Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Science Class 8 > Mind Map: Sound
Mind Map: Sound | Science Class 8 PDF Download
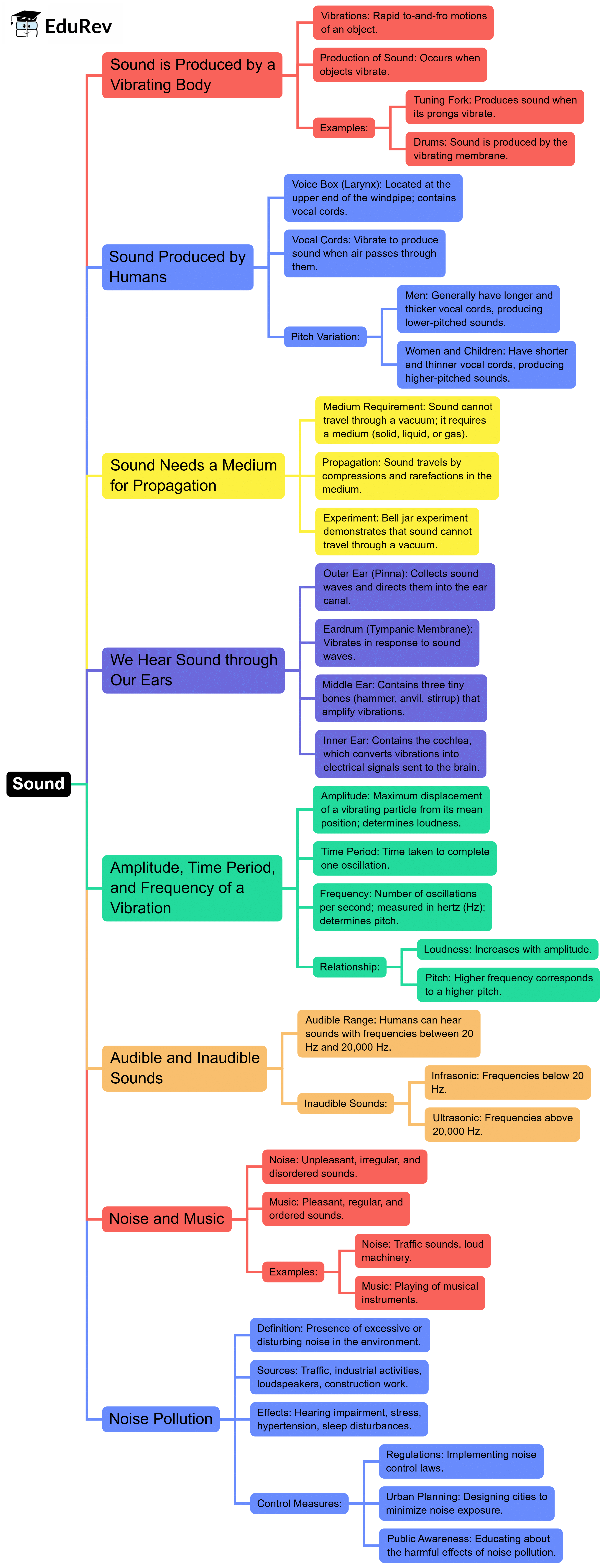
The document Mind Map: Sound | Science Class 8 is a part of the Class 8 Course Science Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
90 videos|415 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Sound - Science Class 8
| 1. What are the different types of sound waves? |  |
Ans. Sound waves can be classified into two main types: longitudinal waves and transverse waves. Longitudinal waves, where the particle displacement is parallel to the direction of wave propagation, are the most common in air. Transverse waves, where particle displacement is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, are typically found in solids.
| 2. How do sound waves travel through different mediums? |  |
Ans. Sound waves travel through different mediums such as solids, liquids, and gases by causing particles in the medium to vibrate. In gases, sound travels slower due to the larger distance between particles, while in solids, sound travels faster because particles are closer together, allowing for quicker energy transfer.
| 3. What factors affect the speed of sound? |  |
Ans. The speed of sound is affected by several factors including the medium's temperature, density, and elasticity. Generally, sound travels faster in warmer temperatures because increased energy causes particles to vibrate more quickly. It also travels faster in denser and more elastic materials.
| 4. What is the relationship between frequency and pitch in sound? |  |
Ans. Frequency refers to the number of vibrations or cycles per second of a sound wave, measured in Hertz (Hz). Pitch is the perceived frequency of a sound; higher frequencies correspond to higher pitches, while lower frequencies correspond to lower pitches. Therefore, frequency directly influences how we perceive the pitch of a sound.
| 5. How do human ears perceive sound? |  |
Ans. Human ears perceive sound through a complex process. Sound waves enter the ear canal, causing the eardrum to vibrate. These vibrations are transmitted through tiny bones in the middle ear to the cochlea in the inner ear, where they are converted into electrical signals that are sent to the brain, allowing us to interpret the sound.
Related Searches
















