CAT Exam > CAT Notes > Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) > Mindmap: Cubes and Dice
Mindmap: Cubes and Dice | Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT PDF Download
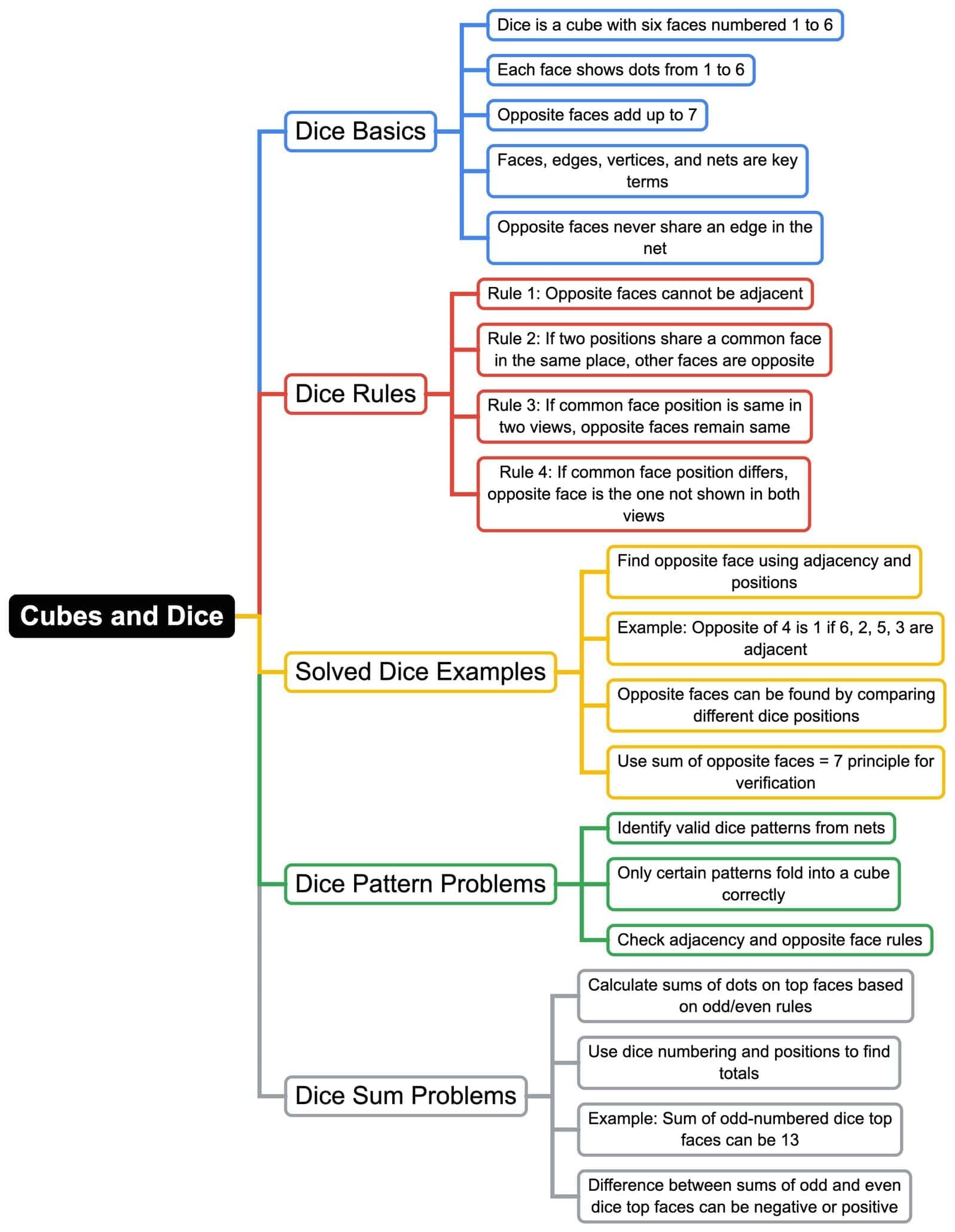
The document Mindmap: Cubes and Dice | Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT is a part of the CAT Course Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI).
All you need of CAT at this link: CAT
|
87 videos|172 docs|99 tests
|
FAQs on Mindmap: Cubes and Dice - Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT
| 1. What are the different types of dice used in games and their characteristics? |  |
Ans. Dice come in various shapes and sizes, with the most common type being the six-sided die (D6), which is used in many board games and role-playing games. Other types include the four-sided die (D4), eight-sided die (D8), ten-sided die (D10), twelve-sided die (D12), and twenty-sided die (D20). Each type has its own unique characteristics, such as the number of faces and how they are numbered. For example, the D20 is commonly used in role-playing games for determining outcomes based on random chance.
| 2. How is probability calculated when rolling a die? |  |
Ans. Probability is calculated by dividing the number of favorable outcomes by the total number of possible outcomes. For a single six-sided die, the probability of rolling a specific number (e.g., a 3) is 1 (favorable outcome) divided by 6 (total outcomes), resulting in a probability of 1/6. This basic principle can be applied to any type of die to determine the likelihood of rolling specific numbers.
| 3. What is the significance of using cubes in mathematical concepts? |  |
Ans. Cubes are significant in mathematics as they represent three-dimensional geometric shapes with equal-length sides. They are commonly used to teach concepts of volume, surface area, and spatial reasoning. The volume of a cube is calculated using the formula V = a³, where 'a' is the length of a side. Understanding cubes helps in visualizing and solving real-world problems related to space and measurement.
| 4. How do you distinguish between fair and biased dice? |  |
Ans. A fair die has an equal probability of landing on each face, while a biased die does not. To determine if a die is biased, one can conduct multiple rolls and analyze the frequency of each outcome. If certain numbers appear significantly more often than others, the die is likely biased. Fair dice are crucial in games to ensure fairness and random outcomes.
| 5. What are the applications of dice in probability theory and statistics? |  |
Ans. Dice serve as practical tools in probability theory and statistics, allowing for the demonstration of random events and the calculation of probabilities. They are often used in experiments to illustrate concepts such as expected value, variance, and distributions. By modeling real-world scenarios with dice, students can gain a deeper understanding of statistical principles and how they apply to everyday decision-making.
Related Searches
















