Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Notes > Electrical Machines > Mind Map: Single Phase Transformers
Mind Map: Single Phase Transformers | Electrical Machines - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
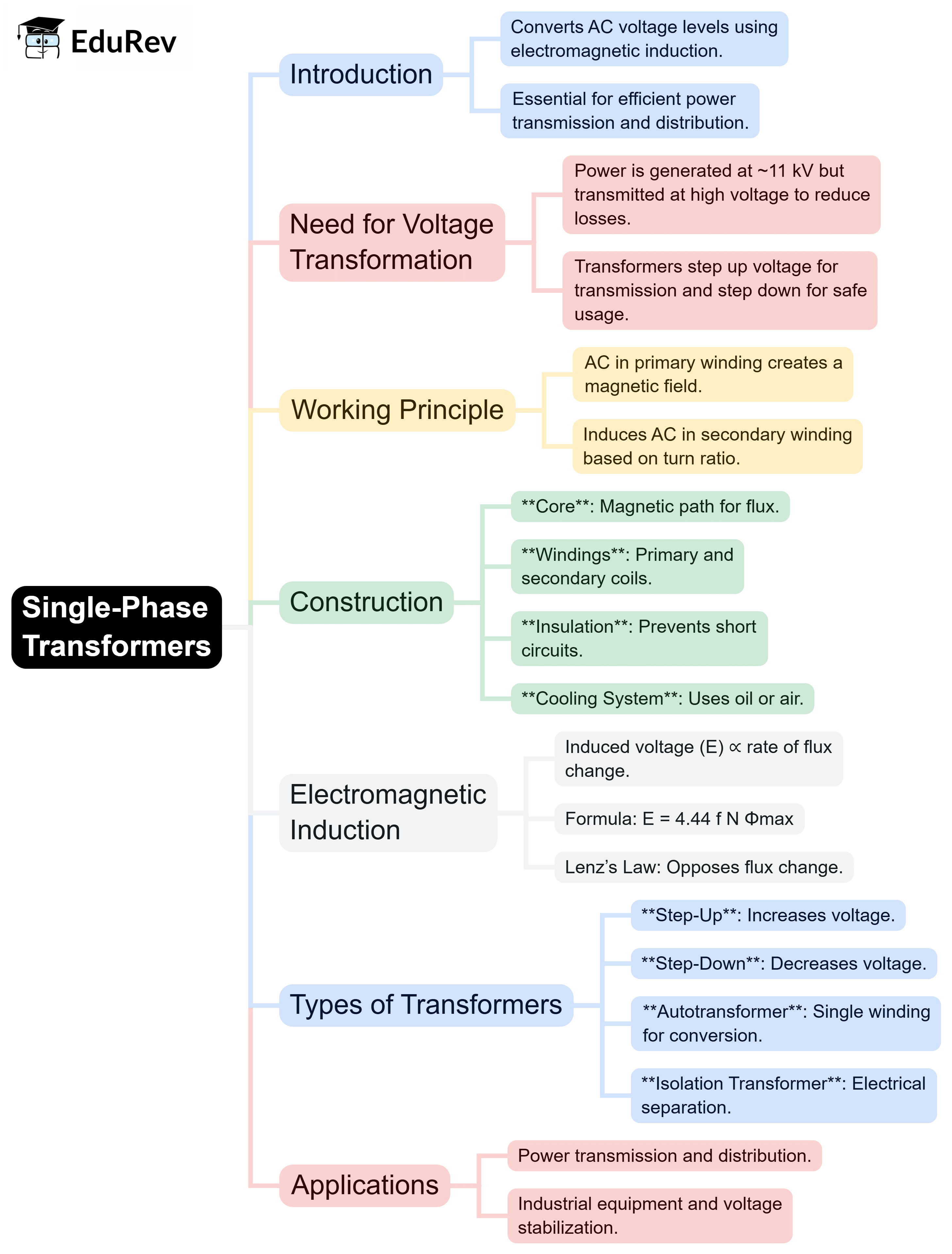
The document Mind Map: Single Phase Transformers | Electrical Machines - Electrical Engineering (EE) is a part of the Electrical Engineering (EE) Course Electrical Machines.
All you need of Electrical Engineering (EE) at this link: Electrical Engineering (EE)
|
19 videos|124 docs|25 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Single Phase Transformers - Electrical Machines - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What is a single-phase transformer and how does it work? |  |
Ans. A single-phase transformer is an electrical device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. It consists of two windings, the primary winding and the secondary winding, which are magnetically coupled through a core. When alternating current (AC) flows through the primary winding, it creates a magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary winding, allowing for voltage transformation.
| 2. What are the main applications of single-phase transformers? |  |
Ans. Single-phase transformers are commonly used in various applications, including residential power supply, small industrial machines, and lighting systems. They are also utilized in power distribution networks to step down high voltages for safe use in homes and businesses, as well as in electronic devices that require specific voltage levels.
| 3. What is the difference between step-up and step-down transformers? |  |
Ans. A step-up transformer increases the voltage from the primary to the secondary winding, which is achieved by having more turns in the secondary winding than in the primary. Conversely, a step-down transformer decreases the voltage from the primary to the secondary winding, with fewer turns in the secondary compared to the primary. Both types serve different purposes in electrical systems based on the required voltage levels.
| 4. How can I calculate the turns ratio of a single-phase transformer? |  |
Ans. The turns ratio of a single-phase transformer can be calculated using the formula: Turns Ratio = Np / Ns, where Np is the number of turns in the primary winding and Ns is the number of turns in the secondary winding. This ratio determines how the voltage changes from primary to secondary; a higher ratio indicates a step-up transformer, while a lower ratio indicates a step-down transformer.
| 5. What factors should be considered when selecting a single-phase transformer for a specific application? |  |
Ans. When selecting a single-phase transformer, consider factors such as the required voltage and current ratings, the power rating (in kVA), efficiency, and the type of load (resistive or inductive). Additionally, environmental conditions (like temperature and humidity), installation space, and regulatory standards should also be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Related Searches
















