SSC CGL Exam > SSC CGL Notes > Quantitative Aptitude for SSC CGL > Mind Map: Pipes and Cisterns
Mind Map: Pipes and Cisterns | Quantitative Aptitude for SSC CGL PDF Download
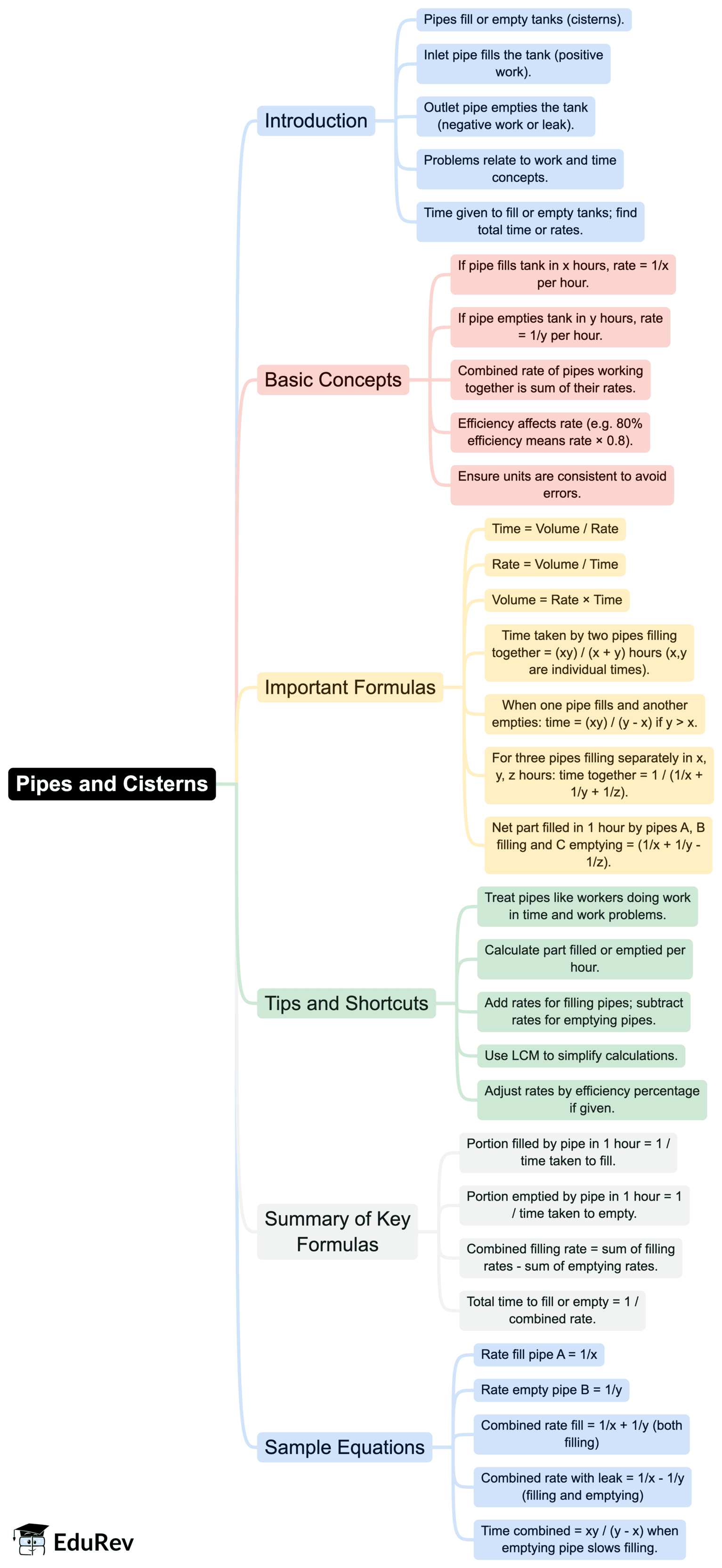
The document Mind Map: Pipes and Cisterns | Quantitative Aptitude for SSC CGL is a part of the SSC CGL Course Quantitative Aptitude for SSC CGL.
All you need of SSC CGL at this link: SSC CGL
|
317 videos|290 docs|185 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Pipes and Cisterns - Quantitative Aptitude for SSC CGL
| 1. What are the basic concepts involved in pipes and cisterns problems? |  |
Ans. Pipes and cisterns problems primarily revolve around the concepts of rates of work and time. A pipe can fill a tank at a certain rate, while a cistern can empty it at another rate. The key is to understand how to calculate the time taken to fill or empty the tank when multiple pipes or cisterns are working together. The formula often used is: Time = Volume / Rate, where Volume is the total capacity of the tank and Rate is the combined rate of filling or emptying.
| 2. How do you calculate the time taken to fill a tank using multiple pipes? |  |
Ans. To calculate the time taken to fill a tank using multiple pipes, first determine the individual rates of each pipe (in terms of tank volume per hour). If Pipe A fills the tank in 'a' hours, its rate is 1/a tanks per hour. Similarly, for Pipe B filling in 'b' hours, its rate is 1/b tanks per hour. The combined rate when both pipes are open is (1/a + 1/b) tanks per hour. Finally, use the formula: Time = Volume / Combined Rate to find the total time taken to fill the tank.
| 3. What is the difference between filling and emptying pipes in cistern problems? |  |
Ans. In cistern problems, filling pipes add water to the tank, whereas emptying pipes remove water from it. The rates of filling and emptying are crucial in solving these problems. When calculating total time or rates, filling pipes contribute positively to the rate, while emptying pipes contribute negatively. Therefore, the combined effect of all pipes must be considered to find the net rate, which determines how quickly a tank can be filled or emptied.
| 4. How can you solve problems involving leakage in cisterns? |  |
Ans. To solve problems involving leakage in cisterns, treat the leak as an emptying pipe. First, calculate the filling rate of the pipe filling the tank. Then, determine the rate at which the leak empties it. The net rate at which the tank fills is the filling rate minus the leakage rate. Use this net rate to find the time taken to fill the tank by applying the formula: Time = Volume / Net Rate.
| 5. What are typical examples of pipes and cisterns problems in competitive exams? |  |
Ans. Typical examples of pipes and cisterns problems in competitive exams include scenarios where multiple pipes fill a tank simultaneously, situations where one pipe is filling while another is emptying, and problems that involve leaks in tanks. Candidates may be asked to calculate the total time taken to fill or empty a tank, the amount of water filled or emptied in a specific time, or the effect of adding or removing a pipe on the overall rate.
Related Searches















