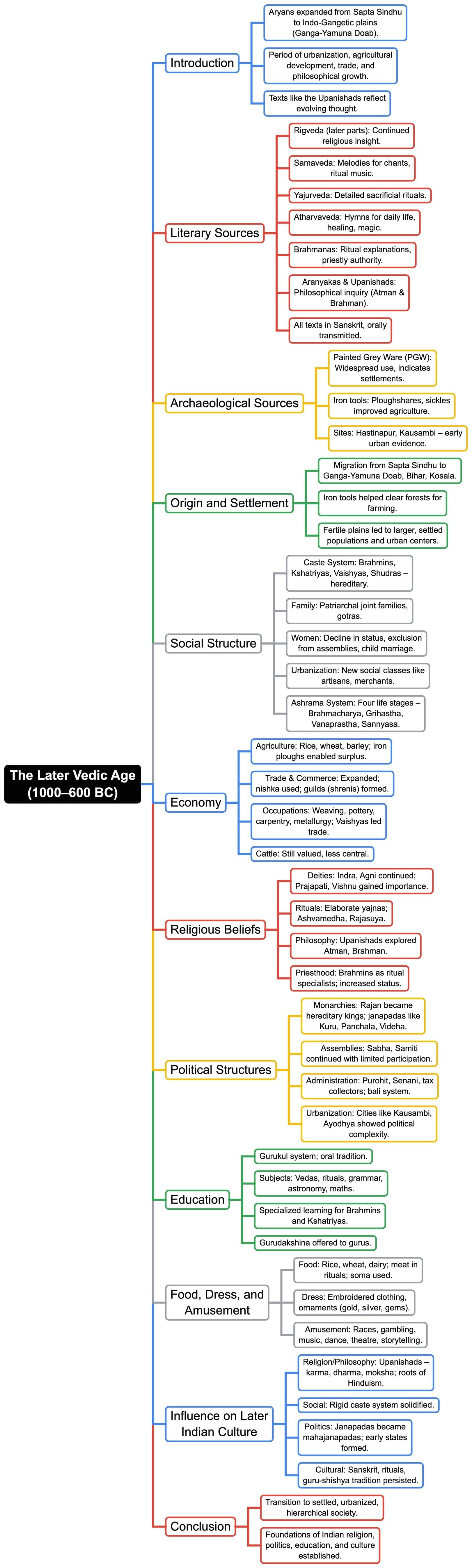
The document Mind Map: Later Vedic Age | History Class 9 ICSE is a part of the Class 9 Course History Class 9 ICSE.
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
14 videos|59 docs|16 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Later Vedic Age - History Class 9 ICSE
| 1. What are the key features of the Later Vedic Age? |  |
Ans. The Later Vedic Age, which followed the Early Vedic period, is characterized by significant developments in society, economy, and culture. Key features include the emergence of urban centers, the establishment of a more complex social structure with the varna system (Brahmins, Kshatriyas, Vaishyas, and Shudras), and the composition of the Upanishads, which are philosophical texts exploring spirituality and the nature of the universe. Additionally, agricultural practices advanced, and trade increased, leading to greater economic prosperity.
| 2. How did the Later Vedic Age influence Indian philosophy? |  |
Ans. The Later Vedic Age had a profound impact on Indian philosophy through the creation of the Upanishads, which introduced concepts like Brahman (the ultimate reality) and Atman (the individual soul). These texts shifted focus from ritualistic practices to introspection and meditation, laying the groundwork for various schools of thought, including Vedanta and Yoga. The exploration of metaphysical questions during this period helped shape the spiritual and philosophical landscape of India for centuries.
| 3. What role did agriculture play in the Later Vedic Age? |  |
Ans. Agriculture was a fundamental aspect of the Later Vedic Age, as it shifted from a primarily pastoral society to one that embraced settled farming. The use of iron tools improved agricultural productivity, leading to surplus food production. This surplus allowed for population growth, the rise of urban centers, and increased trade. Agricultural advancements also facilitated the development of a more structured economy and societal organization, contributing to the overall prosperity of the period.
| 4. What is the significance of the varna system during the Later Vedic Age? |  |
Ans. The varna system became more pronounced during the Later Vedic Age, categorizing society into four main groups: Brahmins (priests and scholars), Kshatriyas (warriors and rulers), Vaishyas (traders and agriculturists), and Shudras (laborers and service providers). This system played a crucial role in organizing social roles and responsibilities, influencing occupational choices, and establishing a hierarchy that affected social interactions. It laid the foundation for the caste system that would evolve in later periods of Indian history.
| 5. How did the Later Vedic Age contribute to the development of urban centers? |  |
Ans. The Later Vedic Age saw the growth of urban centers due to increased agricultural productivity and trade. As surplus crops were produced, populations began to settle in specific areas, leading to the establishment of towns and cities. These urban centers became hubs of economic activity and trade, facilitating interactions among diverse communities. The rise of urbanization also contributed to cultural exchanges and the development of arts, crafts, and other professions, marking a significant transition in ancient Indian society.
Related Searches
















