NEET PG Exam > NEET PG Notes > Biochemistry > Mind Map: Metabolism of Carbohydrates -2
Mind Map: Metabolism of Carbohydrates -2 | Biochemistry - NEET PG PDF Download
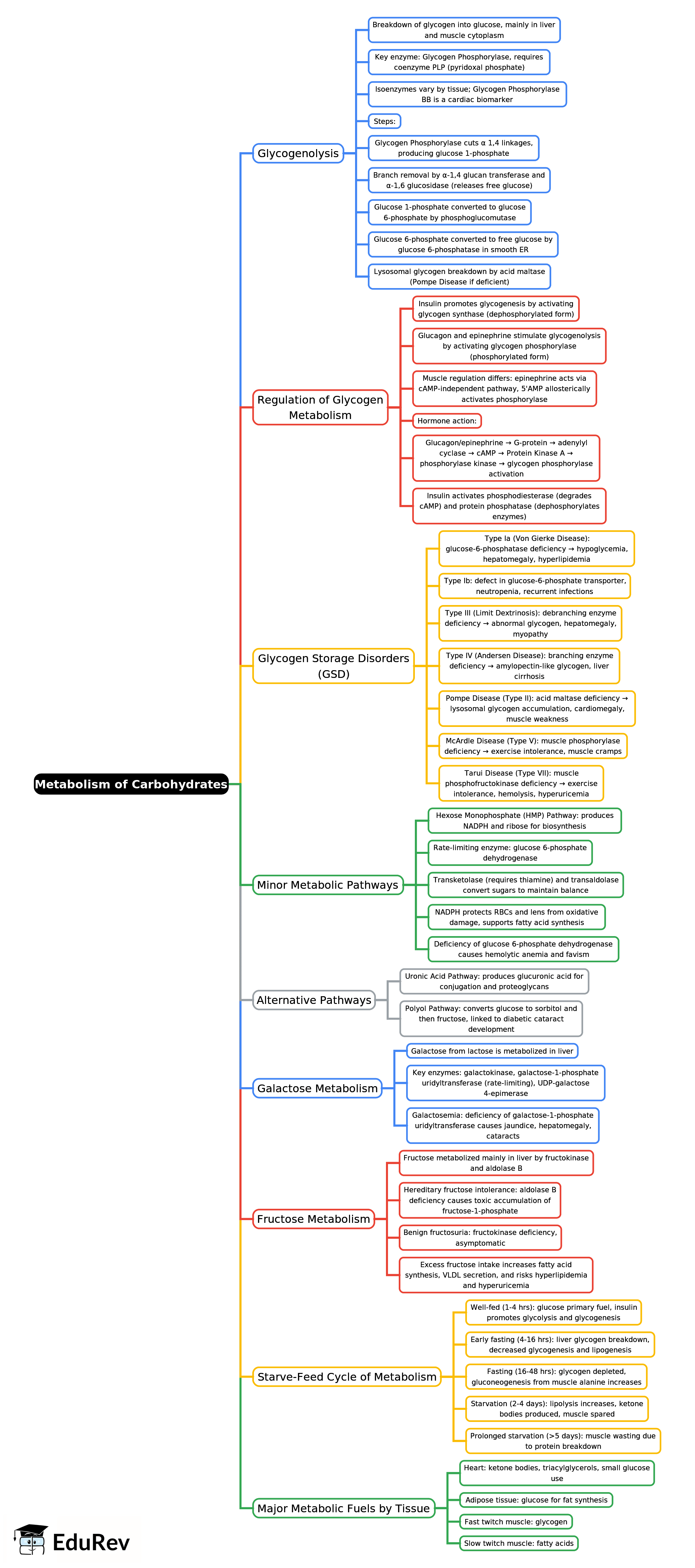
The document Mind Map: Metabolism of Carbohydrates -2 | Biochemistry - NEET PG is a part of the NEET PG Course Biochemistry.
All you need of NEET PG at this link: NEET PG
|
48 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Metabolism of Carbohydrates -2 - Biochemistry - NEET PG
| 1. What are the main pathways of carbohydrate metabolism? |  |
Ans. The main pathways of carbohydrate metabolism include glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), and the pentose phosphate pathway. Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose into pyruvate, generating ATP and NADH. Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources. The citric acid cycle processes acetyl-CoA to produce ATP, NADH, and FADH₂, while the pentose phosphate pathway generates NADPH and ribose-5-phosphate for biosynthetic reactions.
| 2. How does insulin regulate carbohydrate metabolism? |  |
Ans. Insulin plays a crucial role in regulating carbohydrate metabolism by promoting the uptake of glucose into cells, particularly in muscle and adipose tissues. It facilitates the conversion of glucose to glycogen (glycogenesis) and inhibits gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis (the breakdown of glycogen). Insulin also enhances the synthesis of fatty acids from excess glucose, thereby linking carbohydrate metabolism to lipid metabolism.
| 3. What is the significance of glycolysis in cellular respiration? |  |
Ans. Glycolysis is significant in cellular respiration as it is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy. It occurs in the cytoplasm and does not require oxygen (anaerobic). During glycolysis, one molecule of glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvate, yielding a net gain of 2 ATP and 2 NADH. The pyruvate can then enter the aerobic pathways if oxygen is present, or be converted to lactate in anaerobic conditions, making glycolysis a key metabolic pathway for energy production.
| 4. What role do carbohydrates play in energy metabolism? |  |
Ans. Carbohydrates serve as a primary energy source for the body. They are metabolized to produce glucose, which can be utilized immediately for energy or stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles for later use. During periods of fasting or intense exercise, glycogen is broken down to maintain blood glucose levels. Carbohydrates also contribute to the formation of ATP through aerobic and anaerobic metabolic pathways, making them essential for maintaining energy homeostasis.
| 5. How are carbohydrates stored in the body, and what is their significance? |  |
Ans. Carbohydrates are primarily stored in the body as glycogen, which is found mainly in the liver and muscle tissues. The liver stores glycogen to regulate blood glucose levels, while muscle glycogen serves as a local energy reserve during physical activity. The significance of carbohydrate storage lies in its ability to provide a quick source of energy, support metabolic functions, and maintain blood glucose levels, especially during fasting or strenuous exercise.
Related Searches















