Class 5 Exam > Class 5 Notes > Year 5 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) > Mind Map: Magnetism
Mind Map: Magnetism | Year 5 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 5 PDF Download
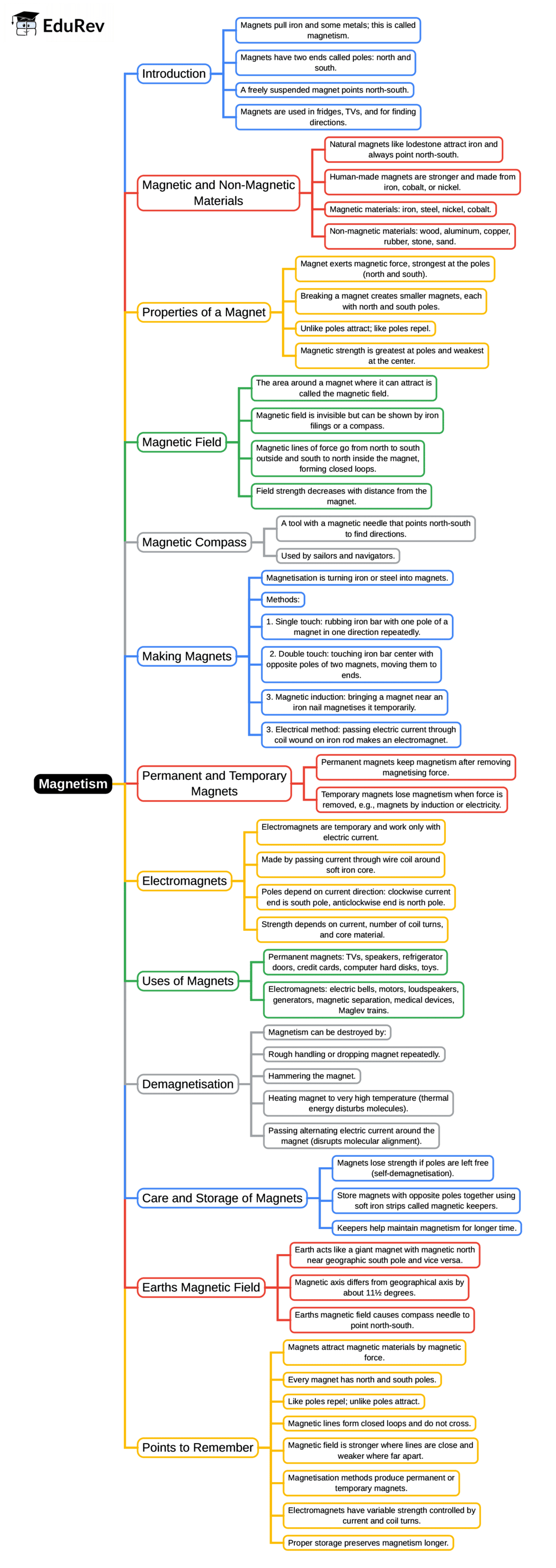
The document Mind Map: Magnetism | Year 5 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 5 is a part of the Class 5 Course Year 5 Science IGCSE (Cambridge).
All you need of Class 5 at this link: Class 5
|
18 docs|6 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Magnetism - Year 5 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 5
| 1. What is magnetism and how does it work? |  |
Ans.Magnetism is a physical phenomenon produced by the motion of electric charge, which results in attractive and repulsive forces between objects. It is primarily associated with magnets, which have north and south poles. Like poles repel each other while opposite poles attract. Magnetism is fundamentally linked to electricity; when an electric current flows through a wire, it generates a magnetic field around it. This principle is utilized in various applications, including electric motors and generators.
| 2. What are the different types of magnets? |  |
Ans.There are mainly three types of magnets: permanent magnets, temporary magnets, and electromagnets. Permanent magnets are materials that maintain their magnetic properties without an external power source, such as iron, cobalt, and nickel. Temporary magnets, like soft iron, exhibit magnetic properties only when they are within a magnetic field. Electromagnets are created by passing an electric current through a coil of wire, producing a magnetic field that can be turned on or off, and are widely used in devices like relays and MRI machines.
| 3. What is the Earth’s magnetic field and why is it important? |  |
Ans.The Earth’s magnetic field is a magnetic field that surrounds the planet and extends from its interior out into space. It is generated by the movement of molten iron and other metals in the outer core. This magnetic field is crucial for life on Earth as it protects the planet from solar wind and cosmic radiation, which can be harmful to living organisms. Additionally, it aids in navigation for various species, including birds and marine animals, which use the magnetic field to orient themselves.
| 4. How do magnetic fields interact with electric currents? |  |
Ans.Magnetic fields interact with electric currents through a principle known as electromagnetic induction. When an electric current flows through a conductor, it creates a magnetic field around it. Conversely, if a conductor is placed in a changing magnetic field, an electric current is induced in the conductor. This principle is the foundation for many technologies, including transformers and electric generators, which convert mechanical energy into electrical energy or vice versa.
| 5. What are some practical applications of magnetism? |  |
Ans.Magnetism has a wide range of practical applications across various fields. In everyday life, it is used in refrigerator magnets and magnetic closures. In technology, it is essential for data storage in hard drives, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in medicine, and the operation of electric motors and generators. Additionally, magnetic levitation technology is utilized in high-speed trains to reduce friction and improve efficiency, showcasing the diverse utility of magnetism in modern society.
Related Searches




















