Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Geography Class 9 ICSE > Mind Map: Weathering
Mind Map: Weathering | Geography Class 9 ICSE PDF Download
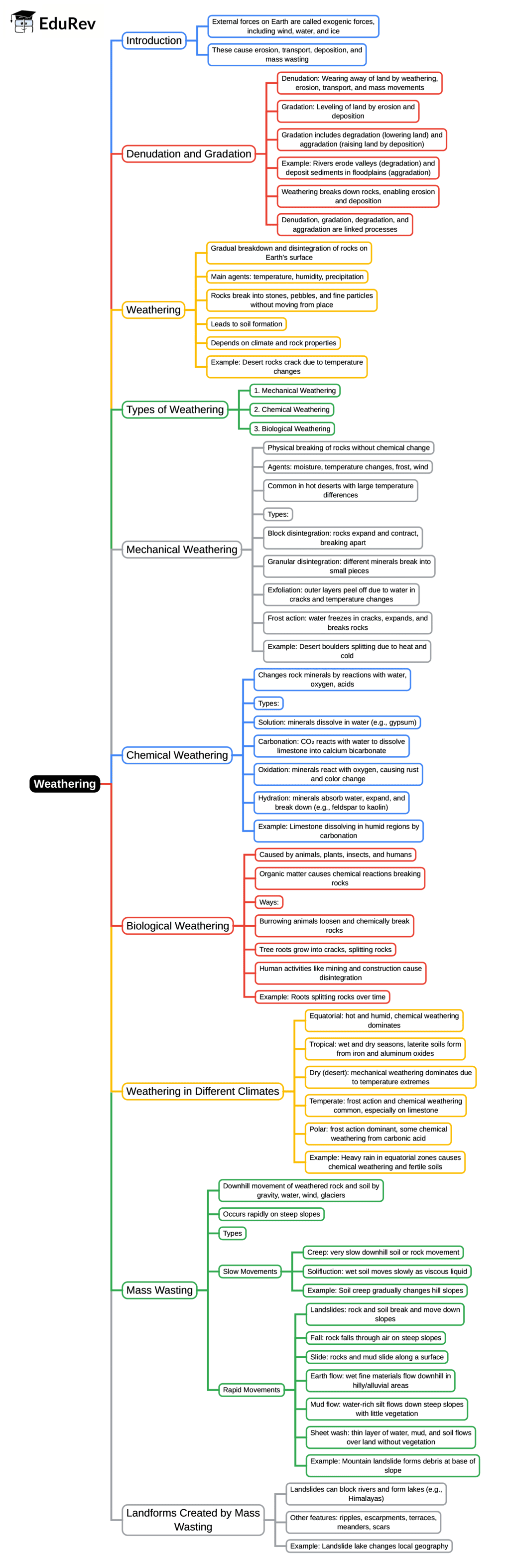
The document Mind Map: Weathering | Geography Class 9 ICSE is a part of the Class 9 Course Geography Class 9 ICSE.
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
66 videos|86 docs|20 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Weathering - Geography Class 9 ICSE
| 1. What is weathering and why is it important in the study of geology? |  |
Ans. Weathering is the process by which rocks and minerals are broken down into smaller pieces or altered in composition due to various environmental factors such as temperature changes, water, and biological activity. It is important in geology because it plays a crucial role in soil formation, landscape development, and the cycling of minerals. Understanding weathering helps geologists predict how landscapes evolve over time and informs practices in agriculture, construction, and conservation.
| 2. What are the main types of weathering and how do they differ from each other? |  |
Ans. The main types of weathering are physical (or mechanical) weathering, chemical weathering, and biological weathering. Physical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks without changing their chemical composition, often due to temperature fluctuations or freeze-thaw cycles. Chemical weathering involves changes in the chemical structure of minerals, typically through reactions with water, acids, or gases. Biological weathering refers to the influence of living organisms, such as plants and microorganisms, which can produce acids or exert pressure that breaks down rocks.
| 3. How does climate influence the weathering process? |  |
Ans. Climate significantly influences weathering processes. In warm, humid climates, chemical weathering is more prevalent due to the increased presence of water and higher temperatures, which accelerate chemical reactions. Conversely, in cold climates, physical weathering, such as freeze-thaw cycles, is more common. Arid climates may experience minimal weathering due to a lack of moisture, leading to the preservation of rock formations. Understanding the climate's role helps in predicting the rate and type of weathering that will occur in a given area.
| 4. What role do human activities play in weathering? |  |
Ans. Human activities can significantly accelerate weathering processes. Urban development, mining, and agriculture can disturb the natural landscape, exposing rocks to more weathering agents. Pollution, particularly acid rain from industrial emissions, enhances chemical weathering by increasing the acidity of rainwater, which can dissolve minerals more rapidly. Additionally, land use changes can lead to soil erosion and degradation, impacting ecosystems and natural resources.
| 5. What are some examples of weathering in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Everyday examples of weathering include the peeling of paint on a house due to moisture and temperature changes, the formation of cracks in sidewalks from freeze-thaw cycles, and the erosion of stone monuments or buildings from acid rain. Additionally, the breakdown of rocks in nature leads to the formation of soil, which is essential for plant growth and agriculture, illustrating the practical implications of weathering in our daily lives.
Related Searches
















