Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Notes > English Grammar for Class 6 > Mind Map: Verbs
Mind Map: Verbs | English Grammar for Class 6 PDF Download
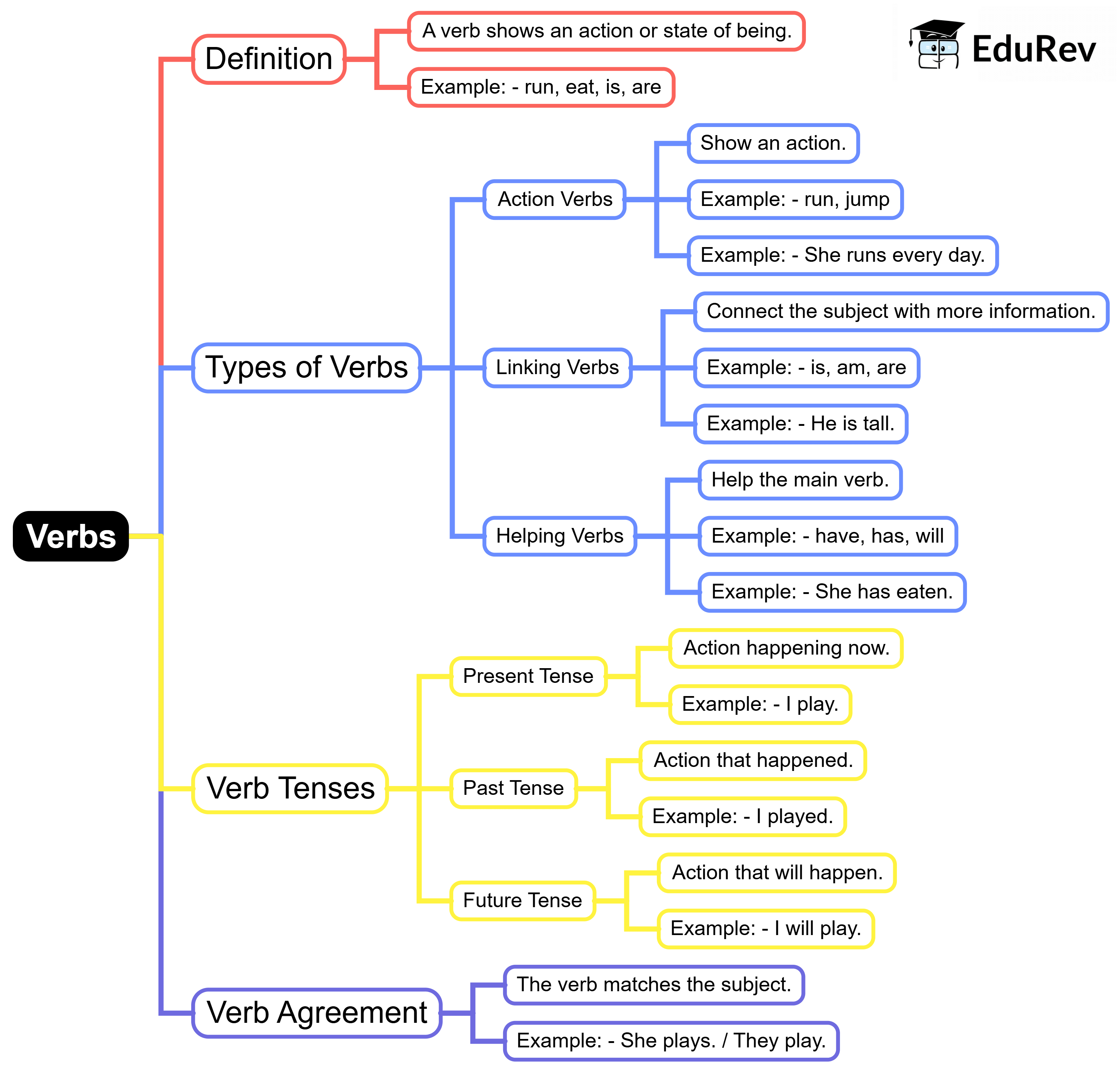
The document Mind Map: Verbs | English Grammar for Class 6 is a part of the Class 6 Course English Grammar for Class 6.
All you need of Class 6 at this link: Class 6
|
50 videos|469 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Verbs - English Grammar for Class 6
| 1. What are the main categories of verbs in English? |  |
Ans. The main categories of verbs in English include action verbs, linking verbs, and auxiliary (helping) verbs. Action verbs express physical or mental activities (e.g., run, think), linking verbs connect the subject to a subject complement (e.g., is, seem), and auxiliary verbs help to form tenses, moods, and voices of other verbs (e.g., have, will).
| 2. How can I identify action verbs in a sentence? |  |
Ans. Action verbs can be identified by looking for words that convey an action or activity in a sentence. They typically describe what the subject is doing. For example, in the sentence "She runs every morning," the word "runs" is the action verb as it describes the action performed by the subject, "she."
| 3. What is the difference between transitive and intransitive verbs? |  |
Ans. Transitive verbs require a direct object to complete their meaning, whereas intransitive verbs do not. For example, in the sentence "She reads a book," "reads" is a transitive verb because it has the direct object "book." In contrast, in "He sleeps," "sleeps" is intransitive as it does not take a direct object.
| 4. Can verbs change form, and if so, how? |  |
Ans. Yes, verbs can change form to indicate tense, mood, or aspect. This includes changing from present to past tense (e.g., 'walk' to 'walked'), adding suffixes like -ing for present participles (e.g., 'running'), or using auxiliary verbs to form perfect tenses (e.g., 'has walked').
| 5. What are some common irregular verbs, and how do they differ from regular verbs? |  |
Ans. Common irregular verbs include 'go' (went), 'have' (had), and 'be' (was/were). They differ from regular verbs in that they do not follow the standard pattern of adding -ed for the past tense. Instead, they have unique forms that must be memorized, as they do not follow a predictable pattern.
Related Searches
















