Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Notes > Analog and Digital Electronics > Mind Map: MOSFET
Mind Map: MOSFET | Analog and Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
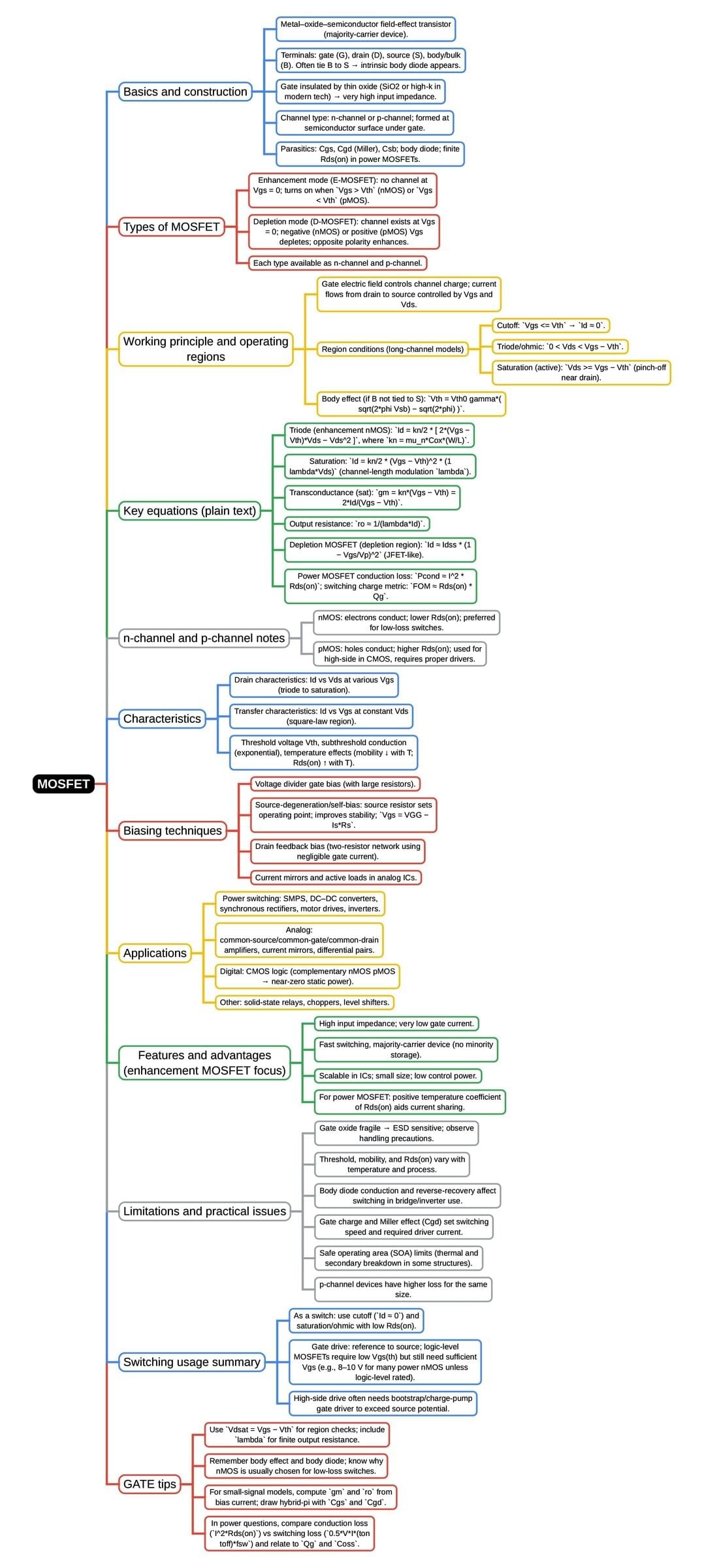
The document Mind Map: MOSFET | Analog and Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE) is a part of the Electrical Engineering (EE) Course Analog and Digital Electronics.
All you need of Electrical Engineering (EE) at this link: Electrical Engineering (EE)
|
135 videos|181 docs|71 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: MOSFET - Analog and Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What is a MOSFET and how does it work? |  |
Ans. A MOSFET, or Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor, is a type of transistor used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. It operates by applying a voltage to the gate terminal, which creates an electric field that controls the flow of current between the source and drain terminals. This allows for efficient control of large currents with minimal power loss.
| 2. What are the different types of MOSFETs? |  |
Ans. There are primarily two types of MOSFETs: n-channel and p-channel. N-channel MOSFETs conduct when a positive voltage is applied to the gate, allowing current to flow from the drain to the source. P-channel MOSFETs, on the other hand, conduct when a negative voltage is applied, allowing current to flow from the source to the drain. Each type has distinct applications based on their characteristics.
| 3. What are the applications of MOSFETs in electrical engineering? |  |
Ans. MOSFETs are widely used in various applications such as power amplifiers, switching power supplies, motor drivers, and digital circuits. They are integral to modern electronics due to their high efficiency and fast switching speeds, making them ideal for applications in computers, telecommunications, and consumer electronics.
| 4. What are the advantages of using MOSFETs over other types of transistors? |  |
Ans. MOSFETs offer several advantages over other transistors, including higher input impedance, which leads to lower power consumption; faster switching speeds; and better thermal stability. These characteristics make them suitable for high-performance applications where efficiency and reliability are crucial.
| 5. How do you calculate the threshold voltage of a MOSFET? |  |
Ans. The threshold voltage (Vth) of a MOSFET can be determined using the equation Vth = Vgs - Vds, where Vgs is the gate-source voltage and Vds is the drain-source voltage. The threshold voltage is the minimum gate voltage that is required to create a conductive channel between the source and drain, allowing current to flow through the device.
Related Searches




















