SSC CGL Exam > SSC CGL Notes > General Awareness for SSC CGL > Mind Map: Metallurgy
Mind Map: Metallurgy | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
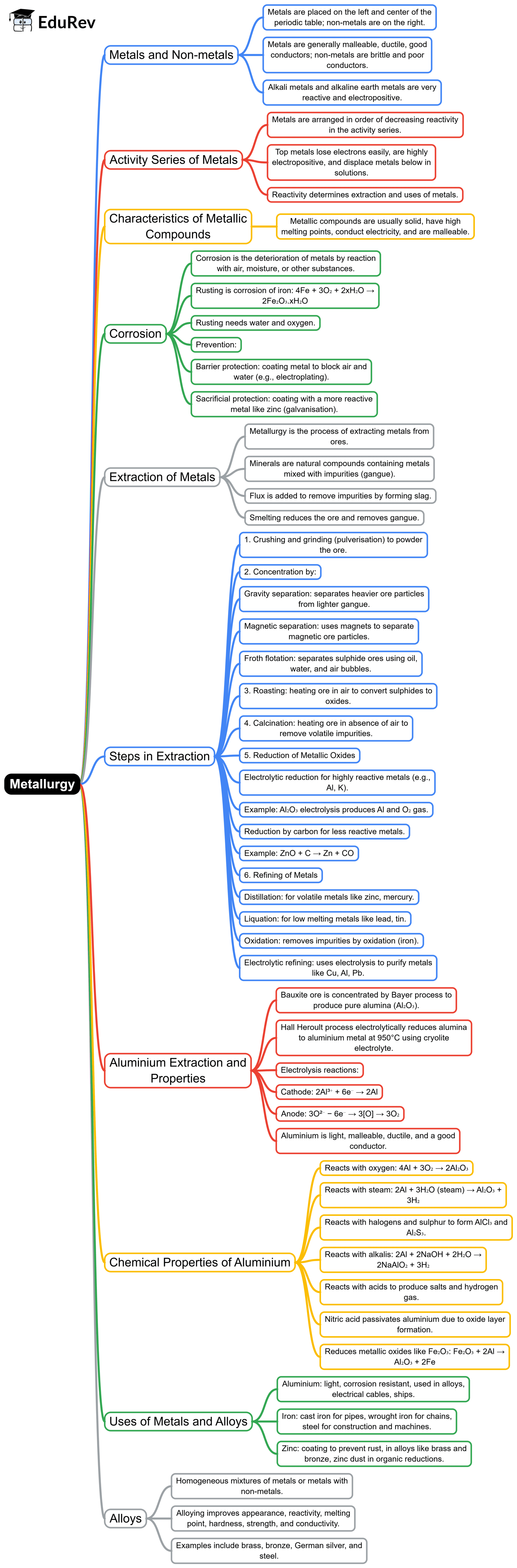
The document Mind Map: Metallurgy | General Awareness for SSC CGL is a part of the SSC CGL Course General Awareness for SSC CGL.
All you need of SSC CGL at this link: SSC CGL
|
486 videos|1936 docs|395 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Metallurgy - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What is metallurgy and why is it important? |  |
Ans.Metallurgy is the science and technology of metals. It involves the study of the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their intermetallic compounds, and their mixtures, known as alloys. Metallurgy is important because it enables the extraction of metals from their ores, the development of new materials, and the enhancement of existing materials' properties, which are crucial for various industries such as construction, manufacturing, and technology.
| 2. What are the main steps involved in the extraction of metals? |  |
Ans.The main steps involved in the extraction of metals include:
1. <b>Mining</b>: The process of obtaining metal ores from the earth.
2. <b>Concentration</b>: The separation of valuable minerals from the non-valuable parts of the ore, often done through processes like crushing and milling.
3. <b>Reduction</b>: The process of converting metal oxides into pure metals, commonly using methods such as smelting or electrolysis.
4. <b>Refining</b>: The purification of the extracted metal to remove impurities and enhance quality.
| 3. What are some common methods of metal extraction? |  |
Ans.Some common methods of metal extraction include:
1. <b>Pyrometallurgy</b>: Involves high-temperature processes to extract metals, such as smelting.
2. <b>Hydrometallurgy</b>: Uses aqueous solutions to extract metals, often involving leaching and precipitation.
3. <b>Electrometallurgy</b>: Utilizes electrical energy to extract metals from their ores, often through electrolysis.
| 4. What is the difference between ferrous and non-ferrous metals? |  |
Ans.Ferrous metals contain iron and are magnetic, which makes them susceptible to rusting (oxidation). Examples include steel and cast iron. Non-ferrous metals do not contain significant amounts of iron and are generally more resistant to corrosion. Common examples include aluminum, copper, and gold. The distinction is important for selecting materials based on strength, weight, and resistance to corrosion.
| 5. How do alloys improve the properties of metals? |  |
Ans.Alloys are mixtures of two or more metals or a metal and a non-metal, designed to enhance certain properties. For example, adding carbon to iron creates steel, which is stronger and more durable than pure iron. Alloys can improve properties such as strength, ductility, corrosion resistance, and hardness, making them suitable for various applications in construction, manufacturing, and other industries.
Related Searches





















